Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2015
Title: Imaging of Rheumatic Diseases Poster I: Ultrasound, Optical Imaging and Capillaroscopy
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
Indocyanine green (ICG) -enhanced fluorescence optical imaging (FOI) is a novel diagnostic tool for the assessment of inflammatory
arthritis through visualizing vascular beds. Ultrasound (US) can detect joint
injury of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) with high sensitivity. We previously
reported that US synovitis scores correlate with
serum biomarkers such as angiogenesis factors. This study is undertaken to
explore the utility of FOI comparing with US and serum biomarkers.
Methods:
Twenty-five active RA
patients (mean disease durations 7.5 years and DAS28-ESR 5.90) who fulfilled
2010 RA classification criteria were consecutively enrolled in this study. They gave their informed consent to be subjected
to the protocol that was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Nagasaki
University. Both FOI and US were performed at the same
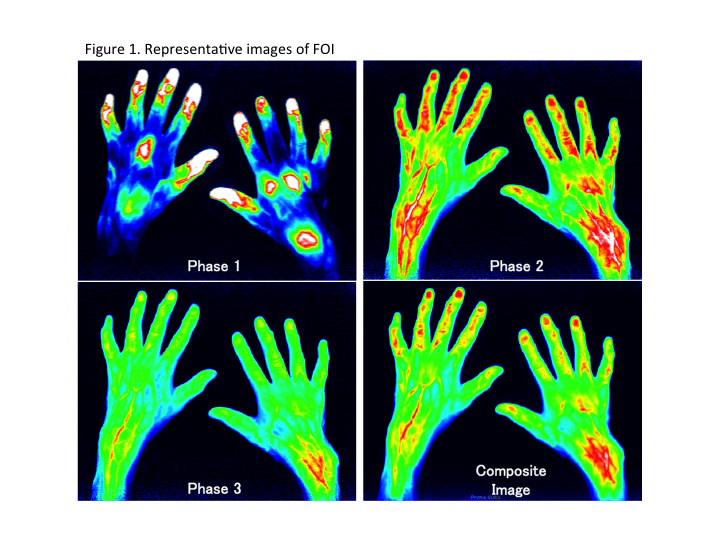
day. Interpretation of FOI images using Xiralite
system was done for an early phase (phase 1, P1), an intermediate phase (phase
2, P2), a late phase (phase 3, P3) and an early electronically generated
composite image (CI) from 18 joints including bilateral 2nd -5th
metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joints, proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joints and wrist joints (Figure 1).
The same joints were scored by gray scale (GS) and power Doppler (PD) by US. FOI assessments of P1, P2,
P3, CI as well as GS score and PD score were semi-quantitatively classified from 0 to 3 as
described (total scores of each parameter are 0 to 54 from the 18 joints,
respectively). Bone erosion was also assessed by US. Forty-five
serum biomarkers at the time of FOI/US examinations were measured by multi-suspension cytokine array.
Results:
Positive
finding (≥ grade 1)
were found in 122, 206, 140, 139 and 148 out of 450 joints in P1, P2, P3, CI
and PDUS, respectively. FOI scores were significantly high in the joints where bone
erosion was detected by US as compared to those without bone erosion (p<0.0001).
Among individual patients, each total FOI scores clearly correlated with both
GS and PD scores (r=0.46-0.71) as well as with DAS28-ESR (r=0.66-0.72). In
addition, serum IL-6, VEGF and TNF- correlated with FOI scores.
Comparing with PDUS ≥ grade 1 or PDUS ≥ grade 2 as the reference, the
positive predictive value (PPV) of FOI scores (≥ grade 1) in whole joints
were 82.0 (P1), 66.5 (P2), 75.7 (P3) and 76.3 % (CI) toward PDUS ≥ grade
1 or 66.4 (P1), 44.7 (P2), 54.3 (P3) and 56.1 % (CI) toward PDUS ≥ grade
2, respectively.
Conclusion:
Since FOI scores correlate with US scores as well as
serum biomarkers, FOI is considered to detect joint inflammation of RA patients
with high accuracy. However, the significance of each phase of FOI may be
different and need to be further clarified.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kawashiri SY, Nishino A, Umeda M, Fukui S, Nakashima Y, Iwamoto N, Ichinose K, Nakamura H, Origuchi T, Aoyagi K, Kawakami A. Indocyanine Green (ICG) -Enhanced Fluorescence Optical Imaging (FOI) in Patients with Active Rheumatoid Arthritis; A Comparative Study with Ultrasound and Association with Biomarkers [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/indocyanine-green-icg-enhanced-fluorescence-optical-imaging-foi-in-patients-with-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-comparative-study-with-ultrasound-and-association-with-biomarkers/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/indocyanine-green-icg-enhanced-fluorescence-optical-imaging-foi-in-patients-with-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-comparative-study-with-ultrasound-and-association-with-biomarkers/