Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 17, 2024
Title: Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Basic Science Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Recent transcriptomic data suggest a prominent involvement of innate immune cells in the pathogenesis of SSc. In this regard, contrasting data on NK cells functional and numeric alterations have been described in SSc.
The aim of this study was to investigate alterations of the circulating innate immune cell in SSc patients.
Methods: Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) were isolated by density gradient centrifugation from 30 SSc(ACR/EULAR 2013 criteria) patients and 10 sex and age matched healthy controls (HC). Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) was performed by using a droplet-based platform (10x Genomics). Sequencing was carried out using Illumina NovaSeq 6000. Raw reads were aligned to the reference human genome using Cellranger 7.0. Transcriptomic data were analyzed using the Seurat package. Canonical Correlation Analysis (CCA) integration was conducted before final PBMC automatic annotation with the Azimuth reference application. Cell proportions were analyzed with the speckle R package. Analysis of Differentially Expressed Genes (DEG) was performed by Wilcoxon Rank Sum test on scRNA-seq data and limma package on pseudobulk data. The final DEG list was generated by intersecting the genes identified from both Wilcoxon Rank Sum test and pseudobulk data. To be included in this list, the genes had to meet the following criteria in both analyses: p-value < 0.05 and │log2FC│ > 0.5. Pathway over-representation analysis was performed using Elsevier Pathway Collection, BioPlanet 2019, MSigDB Hallmark 2020 and Reactome 2022.
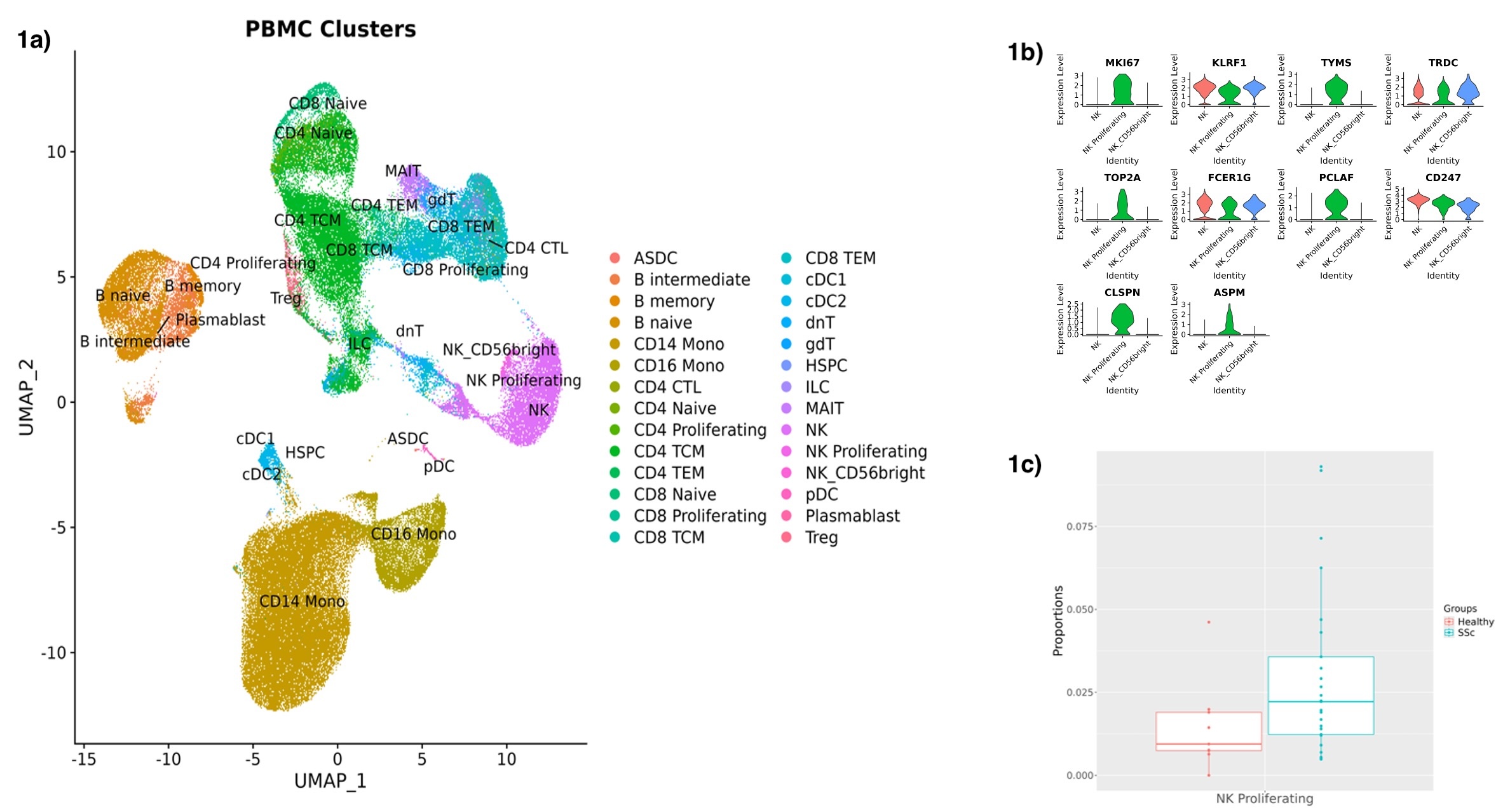
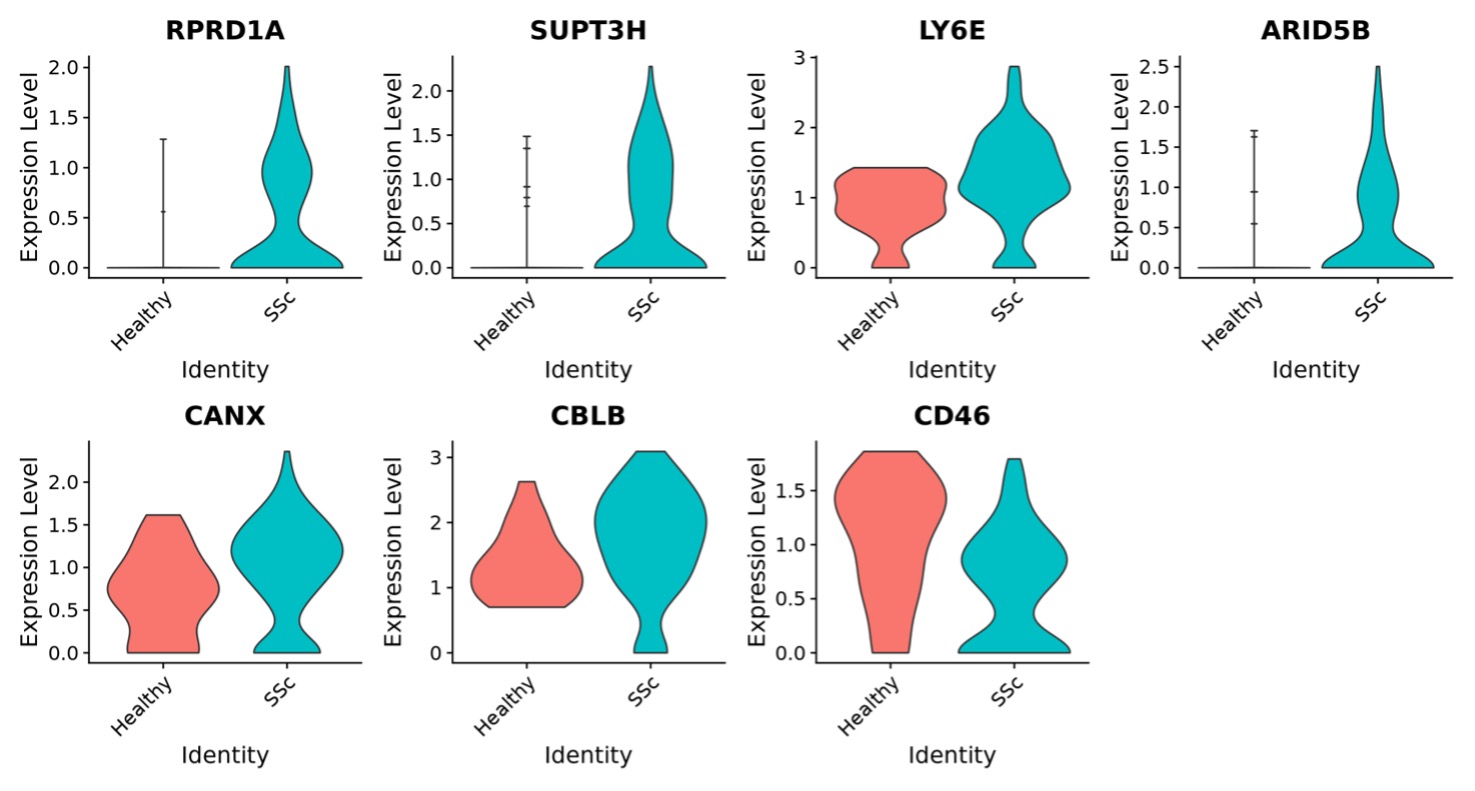
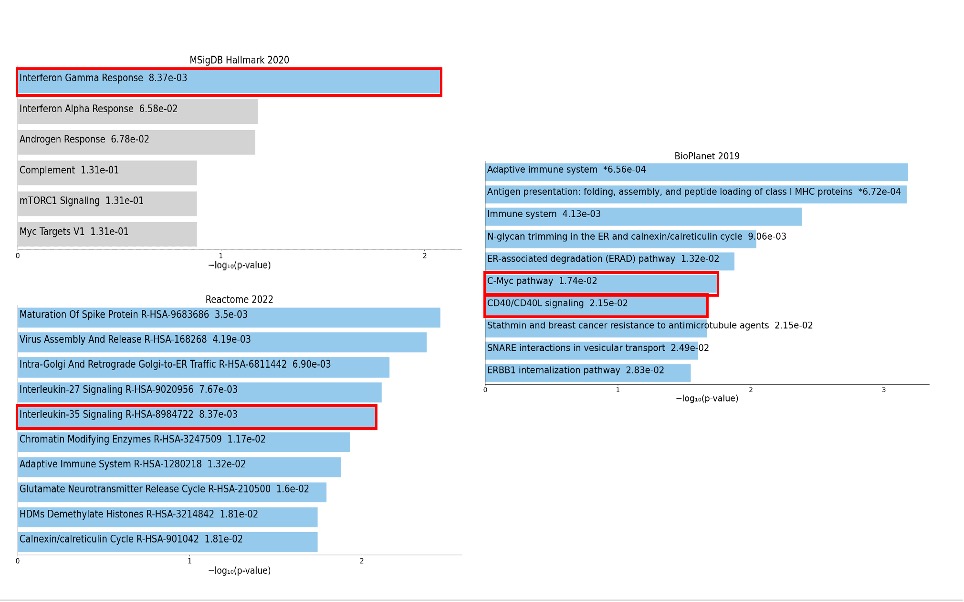
Results: Unsupervised cluster analysis of 108138 PBMCs revealed 21 distinct clusters that were successfully annotated to major PBMC cell types (Figure 1a). When assessing cell type proportions, the NK proliferating subtype (Figure 1b) showed an increase in SSc patients vs HC (Ratio = 1.98, p = 0.027, FDR = 0.71), pointing to a possible abnormal NK turnover. After subsetting and reclustering of NK cells, NK proliferating were confirmed to be increased in SSc patients vs HC (Ratio = 2.08, p = 0.051, FDR = 0.30 – Figure 1c). DEG yielded a total of 34 genes: 20 downregulated genes and 14 upregulated genes. Interestingly, RPRD1A (log2FC = 1.70), a cell cycle regulator, and SUPT3H (log2FC = 0.96), a member of STAGA transcription coactivator complex involved in the pro-proliferative C-Myc signaling, were among the top upregulated genes (Figure 2). The C-Myc pathway emerged as one of the top enriched pathways, indicating a possible hyperproliferative state of these cells. Increased expression of interferon-γ related genes LY6E (log2FC = 1.08) and ARID5B (log2FC = 1.55) and reduced expression of CD46 (log2FC = -0.98), an inhibitor of NK cytotoxicity, might suggest increased activity of SSc NK proliferating cells (Figure 2). Several pro-inflammatory pathways such as “Interferon-γ response”, “CD40/CD40L” and “IL-35 signaling” were also enriched (Figure 3).
Conclusion: Our data suggest that circulating NK proliferating cells are increased in SSc. This specific cell population seems to display a pro-proliferative and inflammatory phenotype with an interferon-γ signature.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bearzi P, Pachera E, Wagner S, Hofman A, Li L, Much L, Becker M, Bürki K, Navarini L, Hoffmann-Vold A, Giacomelli R, Distler O. Increased Proliferating Natural Killer Cells Exhibit an Aberrant Pro-Inflammatory Gene Signature in Systemic Sclerosis Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/increased-proliferating-natural-killer-cells-exhibit-an-aberrant-pro-inflammatory-gene-signature-in-systemic-sclerosis-patients/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/increased-proliferating-natural-killer-cells-exhibit-an-aberrant-pro-inflammatory-gene-signature-in-systemic-sclerosis-patients/