Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 10:00AM-10:50AM
Background/Purpose: Long-term nociceptive pain, as in inflammatory arthritides, can cause Central Sensitization (CS) to pain. CS Inventory (CSI) is a validated screening instrument for clinicians to help identifying patients with CS. We sought to investigate the association between CSI score and clinical, demographic and ultrasonographic parameters of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) or psoriatic arthritis (PsA)
Methods: We conducted a cross-sectional analysis on patients with an established diagnosis of RA or polyarticular PsA. Disease activity was measured with SDAI and DAS28-CRP in RA patients and with DAPSA in PsA patients. The presence and severity of synovitis was also measured with the overall ultrasound (US) 7-joints score and its components (gray-scale ultrasound [GSUS], power-Doppler ultrasound [PDUS] and erosions). CSI questionnaire was analyzed either as a continuous variable or as positiveegative (threshold 40 points) or divided in four categories, i.e., subclinical (≤29), mild (30-39), moderate (40-49), severe/extreme (≥50). Exclusion criteria included: diagnosis of PsA with enthesitis predominant and/or spondylitis subtypes.
Results: A multiple linear regression analysis was performed to predict CSI score based on clinical and demographic characteristics (age, sex, BMI, disease duration, tender and swollen joints, CRP, 7-joints US score and fibromyalgia diagnosis), including HAQ. HAQ was the only significant predictor of the CSI score (figure 1 and 2). CSI score increased of 15.3 points for each point of HAQ (95% CI 7.4-23.3, p < 0.0001). In PsA patients, but not in RA patients, disease activity was strongly correlated with CSI score (figure 3).
Overall, we did not find any correlation between 7-joints US score and CSI score. We found a significant association between 7-joints US score (and its components) and disease duration (year to diagnosis r 0.53, p < 0.0001), interestingly, only the erosion score correlated significantly with the time from symptoms onset to the diagnosis (0.28, p < 0.01). In subgroups analyses, in patients with RA, 7-joints US overall score was positively associated with disease duration (years to onset of symptoms r 0.77, p < 0.0001). We found a strong relationship between 7-joints overall, PDUS scores and disease activity scores of RA (r 0.50 p 0.006 for SDAI and PDUS). In PsA patients, we found no association between 7-joints US overall, GSUS, PDUS or erosion score and DAPSA.
Conclusion: In summary, central sensitization assessed with CSI questionnaire was significantly associated with functional disability measured with HAQ independently from age, sex, BMI, concomitant fibromyalgia diagnosis and other clinical parameters (CRP, time to disease onset, tender and swollen joint count). SDAI and DAS28-CRP were significantly associated with ultrasonographic parameters of synovial inflammation.
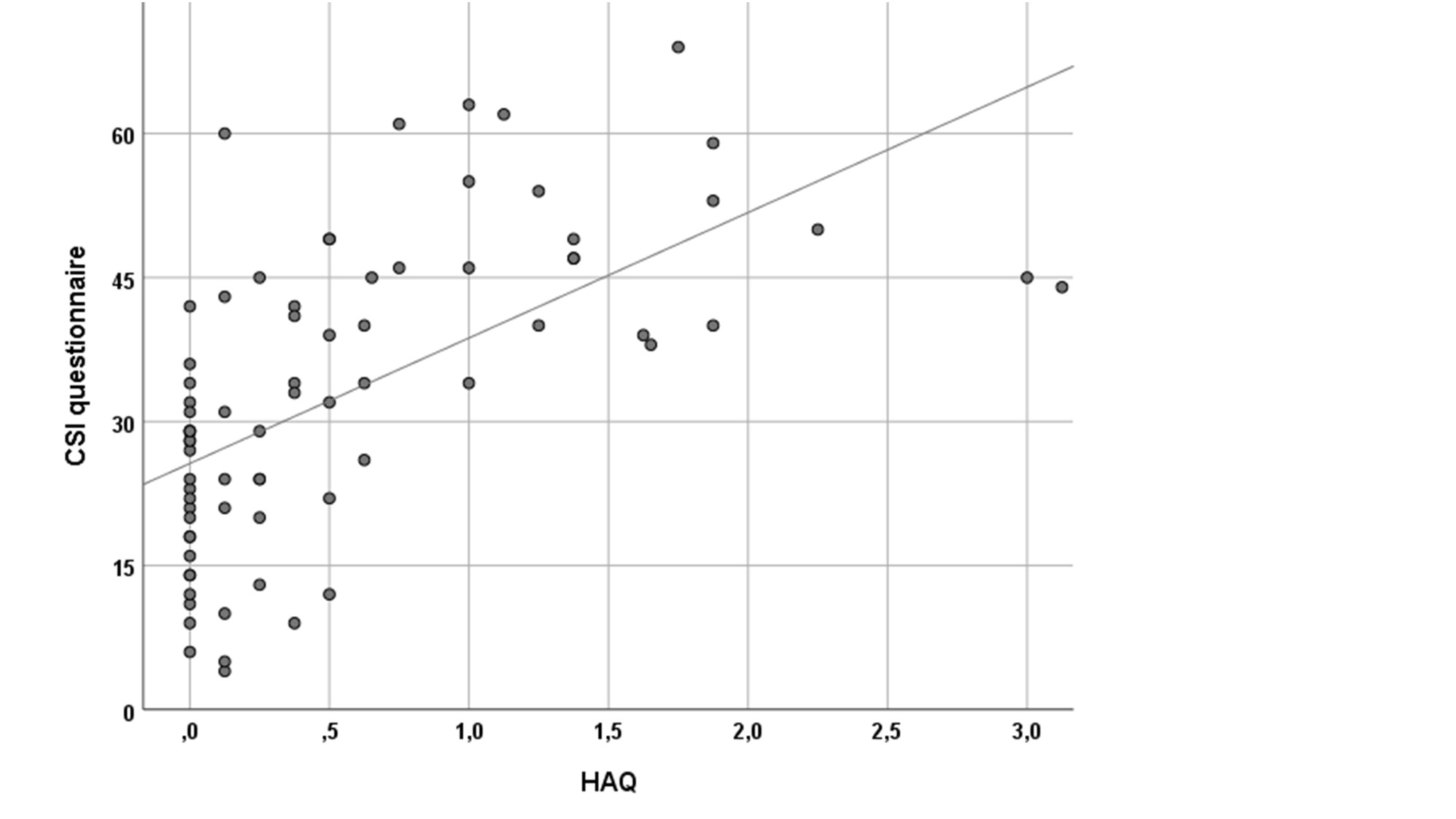 Figure 1. Relationship between HAQ and CSI questionnaire score in patients with inflammatory arthritides. R2 0.361, p < 0.0001
Figure 1. Relationship between HAQ and CSI questionnaire score in patients with inflammatory arthritides. R2 0.361, p < 0.0001
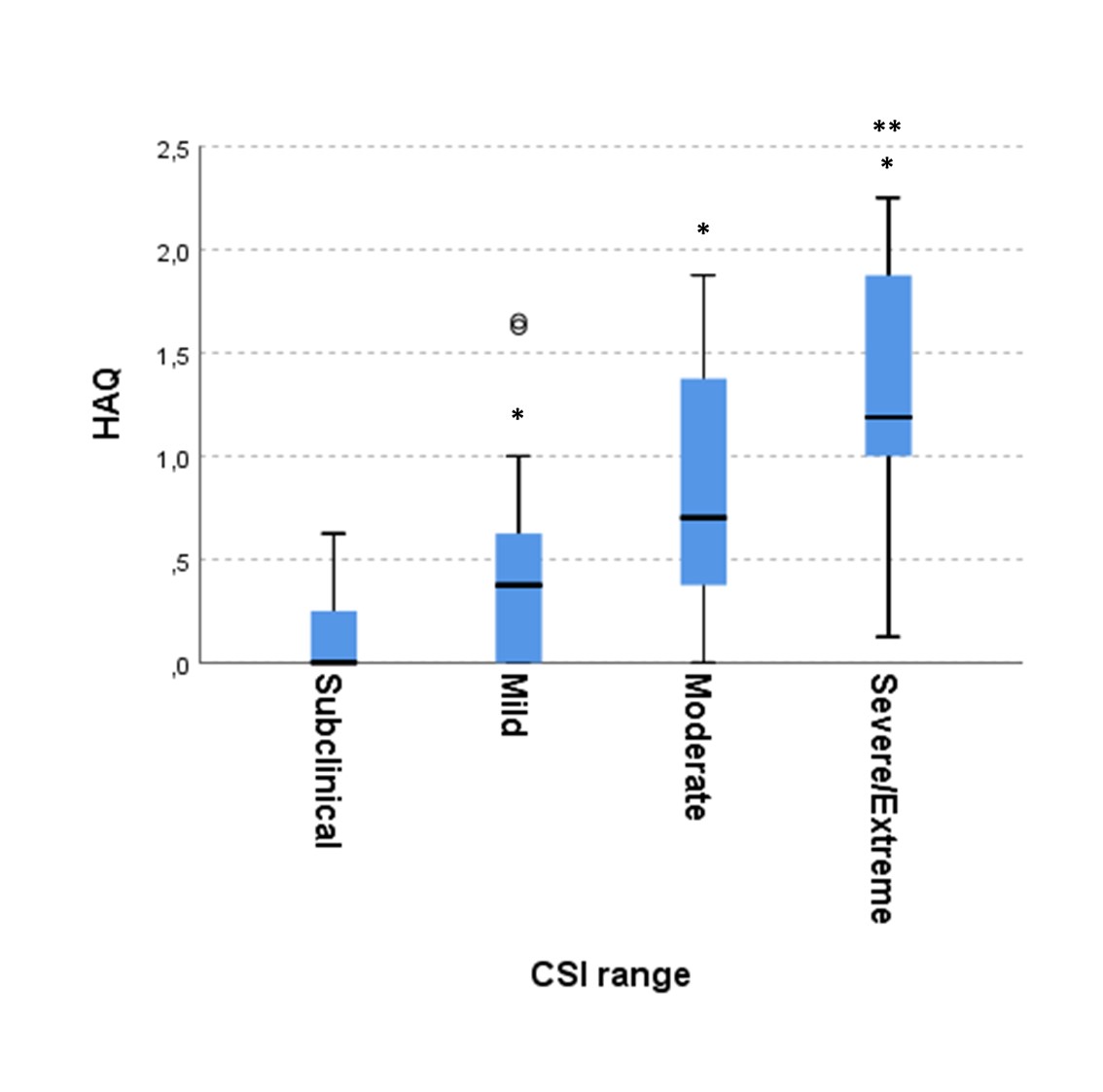 Figure 2. Median HAQ at different CSI questionnaire score ranges
Figure 2. Median HAQ at different CSI questionnaire score ranges
 Figure 3. Relationship between DAPSA and CSI questionnaire score in patients with psoriatic arthritis. R2 0.436, p < 0.0001
Figure 3. Relationship between DAPSA and CSI questionnaire score in patients with psoriatic arthritis. R2 0.436, p < 0.0001
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Adami G, Fassio A, Gerratana E, Giollo A, Benini C, Idolazzi L, Vantaggiato E, Gatti D, Rossini M. In Patients with Inflammatory Arthritides Central Pain Sensitization Is Strictly Associated with Functional Disability [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/in-patients-with-inflammatory-arthritides-central-pain-sensitization-is-strictly-associated-with-functional-disability/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/in-patients-with-inflammatory-arthritides-central-pain-sensitization-is-strictly-associated-with-functional-disability/
