Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 9, 2021
Title: Reproductive Issues in Rheumatic Disorders Poster (1711–1731)
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Pregnant women with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) are at high risk of preeclampsia, leading to substantial maternal and fetal morbidity. Aspirin reduces preeclampsia risk but recent studies suggest aspirin is used only in a minority of SLE pregnancies. There is an urgent need to improve preeclampsia counselling and management in this vulnerable population. Therefore, we are conducting the PREPARE (PREeclamPsia knowledge & Aspirin adheRence in lupus prEgnancies) trial, a randomized controlled trial (RCT) evaluating an educational tool on preeclampsia knowledge and aspirin adherence among pregnant women with SLE. We present preliminary analyses of the effect of this tool on preeclampsia knowledge.
Methods: We are recruiting consecutive pregnant SLE women (diagnosed according to the SLICC criteria) until the 16th gestational week at 5 Canadian SLICC centers (i.e. Montreal, Halifax, Quebec, Winnipeg, and Calgary) since May 2018. Participants are randomly assigned to receive either the specifically-designed educational tool (intervention group) or standard of care (control group). At baseline (i.e. first trimester) and second trimester visits, the participants complete self-administered preeclampsia knowledge questionnaires (scored out of 30 by the research team blinded to the intervention). We restricted the current analysis to participants enrolled at the coordinating center (accounting for nearly half of the total planned sample size). We performed a univariate linear regression analysis to assess the effect of the educational tool on preeclampsia knowledge (i.e. mean score difference between the two groups from baseline to second trimester visit).
Results: Thirty-three pregnant SLE women were included in the study, among which 16 were exposed to the intervention and 17 were unexposed. Baseline characteristics were well-balanced between the two groups with similar mean maternal age between intervention group (32.2 years, standard deviation, SD, 4.6) and control group (34.1 years, SD 4.2) and identical proportion of participants with post-secondary education (i.e. 80%) (Table 1). The difference in mean preeclampsia knowledge scores between second trimester and baseline visits in the intervention group was 4.4 points (95% CI -0.1, 9.0) and in the control group was 1.5 points (95% CI -2.7, 5.7). The mean difference in knowledge scores (from baseline to second trimester) for those receiving the educational tool was 2.7 points higher (95% CI -1.5, 6.9) than those receiving standard of care.
Conclusion: Approximately midway into the trial, we observed a trend for improvement in preeclampsia knowledge from the baseline to the second trimester visit in pregnant women with SLE who received a specifically-designed educational tool compared to the control group, although the CIs included the null. Our RCT is well-poised to provide a new evidence-based approach to improve preeclampsia knowledge in pregnant women with SLE, which could help to optimize aspirin use and outcomes in this vulnerable population.
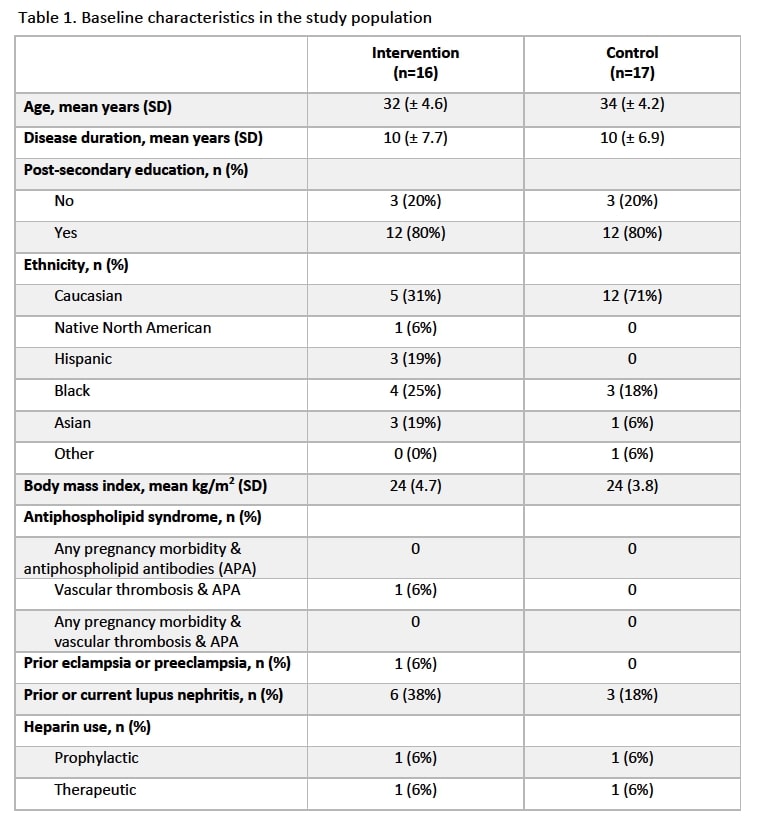 Table 1. Baseline characteristics in the study population.
Table 1. Baseline characteristics in the study population.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lee J, Mendel A, Malhamé I, Bernatsky S, Vinet E. Increasing Preeclampsia Knowledge in SLE with a Specific Educational Tool: Preliminary Results [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/increasing-preeclampsia-knowledge-in-sle-with-a-specific-educational-tool-preliminary-results/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/increasing-preeclampsia-knowledge-in-sle-with-a-specific-educational-tool-preliminary-results/
