Session Information
The 2020 Pediatric Rheumatology Symposium, originally scheduled for April 29 – May 2, was postponed due to COVID-19; therefore, abstracts were not presented as scheduled.
Date: Saturday, May 2, 2020
Title: Poster Session 3
Session Type: ACR Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:15PM-5:15PM
Background/Purpose: Long-term outcomes of systemic JIA are highly variable. approximately half of the patients have chronic persistent arthritis requiring extended anti-inflammatory therapy, sometimes into adulthood. However, pathology of the chronic arthritic sJIA has not been fully understood whereas early acute febrile sJIA is driven by innate immune mechanisms. The purpose of this study is to evaluate the pro-inflammatory cytokine profile and therapeutic response in patients with chronic arthritic sJIA.
Methods: Patients with acute febrile sJIA, chronic arthritic sJIA, and polyarticular JIA or rheumatoid arthritis were included in this study. Chronic arthritic sJIA was defined as the condition of persistent arthritis lack of systemic inflammation such as fever and skin rash for more than 6 months or the condition of persistent arthritis lack of systemic inflammation under the treatment of tocilizumab, anti-IL-6 receptor monoclonal antibody, without glucocorticoid. Serum samples were obtained from the individuals during the active phase. The serum concentrations of IL-18, IL-6, and calprotectin, a complex of the proteins S100 A8 and S100 A9, were evaluated using commercial enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Intra-group comparisons were performed using the Mann–Whitney test or Fisher’s exact probability test, where appropriate. A p value of < 0.05 was considered to indicate a significant difference. Responses to disease modifying antirheumatic drugs were reviewed from medical records.
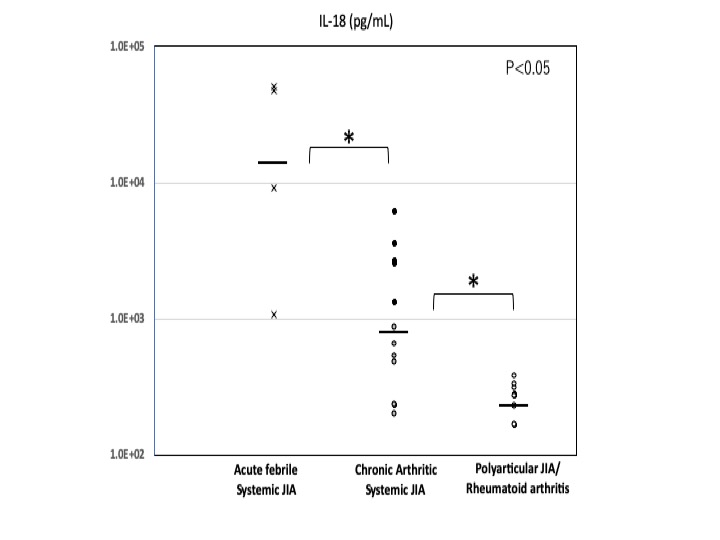
Results: Four patients with acute febrile sJIA, 12 with chronic arthritic sJIA, and 9 with polyarticular JIA or rheumatoid arthritis were enrolled. The serum IL-18 levels in patients with chronic arthritic sJIA (1,597.6 ± 1,793.2 pg/mL) were significantly lower than those in patients with acute febrile sJIA (26,799.9 ± 24568.3 pg/mL; p < 0.05) and significantly higher than those in patients with pJIA/RA (264.3 ± 72.4 pg/mL; p < 0.05). In the comparison of chronic arthritic sJIA and polyarticular JIA/RA, both calprotectin and IL-6 showed higher in chronic arthritic sJIA, but there were no significant differences. Seven patients with serum IL-18 level under 1,000 pg/mL (488.9±247.2 pg/mL) in chronic arthritic sJIA were successfully treated by conventional medication such as NSAIDs and/or methotrexate whereas the other group with IL-18 level over 1,000 pg/mL (3205.6±1791.8 pg/mL) required tocilizumab.
Conclusion: Albeit a small number of patients, this study indicated that serum IL-18 levels vary in patients with chronic arthritic sJIA. IL-18 may serve as a key cytokine to estimate whether the pathology of the patient is more likely driven by innate or acquired immunity and to guide into appropriate therapeutic strategy.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Miyamae T, Tani Y, Kawamoto M, Kishi T, Harigai M. Interleukin-18 as a Key Cytokine to Understand Pathology and to Decide Appropriate Therapeutic Strategy in Chronic Arthritic Systemic Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 4). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/interleukin-18-as-a-key-cytokine-to-understand-pathology-and-to-decide-appropriate-therapeutic-strategy-in-chronic-arthritic-systemic-juvenile-idiopathic-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2020 Pediatric Rheumatology Symposium
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/interleukin-18-as-a-key-cytokine-to-understand-pathology-and-to-decide-appropriate-therapeutic-strategy-in-chronic-arthritic-systemic-juvenile-idiopathic-arthritis/