Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 6, 2021
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Basic Science Poster (0046–0068)
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Gender has been shown to impact disease expression in ankylosing spondylitis. Men with AS are more likely to develop radiographic joint damage, while women have latter onset of disease, higher symptomatic burden but slow progression of structural damage and impaired response to treatment. An important observation was made in a recent study which showed that male patients with AS had a distinctive up-regulation of the Th17 signature, while female patients with AS had Th17 cell profiles comparable with those of the healthy control subjects (1). We propose that mRNAs are differentially expressed in IL-17 producing cells between males and females with AS and disparately regulate the genes in males and females and subsequently contribute to the difference in disease phenotype.
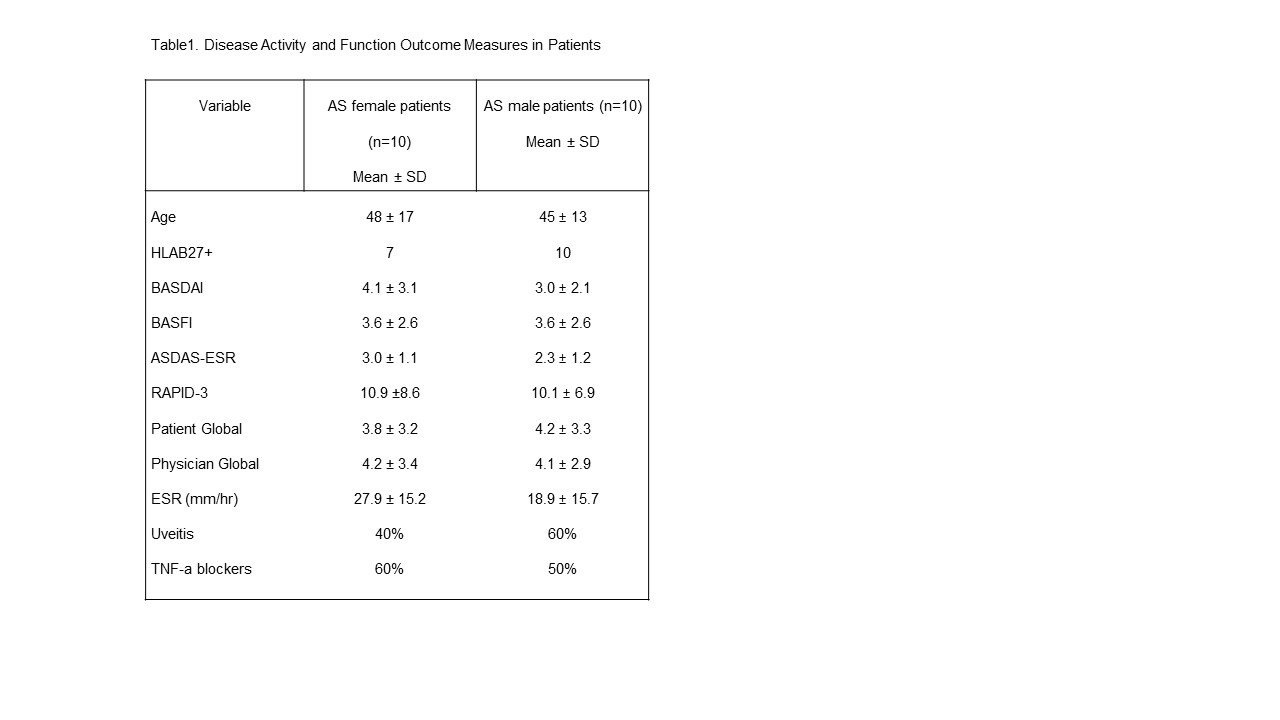
Methods: 10 female and 10 male subjects ≥18 years of age with AS based on NYCS, were enrolled. Patients were recruited as per approved IRB protocol. Peripheral blood samples (30 ml) were obtained in the Clinical Research Unit of MetroHealth Medical Center. The PBMCs obtained were stimulated with CytoStim for 4 h (Miltenyi Biotec GmbH, Bergisch Gladbach, Germany). After stimulation, the cells were processed through the interleukin (IL)-17-phycoerythrin (PE) cytokine secretion assay enrichment kit (Miltenyi Biotec). The IL-17 positive cells were counted and total RNA was extracted as per Takara kit (Takara Biotech, Japan). Changes in mRNA expression were identified using next generation RNA-sequencing (RNA-seq). To proceed 500 ng of RNA from each sample was sent to Novogene for sequencing. Analysis of the data was done using Ipathway guide by Advaita Bioinformatics (ipathwayguide.advaitabio.com). Genes were identified using a threshold of 0.05 for statistical significance (p-value) and a log fold change of expression with absolute value of at least 0.6. These data were analyzed in the context of pathways obtained from the KEGG database, miRNAs from the miRBase and TARGETSCAN databases, network of regulatory relations from BioGRID, and diseases from the KEGG database.
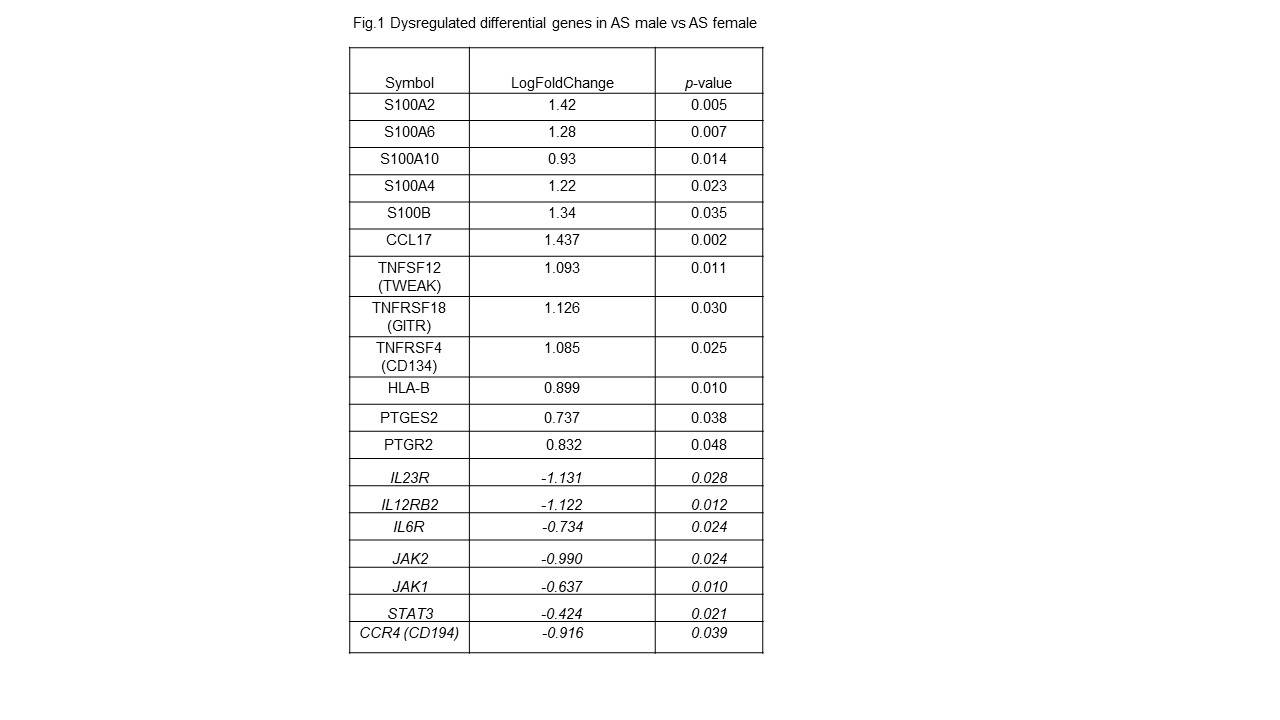
Results: Patient demographics and disease activity and functional outcomes are reported in table 1. In this experiment, 2,373 differentially expressed (DE) genes B were identified out of a total of 15,294 genes with measured expression as in Fig 1. 613Gene Ontology (GO) terms, 40 miRNAs, 201 upstream regulators, and 14 diseases were found to be significantly enriched before the correction for multiple comparisons. In summary, 15 pathways were found to be significantly impacted.
Conclusion: The study revealed multiple cytokine genes were found to be dysregulated between men and women with AS. The IL23R, IL12R, IL6R, JAK, STAT and TYK2 genes were downregulated in men compared to women while S100A2, S100A4, S100A6, S100B, chemokine CCL-17 and PGE2 related genes were upregulated. These data need to be confirmed by RTPCR and may provide clues for understanding the pathogenesis and phenotypic differences.
1.Gracey E, Yao Y, Green B, Qaiyum Z, Baglaenko Y, Lin A, Anton A, Ayearst R, Yip P, Inman RD. Sexual Dimorphism in the Th17 Signature of Ankylosing Spondylitis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016 Mar;68(3):679-89. doi: 10.1002/art.39464. PMID: 26473967.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Haghiac M, Breitman M, Chan R, Khalil A, Magrey M. Integrative Analysis of mRNAs to Identify Sex Differences in Th-17 Mediated Inflammation in Ankylosing Spondylitis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/integrative-analysis-of-mrnas-to-identify-sex-differences-in-th-17-mediated-inflammation-in-ankylosing-spondylitis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/integrative-analysis-of-mrnas-to-identify-sex-differences-in-th-17-mediated-inflammation-in-ankylosing-spondylitis/