Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Zymosan (Zym) induces arthritis through TLR2- and Dectin-1-activated NK-κB signaling and inflammatory myeloid cell infiltration into the synovium of the injected joint. Innate immune tolerance after an initial TLR challenge dampens inflammatory responses induced by a second challenge. It is currently unknown if this innate immune tolerance affects Zym responses and can attenuate the effector phase of inflammatory arthritis. We hypothesize that LPS preconditioning dampens zymosan-induced innate inflammatory response and arthritis.
Methods: C57BL6 mice were administrated 10ul/g PBS or 0.5mg/kg lipopolysaccharide (LPS) intraperitoneally for 24 h and then given intraarticular (IA) injections of 180μg Zym in the right knees (n=5-12/group). H&E histology on D7 after IA Zym was performed to measure synovitis. Serum cytokine analysis at 3 h after IA Zym (n=3-4/group) and flow cytometry (FC) for myeloid cell subsets in the periarticular tissue at D2 and D7 after IA Zym (n=6-8/group) were conducted. CD14+ cells from healthy human whole blood donors were isolated, cultured with M-CSF overnight, and either allowed to “rest” (R), treated with 10 ng/ml LPS for 24 h (L), stimulated with 16 μg/ml Zym for 3 h (Z), or LPS-24 h + Zym-3 h (L+Z). Cells were then harvested for mRNA expression (n=7) or stained for intracellular cytokine (n=3) analysis via FC. Western blot of TBK1, NF-κB and MAPK p38 signaling activation at 5, 15, 30, and 60 min after Zym treatment was performed (n=3).
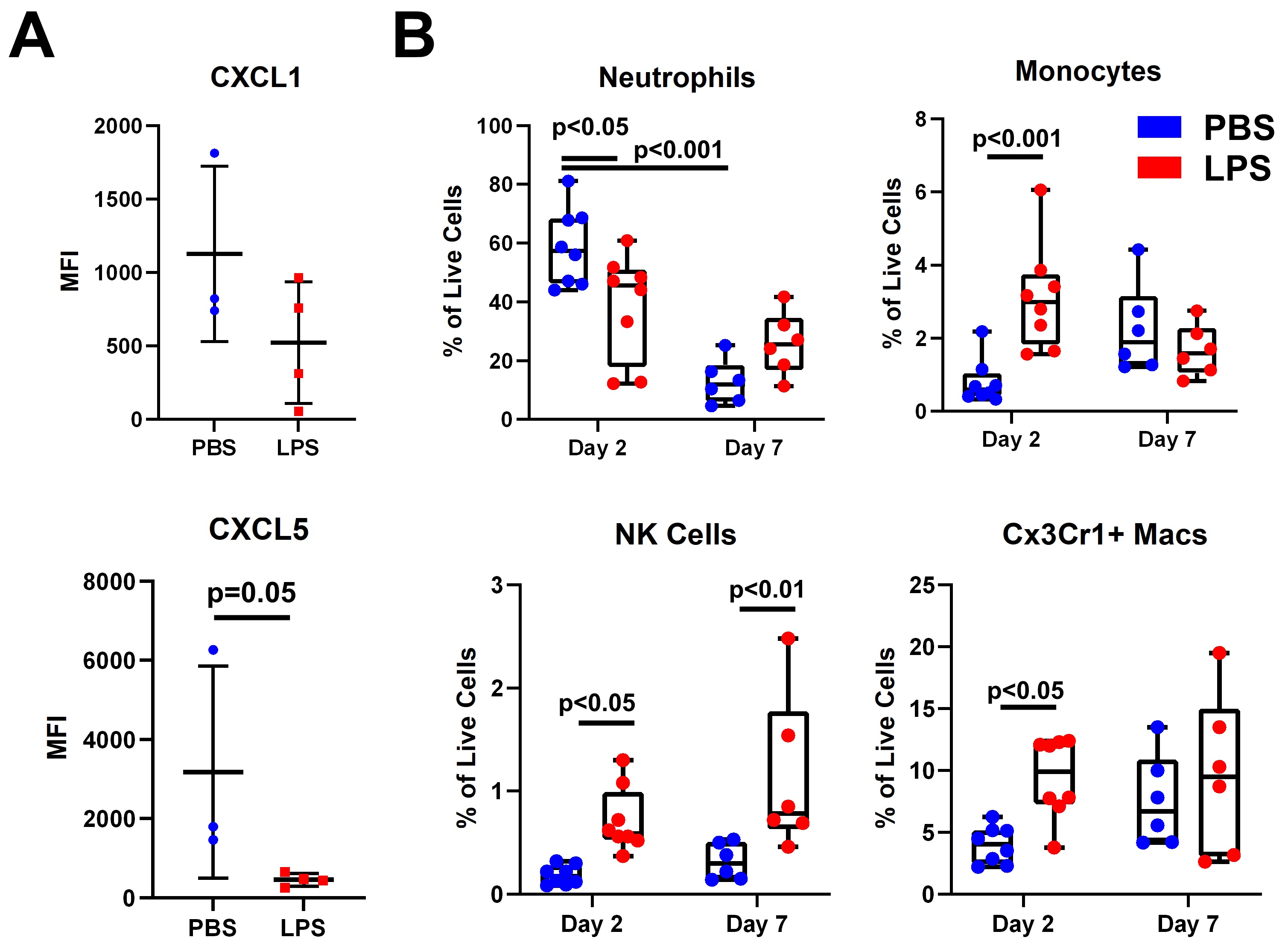
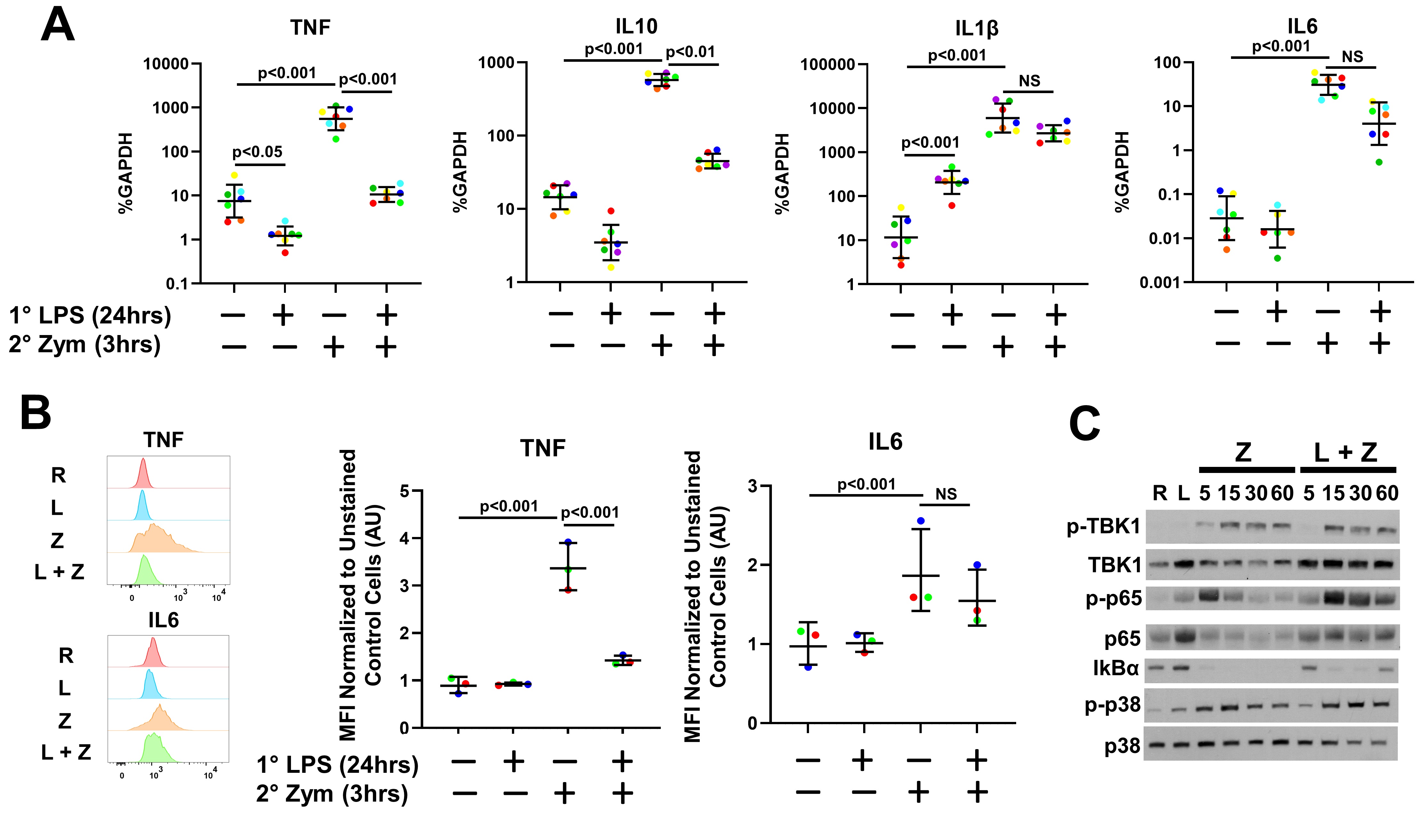
Results: IA injection of Zym significantly induced synovitis, periarticular inflammation and immune cell infiltration while LPS pretreatment significantly attenuated synovitis (Fig 1). Serum neutrophil chemoattractant proteins CXCL1 and CXCL5 were reduced at 3 h after IA Zym in the LPS pretreated group compared to PBS group (Fig 2A). FC analysis revealed a significant reduction of synovial neutrophils at D2, while Ly6C+/Cd11c- monocytes, NK cells and CX3CR1+/CD11b+/F4-80+ macrophages were increased at D2 after arthritis induction (Fig 2B). RNA and intracellular cytokine expression of CD14+ cells challenged with Zym showed gene-specific tolerization of Tnf and Il10 expression by LPS pretreatment, while Il1b and Il6 induction remained intact (Fig 3 A, B). Western blots of NF-kB, TBk1 and MAPK p38 signaling suggested that LPS pretreatment minimally affects Zym-induced signaling (Fig 3C). Zym-induced expression of CXCL2 and CXCL8 in the human monocytes was also suppressed by LPS.
Conclusion: LPS attenuated production of neutrophil chemokines in vivo and in vitro and reduced neutrophil abundance in the synovium, thereby decreasing Zym induced synovitis. LPS pretreatment displayed gene-specific tolerization of Zym-induced gene expression in human monocytes in vitro. Monocyte, macrophage and NK cell infiltration were increased in vivo, however, our in vitro data suggests these populations could be partially tolerized. Interestingly, gene-specific tolerance occurred in the context of intact signaling, suggesting epigenetic mechanisms of gene silencing. Overall, these results suggest that LPS significantly disrupts the inflammatory response to Zym and that innate immune memory could play a role in the effector phase of inflammatory arthritis.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bell R, Yang C, Brauner C, Sohki U, Yuan R, Mishra B, Bachu M, Ivashkiv L. Innate Immune Tolerance Attenuates Zymosan-Induced Arthritis, Inflammatory Gene Expression and Synovial Neutrophil Infiltration [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/innate-immune-tolerance-attenuates-zymosan-induced-arthritis-inflammatory-gene-expression-and-synovial-neutrophil-infiltration/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/innate-immune-tolerance-attenuates-zymosan-induced-arthritis-inflammatory-gene-expression-and-synovial-neutrophil-infiltration/