Session Information
Date: Monday, November 11, 2019
Title: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster II: Treatments, Outcomes, & Measures
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
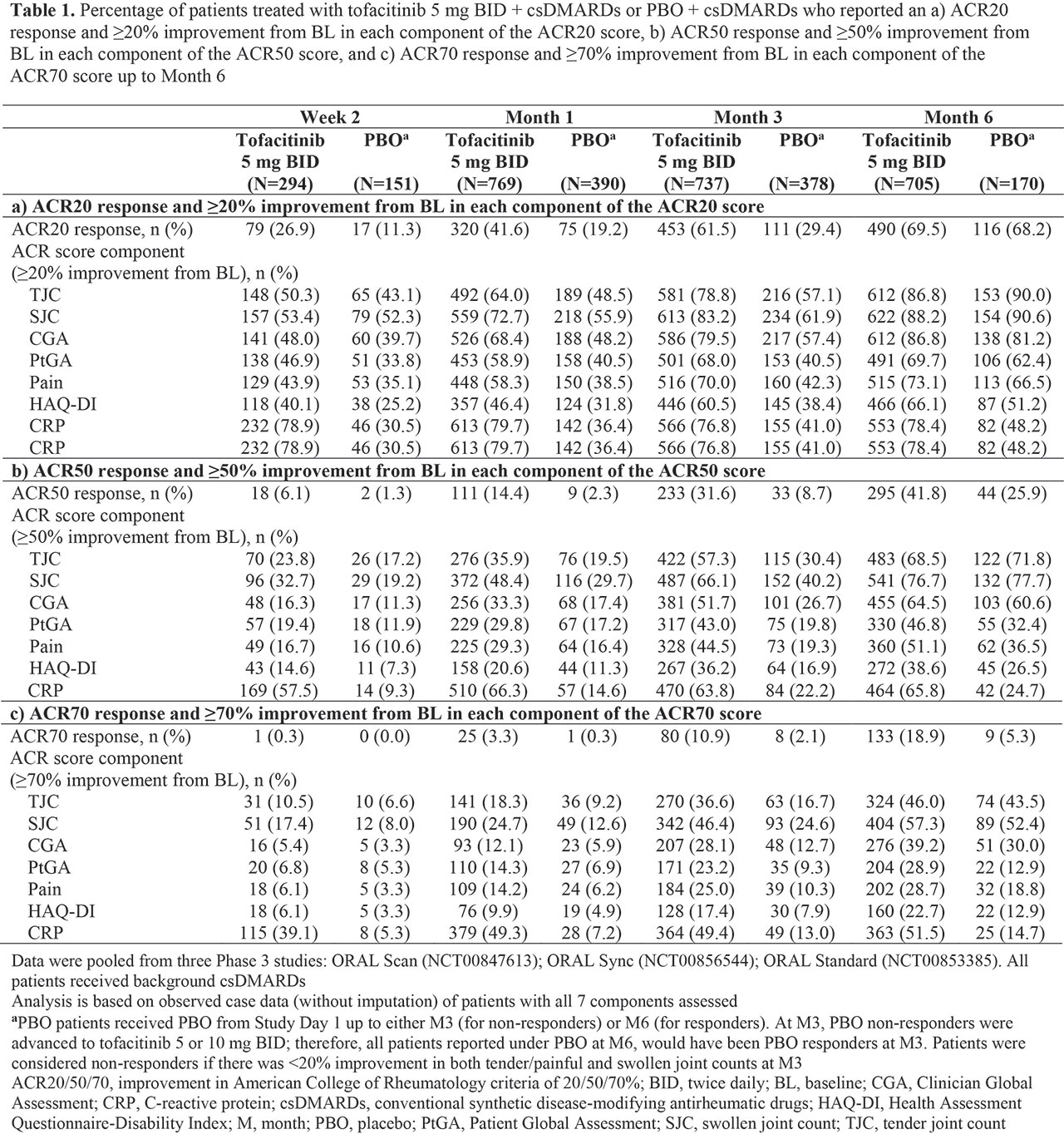
Background/Purpose: Tofacitinib is an oral JAK inhibitor for the treatment of RA. In clinical trials, standard criteria for measuring treatment efficacy in patients (pts) with RA include ACR response rates, composite scores that represent ≥ 20/50/70% improvement in seven components of disease activity. This post hoc analysis evaluated the impact of tofacitinib 5 mg BID + csDMARDs, and placebo (PBO) on each ACR score component.
Methods: Efficacy data for tofacitinib 5 mg BID and PBO were pooled from three Phase (P)3 PBO-controlled trials (ORAL Scan, NCT00847613; ORAL Sync, NCT00856544; ORAL Standard, NCT00853385) of tofacitinib + csDMARDs (mostly MTX) in RA pts with inadequate response to ≥ 1 csDMARD. Endpoints summarized descriptively included proportions of pts achieving: ACR20/50/70 responses, and ≥ 20/50/70% improvements from baseline (BL) in individual ACR components (TJC, SJC, CGA, PtGA, Pain, HAQ-DI, and CRP) from Week (W)2 through Month (M)6, and mean percent improvement from BL in all components for ACR20 responders at M3.
Results: Compared with csDMARD-IR pts receiving PBO, greater proportions of csDMARD-IR pts receiving tofacitinib + csDMARDs achieved ≥ 20% improvement from BL in all ACR components by W2, with proportions generally increasing at all subsequent time points to M6 (Table 1a); typically, higher proportions of pts achieved ≥ 20% improvement from BL in individual components vs overall ACR score. Overall, through M6, a higher proportion of pts achieved ≥ 20% improvement for primary components (TJC and SJC) vs the secondary components CGA, PtGA, Pain, and HAQ-DI; among secondary components, ≥ 20% improvement rates were numerically highest for CGA (excepting CRP at W2 and M1 in pts receiving tofacitinib). In contrast, ≥ 50% and ≥ 70% improvement rates with tofacitinib were numerically higher for PtGA and Pain vs CGA at W2 (Table 1b‑c). Among pts achieving an ACR20 response at M3, mean percent improvement from BL was > 70% for primary components, and ranged from 18.6% to 58.9% for secondary components (Table 2).
Conclusion: In this post hoc analysis of pooled P3 data, tofacitinib treatment was associated with rapid and sustained improvements in all ACR components. In tofacitinib- and PBO-treated pts, physician-reported measures (TJC, SJC, and CGA) were found to contribute somewhat more to the achievement of overall ACR20 response, compared with pt-reported outcomes (PROs; PtGA, Pain, and HAQ-DI). This numerical trend may be reflective of the subjective nature of PROs and overall wellbeing of the pt, and thus, their reduced sensitivity to anti‑inflammatory treatment. Intriguingly, with more stringent endpoint criteria at earlier time points, some PROs had a somewhat greater contribution to overall ACR response, which may be attributable to rapid symptomatic improvement in these pts. While ACR scores are not generally used in the clinic, individual components may be measured; thus, these data may help guide clinical expectations with new therapies.
Acknowledgments: Study sponsored by Pfizer Inc. Medical writing support was provided by Kirsten Woollcott of CMC Connect and funded by Pfizer Inc.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bessette L, Dougados M, Mysler E, Genovese M, Kinch C, Kwok K, Lukic T, Girard T, Landry P, van Vollenhoven R. Impact of Tofacitinib on the Individual Components of the ACR Composite Score in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Post Hoc Analysis of Phase 3 Trials [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-tofacitinib-on-the-individual-components-of-the-acr-composite-score-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-post-hoc-analysis-of-phase-3-trials/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-tofacitinib-on-the-individual-components-of-the-acr-composite-score-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-post-hoc-analysis-of-phase-3-trials/