Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 10:30AM-11:30AM
Background/Purpose: Spondyloarthritis (SpA) development is associated with type 3 immune response activation. In HLA-B27/human β2-microglobulin transgenic rat model (B27-rat), this might at least be related to enhanced differentiation of naive CD4+ T cells into T helper-17 (Th17). Here, we aimed to decipher the molecular mechanisms that might lead to altered naive CD4+ T cells differentiation in SpA.
Methods: Naive CD4+ T cells were sorted by flow cytometry from mesenteric lymph nodes (mLN) of B27-rat, control healthy nontransgenic (NTG) littermates or healthy transgenic B7-rats, and from peripheral blood of patients with axial SpA (N=28, including 7 with juvenile onset), healthy controls (N=17) or patients with rheumatoid arthritis (N=8). The transcriptome and epigenome were characterized ex vivo rat naive CD4+ T cells, by using RNA-seq and ChIP-seq of 2 activating histone marks (H3K4me3, H3K27ac). In addition, selected genes expression was studied by q-RT-PCR. Differentiation of rat naive CD4+ T cells was analyzed 3 to 6 days after stimulation with anti-CD3/anti-CD28 alone or in the presence of rat IFNγ or a selective STAT1 transcriptional activator (2-(1,8-Naphthyridin-2-ly)phenol).
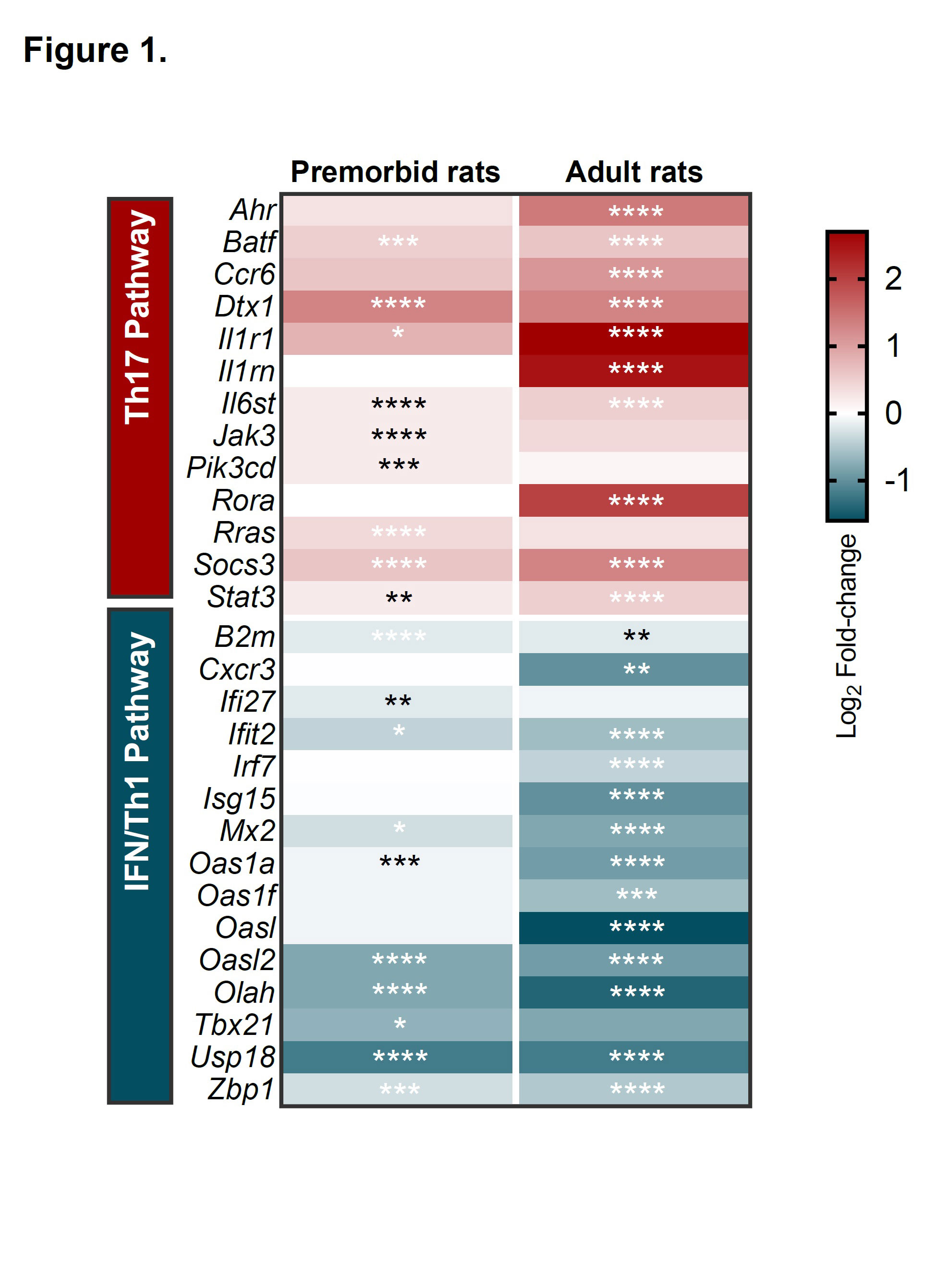
Results: Under anti-CD3/anti-CD28 neutral stimulation B27-rat (but not B7-rat) naive CD4+ T cells were skewed to develop a Th17 proinflammatory profile, even before disease onset, as compared to NTG rats. Both transcriptomic (Figure 1) and epigenomic studies consistently revealed pro-Th17 and decreased interferon signatures in ex vivo-sorted B27-rat CD4+ naive T cells. Imbalance between increased STAT3 and decreased STAT1 was predicted to be a critical upstream regulator of this molecular signature (Table 1). At the protein level, STAT3 increased upon disease establishment, whereas STAT1 decrease was an early and persistent characteristic of B27-rat naive CD4+ T cells, occurring before disease onset. Moreover, Stat1 and STAT1-related genes mRNA expression was precociously deficient in thymic precursors of B27-rat naive CD4+ T cells, even in newborn. Furthermore, STAT1 mRNA expression was also significantly decreased in naive CD4+ T cell from SpA patients, as compared to healthy controls and rheumatoid arthritis patients (p < 0.05 and p < 0.01, respectively). Finally, in vitro stimulation of B27-rat naive CD4+ T cells with either IFNγ or a selective STAT1 transcriptional activator abolished IL-17A overexpression, confirming that STAT1 deficiency might be an upstream determinant of Th17 differentiation bias in SpA.
Conclusion: STAT1 deficiency appears a precocious signature in naive CD4+ T cells from B27-rat, preceding disease onset. Similar observation was evidenced in SpA patients. This phenomenon was associated with heightened Th17 signature that paralleled disease development in B27-rat, was determined at the epigenomic level and predicted to be orchestrated by STAT3 hyperactivity. Thus imbalance between STAT1 and STAT3 pathways appears a fundamental mechanism explaining Th17 expansion in B27-rat and SpA patients.
Expression heatmap showing the log2 fold-change expression of IFN/Th1 and Th17 pathways-related genes, in naive CD4+ T cells, as compared to controls, before (premorbid) of after (adult) disease onset. * p<0.05, ** p<0.01, *** p<0.001, **** p<0.0001.
Upstream transcription factors (TF) predicted to explain differentially enriched genes profile in naive CD4+ T cells from B27-rats, as compared to controls; -log (adj p value) calculated by Fisher’s exact test; z-score refers to the activation (red), inhibition (blue) or undefined (white) state of the downstream regulated genes in B27-rats.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
CHERQAOUI B, Cremazy F, Lauraine M, Shammas G, Said-Nahal R, Mambu Mambueni H, Costantino F, Fourmont M, Glatigny S, Araujo L, Breban M. Intrinsic STAT1 Deficiency Underlies Proinflammatory Imprint of Naive CD4+ T Cells in Spondyloarthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/intrinsic-stat1-deficiency-underlies-proinflammatory-imprint-of-naive-cd4-t-cells-in-spondyloarthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/intrinsic-stat1-deficiency-underlies-proinflammatory-imprint-of-naive-cd4-t-cells-in-spondyloarthritis/