Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 26, 2025
Title: Plenary I (0772–0776)
Session Type: Plenary Session
Session Time: 10:30AM-10:45AM
Background/Purpose: Microbial small RNAs (sRNAs) can regulate human genes, often with anti-inflammatory effects. We previously showed that an increased plasma concentration of a tRNA-derived RNA (tDR-1), produced by multiple bacteria from the phylum Proteobacteria, was associated with lower RA disease activity, particularly fewer tender joints, in 2 independent cohorts, and better treatment response to multiple disease modifying antirheumatic drugs. The purpose of this study was to determine if tDR-1 is a biomarker associated with decreased future development of clinical RA among individuals at-risk for the disease and exhibits in vitro anti-inflammatory effects which may affect RA development.
Methods: Archived longitudinal plasma and clinical data from participants from the Studies of the Etiology of Rheumatoid Arthritis cohort were used for this study. Microbial tDR-1 was measured in plasma by quantitative PCR by investigators blinded to clinical details. Human THP-1 monocyte-derived macrophages were treated with tDR-1, scramble control or transfection reagent alone in triplicate. After 24 hours, gene expression was assessed by the Nanostring Immunology panel. Pathway analysis was performed using Ingenuity Pathway Analysis.
Results: The study included 60 participants at-risk for development of RA with anti-CCP3 antibody positivity (CCP3+) without synovitis at baseline and 123 seronegative control participants. Among the CCP3+ participants, 25 later developed clinical RA (defined by meeting 2010 classification criteria or presence of inflammatory arthritis) and 35 did not (Table). Microbial tDR-1 was 7.7-fold (p=2E-06) (Figure 1) enriched at baseline among CCP3+ participants who did not develop RA versus those who did, and remained independently associated with decreased RA development after adjustment for the presence or absence of any other autoantibody (including CCP2, CCP3.1, RF IgA, RF IgM, or RF IgG), shared epitope, and ever smoker status (p=0.006). Among CCP3+ at-risk participants, plasma tDR-1 concentration had an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of 0.856 (95% CI 0.768, 0.951) for prediction of not developing RA (p=1.2E-14). Compared to scramble control, tDR-1 significantly downregulated many interferon response genes including MX1 (Figure 2), and pathway analysis identified interferon signaling as most downregulated by tDR-1.
Conclusion: Enrichment of circulating microbial tDR-1 is independently associated with decreased development of future RA among those at high risk for disease. Its ability to reduce interferon response genes, which are typically elevated in early RA, suggests a potential mechanism by which the microbiome could affect the development of RA via sRNAs.
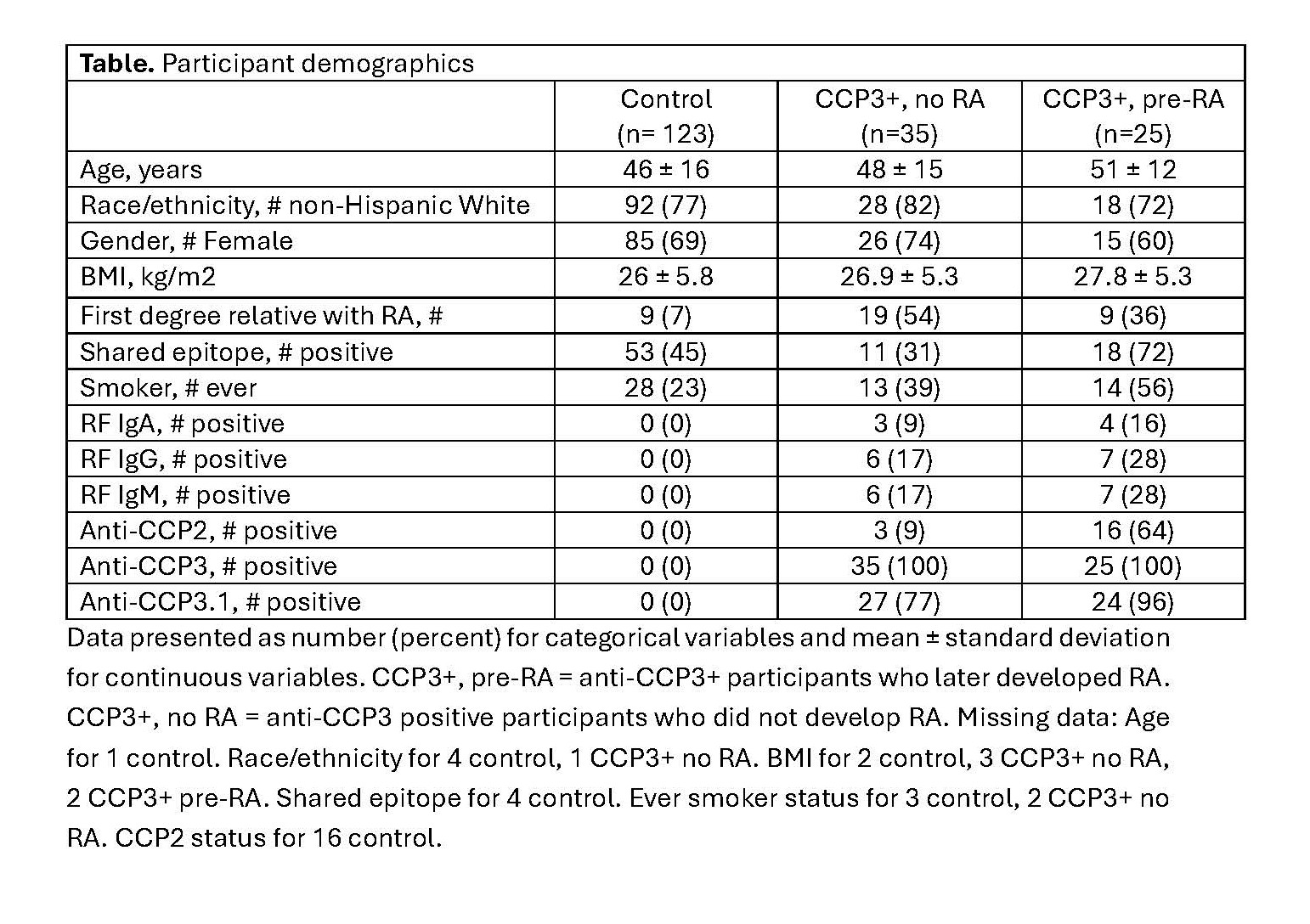 Table. Participant demographics
Table. Participant demographics
.jpg) Figure 1. Plasma tDR-1 concentration in seronegative controls, CCP3+ participants who did not develop future RA (CCP3+, no RA), and CCP3+ participants who later developed RA (CCP3+, pre-RA). The Y axis is presented in log-scale. Comparison by Mann-Whitney U test.
Figure 1. Plasma tDR-1 concentration in seronegative controls, CCP3+ participants who did not develop future RA (CCP3+, no RA), and CCP3+ participants who later developed RA (CCP3+, pre-RA). The Y axis is presented in log-scale. Comparison by Mann-Whitney U test.
.jpg) Figure 2. Change in gene expression in human THP-1 monocyte derived macrophages after treatment with tDR-1 versus scramble control. The majority of significantly downregulated genes are interferon response genes.
Figure 2. Change in gene expression in human THP-1 monocyte derived macrophages after treatment with tDR-1 versus scramble control. The majority of significantly downregulated genes are interferon response genes.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Phothisane A, Joishy T, Ramirez-Becerra C, Wang Z, Wu Q, Seifert J, Feser M, Norris J, Demoruelle K, Moss L, Deane K, Holers V, Ormseth M. Increased Circulating Microbial Small RNA tDR-1 is Associated with Decreased Progression to Future Clinical Rheumatoid Arthritis In High Risk Individuals and Reduces In Vitro Type 1 Interferon Response Gene Expression [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/increased-circulating-microbial-small-rna-tdr-1-is-associated-with-decreased-progression-to-future-clinical-rheumatoid-arthritis-in-high-risk-individuals-and-reduces-in-vitro-type-1-interferon-respons/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/increased-circulating-microbial-small-rna-tdr-1-is-associated-with-decreased-progression-to-future-clinical-rheumatoid-arthritis-in-high-risk-individuals-and-reduces-in-vitro-type-1-interferon-respons/
