Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 10, 2015
Title: Spondylarthropathies and Psoriatic Arthritis - Pathogenesis, Etiology Poster II
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
Immunological,
genetic and therapeutic studies have implicated the IL-17A/IL-23 inflammatory
axis in SpA. GM-CSF is emerging as a cytokine
that marks out a pathogenic subset within this inflammatory axis, and
inhibition of this cytokine pathway is currently in clinical trials for
rheumatoid arthritis. We sought to investigate the role of GM-CSF in SpA pathogenesis.
Methods:
Blood,
synovial fluid and synovial tissue from patients with SpA
was studied ex-vivo and in-vitro using SpA joint
tissue explant assays. GM-CSF production from different cell types were
characterised using multi-colour flow cytometry
(FACS) and time-of-flight cytometry (CyTOF).
Results:
CyTOF analysis revealed ex-vivo GM-CSF production from multiple lymphoid
but not myeloid cell lineages with CD4 cells clearly the main producers upon
whole PBMC stimulation (Fig. 1). CyTOF findings were
validated with flow cytometry (fig 2). The percentage
of CD4 cells producing GM-CSF was significantly increased in AS PBMCs ex-vivo
compared to healthy controls (mean 6.89% vs 3.30%
n=31, p=0.006). Further characterisation of GM-CSF-producing T cells showed
overlap with both classical Th1 and Th17 phenotypes. The mean percentage
of GM-CSF-positive CD4 cells from ex-vivo synovial fluid mononuclear cells
(SFMCs) was 34.27% and significantly higher compared to matched
PBMCs (n=3, p=0.0391). CD4 cells
from SpA synovial tissue mononuclear cell explant
cultures also showed high levels of GM-CSF production by CD4 cells (n=6).
Conclusion:
Increased
numbers of CD4 T cell produce GM-CSF in the blood and joint in SpA. GM-CSF may be a key pathogenic cytokine in SpA and can potentially be targeted therapeutically.
Anti-GM-CSF monoclonal antibodies are already in phase three clinical trials
for other inflammatory diseases and have shown an acceptable safety profile.
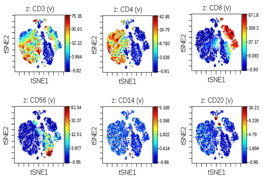
Figure 1: CyTOF shows CD4 cells
to be the main producers of GM-CSF upon ex-vivo PBMC stimulation in AS.
Representative
multi-dimensional viSNE analysis of all GM-CSF
producers upon ex-vivo AS PBMC stimulation shows CD4 cells to be the
predominant GM-CSF producing population. GM-CSF is also
produced by populations of CD8, CD56+ NK cells.
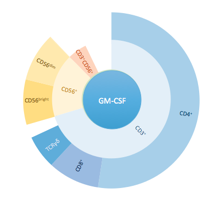
Figure
2: Flow cytometry confirms CD4 cells to be the predominant
GM-CSF producers upon ex-vivo PBMC stimulation in AS.
Pooled
sunburst analysis (Cytobank) from ex-vivo stimulated
PBMCs of AS patients (n=5). CD4 cells account for greater than 50% of all
GM-CSF production with smaller contributions from the CD8, γd-T
Cell and CD56+ NK cells.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Al-Mossawi MH, De Wit J, Ridley A, Bowness P. Increased CD4 T Cell GM-CSF Production in Spondyloarthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/increased-cd4-t-cell-gm-csf-production-in-spondyloarthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/increased-cd4-t-cell-gm-csf-production-in-spondyloarthritis/