Session Information
Date: Monday, November 8, 2021
Title: SLE – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster III: Outcomes (1257–1303)
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disease characterized by multiple and heterogeneous clinical manifestations that may negatively affect these patients’ quality of life (QoL) and their levels of activity and productivity, despite overall progress in treatment of the disease. The aim of this study is to assess lupus quality of life (LupusQol) and work productivity and activity impairment (WPAI) of daily life in a SLE multicenter Latin American cohort (GLADEL 2.0, Grupo Latino Americano De Estudio del Lupus) among patients with active lupus nephritis (LN) versus those without LN (never) and/or currently inactive LN.
Methods: The GLADEL 2.0 cohort enrolled SLE patients >18 years of age, from three different subsets: Group I: SLE patients, without renal involvement (never); Group II: SLE patients with prevalent renal involvement (at any time during their disease course), currently inactive; Group III: SLE patients with prevalent or incident renal involvement, currently active. Disease activity was ascertained with the Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index (SLEDAI-2k) and the Physician Global Assessment (PGA) and damage with the SLICC/ACR Damage Index (SDI). The differences in the baseline Lupus QoL (questions were categorized as never or present at different degree) and WPAI-Lupus [Questions 1 (Currently employed), 5 (Degree health affected productivity while working) and 6 (Degree health affected regular activities)] were analyzed among these three groups. We particularly were interested in examining in more detail Question 6 of the WPAI, that focus on activities of daily living and which is answered by everybody regardless of whether they are working or not. Numeric variables are reported as medians (interquartile ranges IQR) and compared using Wilcoxon test; categorical variables are reported as frequencies (percentages) and compared using Chi-square or Fisher test, as appropriate. To evaluate the impact of active versus inactive LN in WPAI (Question 6), a multivariate analysis (MV) was adjusted for possible confounders such as: sex, age, socioeconomic level, ethnicity, education, activity and damage in a negative binomial model.
Results: A total of 849 patients with a diagnosis of SLE were included; 344 in Group I, 205 in Group II and 300 in Group III. Their main sociodemographic and clinical features are shown in Table 1. Patients with active LN (group III) had a higher proportion of male patients, were younger at diagnosis, had a shorter disease duration and higher SLEDAI and PGA scores. This group of patients also presented greater impact in all LupusQoL domains (Table 2) and in the WPAI (Table 3). Moreover, the MV analysis for Question 6 of the WPAI demonstrate a significant higher degree health regular activities impairment and active LN after adjusting for confounders (p=0.02) (Data not shown).
Conclusion: In this cohort, we have shown that active LN significantly affects the patients’ QoL especially in their physical health, emotional health, body image and fatigue. In addition, an impact in work productivity and activity impairment was observed in this group.
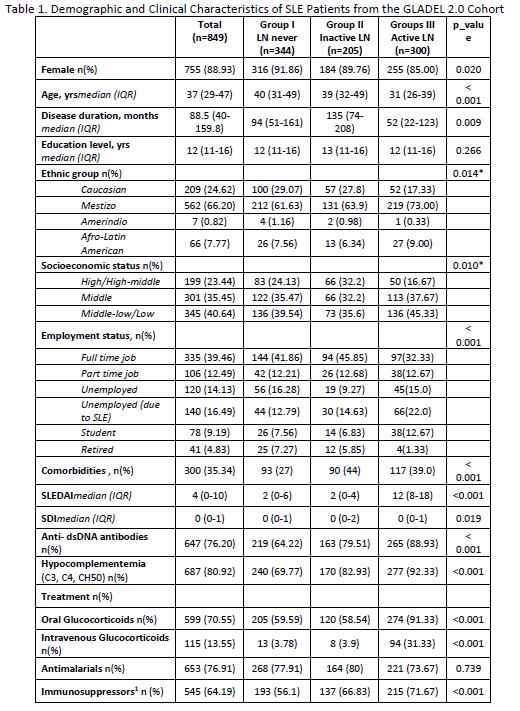 PGA: Physician Global Assessment. SLEDAI_2k: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index. SDI: damage with the SLICC/ACR Damage Index. Immunosuppressors1: Mycophenolate, Methotrexate, Azathioprine, Oral Cyclophosphamide, Intravenous Cyclophosphamide, Tacrolimus, Ciclosporin A.
PGA: Physician Global Assessment. SLEDAI_2k: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index. SDI: damage with the SLICC/ACR Damage Index. Immunosuppressors1: Mycophenolate, Methotrexate, Azathioprine, Oral Cyclophosphamide, Intravenous Cyclophosphamide, Tacrolimus, Ciclosporin A.
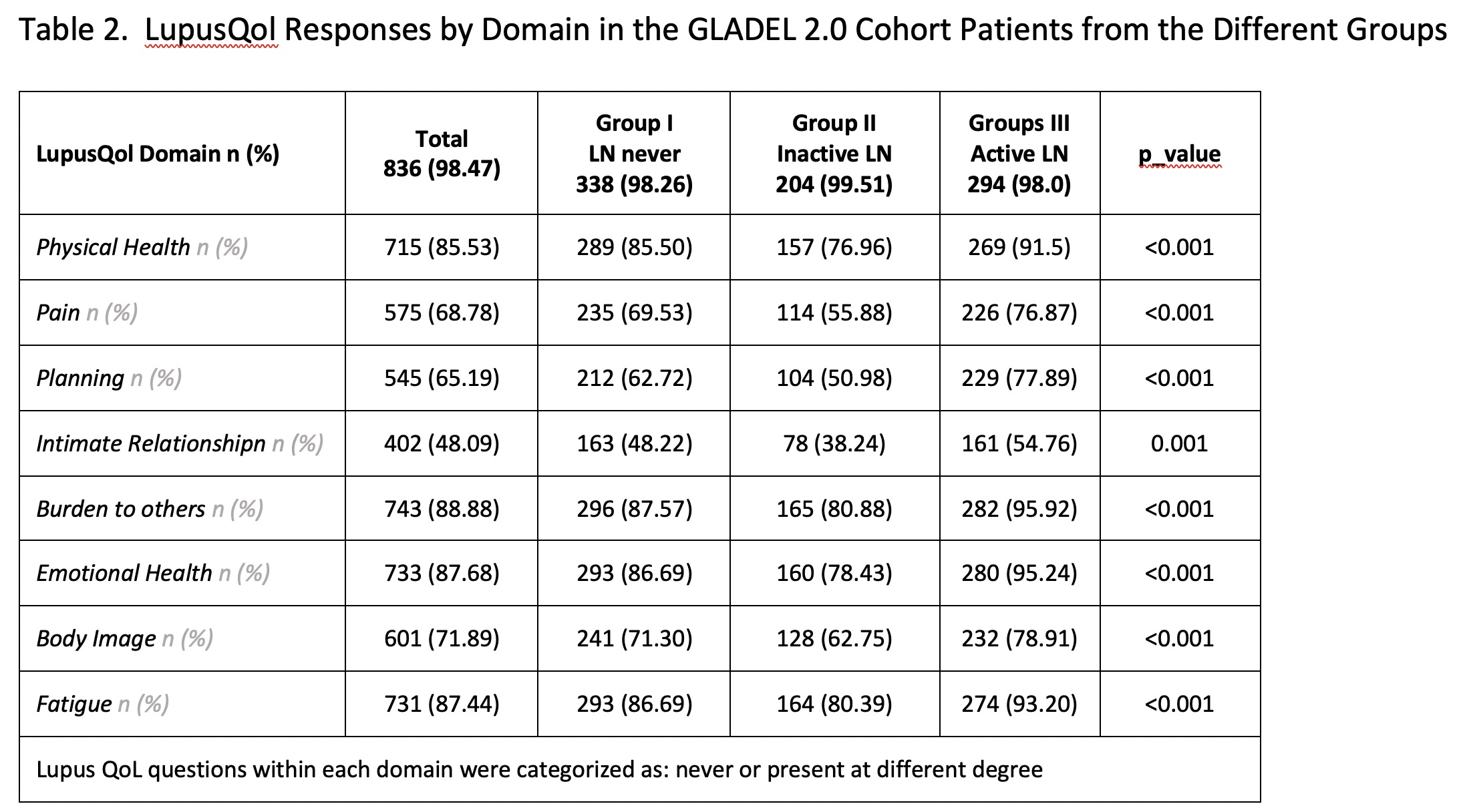 Lupus QoL questions within each domain were categorized as: never or present at different degree Percentages reflect positive responses (i.e., present) on the QOL questions
Lupus QoL questions within each domain were categorized as: never or present at different degree Percentages reflect positive responses (i.e., present) on the QOL questions
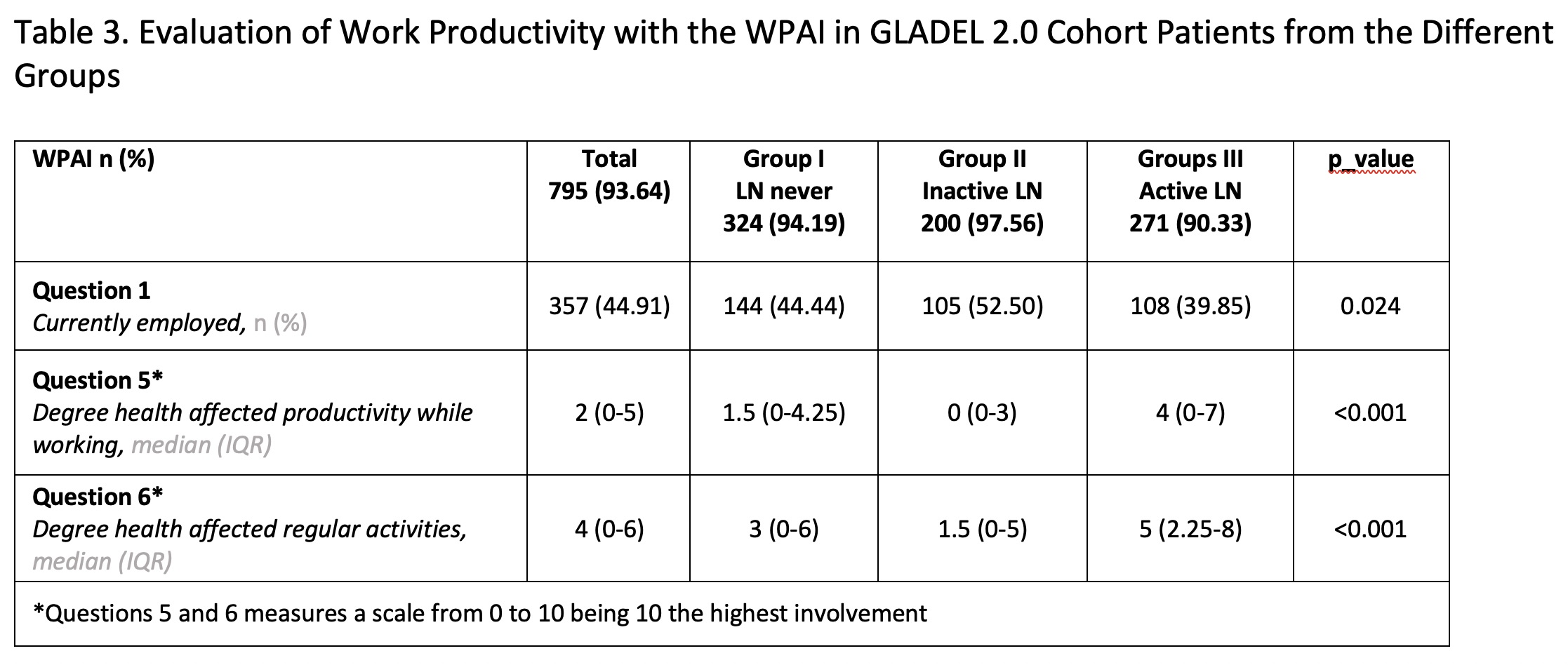 *Questions 5 and 6 measures a scale from 0 to 10 being 10 the highest involvement
*Questions 5 and 6 measures a scale from 0 to 10 being 10 the highest involvement
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Nieto R, Ferreira Borba E, Settecasse E, Fernandez-Avila D, Maurelli L, Gobbi C, Saurit V, Arizpe F, Daniele J, Bertolaccini M, Kerzberg E, Gargiulo M, Rodriguez A, Londe A, Barbosa V, Gasparin A, Albanez A Cunha Andrade C, Parente Costa Seguro L, Victoria de Oliveira Martins L, Neira O, Llanos C, Massardo L, Iglesias A, Nieto Aristizábal I, Vasquez G, Mendez-Patarroyo P, Rueda L, Martínez Pérez J, Sánchez Briones R, Pérez Cristóbal M, Martin-Nares E, Juárez-Vicuña Y, Gonzalez Bello Y, González García J, Galarza-Delgado D, Vázquez M, Langjarh P, Alva Linares M, Reategui-Sokolova C, Calvo Quirós A, Rodriguez E, Robaina R, Rebella M, Alarcn G, Orillion A, Karyekar C, Zazzetti F, Pons-Estel G. Impact of Active Lupus Nephritis in Patient-Reported Outcomes from a Latin American, Multicenter Lupus Cohort [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-active-lupus-nephritis-in-patient-reported-outcomes-from-a-latin-american-multicenter-lupus-cohort/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-active-lupus-nephritis-in-patient-reported-outcomes-from-a-latin-american-multicenter-lupus-cohort/
