Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 19, 2024
Title: Abstracts: Miscellaneous Rheumatic & Inflammatory Diseases II
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 11:00AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: CAR T cell therapy promises to revolutionize the treatment of hematologic malignancies, and more recently has generated early data that it may afford long term, drug free remissions in patients with a variety of autoimmune diseases. However, accessing commercial autologous CAR T therapy remains a major challenge in the oncology setting due to high costs, manufacturing complexity, requirements for lymphodepleting chemotherapies, and lengthy wait times to receive therapy. Application of these individualized therapies to autoimmune diseases is anticipated to apply additional strain on manufacturing and healthcare infrastructure. Herein, we describe an off-the-shelf approach to generate CAR T cells in vivo through administering multidomain fusion surface engineered lentiviral particles (VivoVec™) in the absence of lymphodepleting chemotherapy and demonstrate that the in vivo generated CAR T cells function to achieve deep B cell depletion and immune reset in non-human primates (NHP).
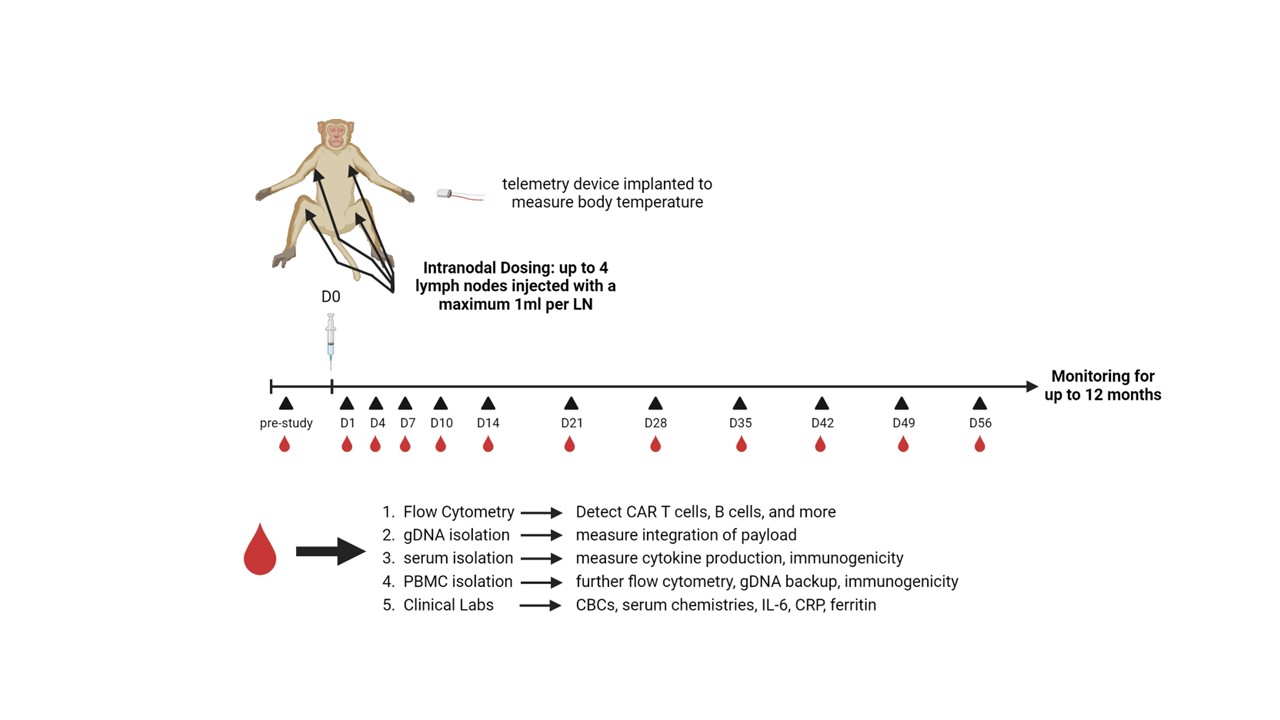
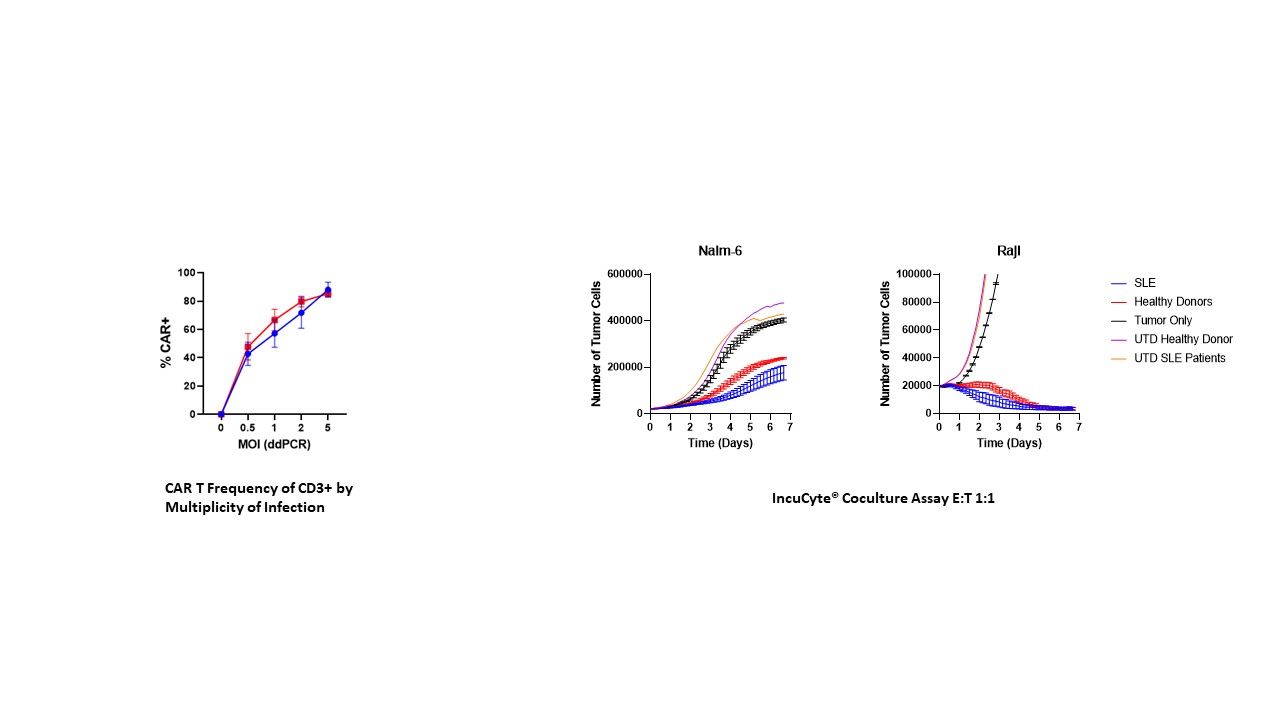
Methods: (1) In vitro evaluation: Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from human SLE patients were transduced with surface engineered VivoVec™ particles carrying an anti-CD20 CAR payload. CAR T cell frequencies were assessed by flow cytometry, and functionality of CAR T cells was evaluated by coculture killing of autologous B cells in the same PBMCs, and CD20 expressing human cell lines, Raji and Nalm6. (2) In vivo model: To demonstrate VivoVec™’s ability to generate anti-CD20 CAR T cells in vivo, 8 healthy, immune competent southern pig-tailed macaques received 1 dose of VivoVec™ particles intralymphatically and were then evaluated for anti-CD20 CAR T cell generation and persistence by flow cytometry and ddPCR, and anti-CD20 CAR T cell mediated function by B cell depletion. Animals were monitored for signs of CAR T cell mediated cytokine release syndrome (CRS) and immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome (ICANS) (Figure 1).
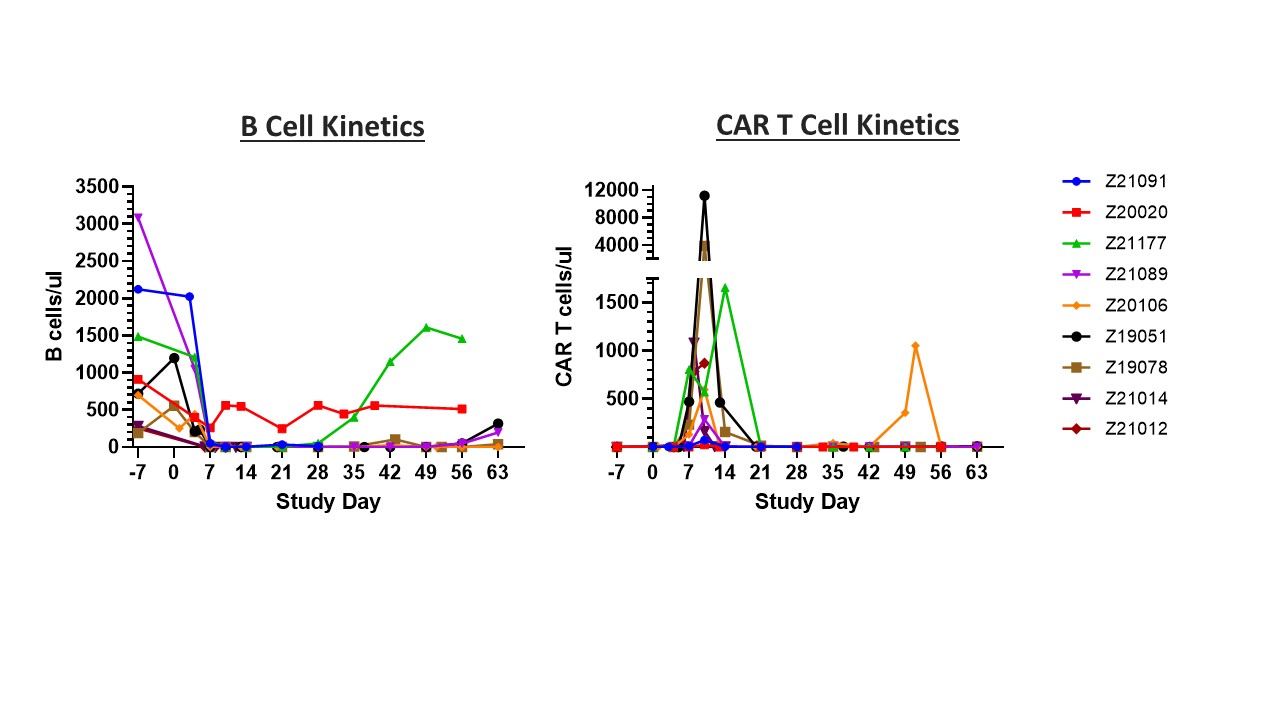
Results: Transduction of SLE patient PBMCs with VivoVec™ particles resulted in anti-CD20 CAR T cell generation similar to that of healthy donor PBMCs. CAR T cells were highly functional in coculture killing evaluations where SLE patient derived CAR T cells eliminated CD20 expressing Nalm6 and Raji cells similarly to healthy donor controls (Figure 2). In vivo, NHPs tolerated VivoVec™ injection with mild to moderate CRS and ICANS associated with CAR T cell expansion that resolved with standard of care interventions. CAR T cell Cmax in vivo occurred 8 to 10 days after VivoVec™ administration and was associated with complete B cell depletion in all but 1 animal with low dose (Figure 3).
Conclusion: A single intralymphatic injection of VivoVec™ particles into non-lymphodepleted, immune competent NHPs is able to generate CAR T cells in vivo, and these CAR T cells expanded and mediated complete B cell depletion in circulation and secondary lymphoid organs. With further development, this approach has the potential to become an off-the-shelf, in vivo, patient specific CAR T cell approach to achieving an “immune reset” that could be impactful in the treatment of multiple autoimmune diseases and would address many issues seen with current ex vivo manufactured autologous CAR T cell therapies.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Beitz L, Parker M, Ulrich-Lewis J, Mittelsteadt K, Gottschalk R, Nicolai C, Qin J, Scharenberg A, Larson R, Ryu B, Cavanaugh E, Tang W, Shin S, Lynch K, Kiem H. In Vivo Generation of B Cell Depleting CAR T Cell Therapies for Treatment of Autoimmune Diseases [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/in-vivo-generation-of-b-cell-depleting-car-t-cell-therapies-for-treatment-of-autoimmune-diseases/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/in-vivo-generation-of-b-cell-depleting-car-t-cell-therapies-for-treatment-of-autoimmune-diseases/