Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: Abstracts: Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders II: Clinical Research
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:00PM-5:30PM
Background/Purpose: Systemic sclerosis (SSc) associated pre-capillary pulmonary hypertension (precapPH) is a severe condition that requires prompt treatment. Although immunosuppressants (IMS) are standard of care for treating interstitial lung disease (ILD) and diffuse skin fibrosis (dcSSc), their effect on SSc-precapPH remains unclear. We aimed to test whether IMS affect morbidity and mortality in SSc-precapPH in the EUSTAR cohort.
Methods: SSc-precapPH patients (mPAP≥ 21 mmHg, PWP≤15 mmHg, PVR≥2 WU) with at least 3 months follow-up were eligible. IMS included csDMARDS (prednisone ≥10 mg/day, cyclophosphamide, mycophenolate mofetil, azathioprine, methotrexate) and targeted therapies (abatacept, rituximab, tocilizumab, TNFi, JAKi), administered after the diagnostic right heart catheterization. The WHO precapPH class was categorized into WHO group 1 (no ILD), mild WHO group 3 (ILD and forced vital capacity – FVC ≥70%) and severe WHO group 3 (ILD and FVC< 70%).
The morbidity-mortality outcome was defined by the occurrence of either death or precapPH worsening (one of 6MWD decrease≥15%, worsening of NYHA class, onset of right heart failure, additional PAH medication, starting iv/sc prostanoids, lung transplantation, atrial septostomy). Death and precapPH worsening were also separate secondary outcomes.
We evaluated the association between IMS and time to first event with a multiple Cox regression model. Baseline covariates were chosen by expert opinion, including the WHO precapPH class, SSc-related risk factors for mortality (e.g., sex, age, dcSSc, renal crisis, digital ulcers), reasons for IMS use (e.g., muscle weakness, joint synovitis), and PAH parameters for risk stratification (mPAP, BNP/NTproBNP, NYHA class, cardiac index, 6MWD). IMS and pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) drugs were treated as time-dependent variables.
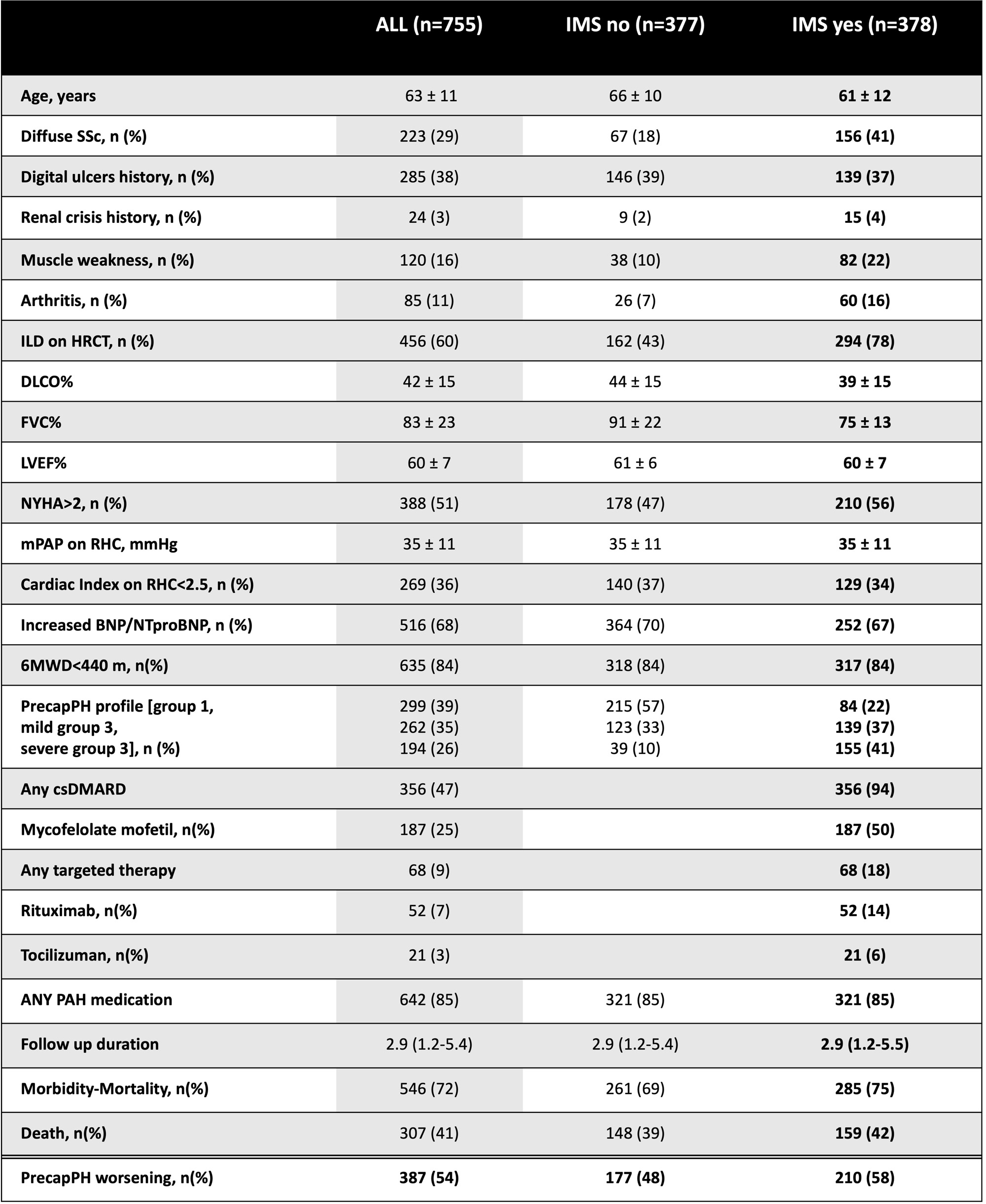
Results: 755 SSc-precapPH patients were included (18% males, age 63±11 years, disease duration 11±9 years, 29% dcSSc, 60% ILD on HRCT). 377 (50%) received IMS [365 (47%) csDMARDs, 68 (9%) targeted therapies]. Patients receiving IMS had more frequently ILD, dcSSc, joint and muscle involvement (Table 1).
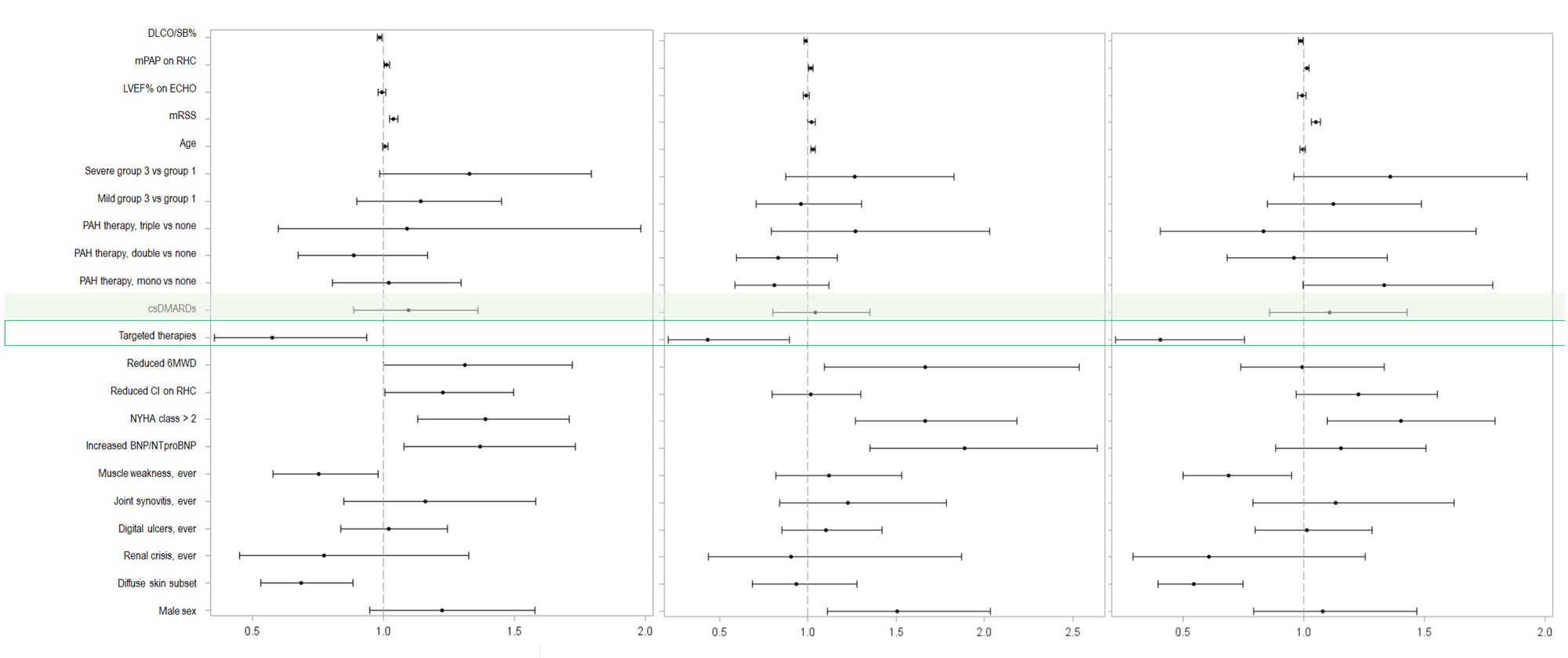
In median follow-up of 2.9 years, 70% of patients developed a morbidity-mortality event. While overall IMS exposure did not associate with outcomes, targeted therapies were associated with reduced risk of morbidity-mortality [HR 0.58, 95% CI 0.35-0.95, p=0.03] and both secondary outcomes [death, HR 0.43, 95% CI 0.21-0.89, p=0.02; precapPH worsening, HR 0.41, 95% CI 0.22-0.78, p< 0.01] – Figure 1.
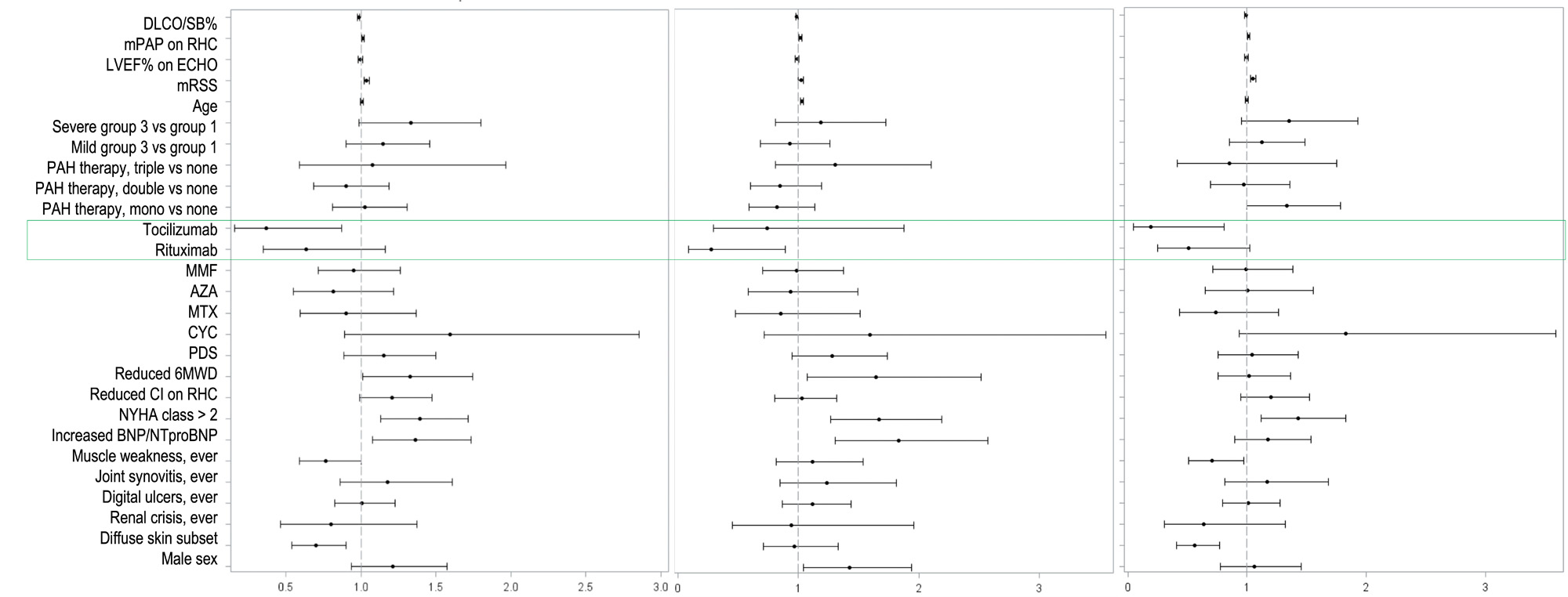
When looking at specific targeted therapies, tocilizumab showed a risk reduction for morbidity-mortality and precapPH worsening (HR 0.37, 95% CI 0.17-0.81, p=0.02 and HR 0.19, 95% CI 0.05-0.78, p=0.02, respectively), while rituximab for death (HR 0.28, 95% CI 0.08-0.93, p=0.04) with a trend for precapPH worsening (HR 0.51, 95% CI 0.25-1.04, p=0.06) – Figure 2.
Conclusion: In this large EUSTAR SSc-precapPH cohort, targeted therapies are associated with reduced risk of mortality and precapPH worsening, which is independent from WHO group and other confounders. The impact of targeted therapies on long-term outcomes should be further explored in RCTs.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bruni C, Fretheim H, Tofani L, Weber Y, Hachulla E, Carreira P, Giuggioli D, Airò P, Siegert E, Müller-Ladner U, Matucci Cerinic m, Riemekasten G, Simeon-Aznar C, de Vries-Bouwstra J, Saketkoo L, Distler J, Balbir-Gurman A, Castellvi I, Zanatta E, Smith V, Denton C, Maurer B, Giollo A, Iannone F, Dagna L, Truchetet M, Kuwana M, ALLANORE Y, Tanaka Y, Martin M, Rosato E, Gheorghiu A, Del Galdo F, Solanki K, Vacca A, RESENDE C, VIEIRA S, Czirjak L, Barisic M, Cantatore F, Riccieri v, Andréasson K, Chung L, Muller C, OPRIS-BELINSKI D, Rednic S, Sfikakis P, Levy Y, Hoffmann-Vold A, Distler O, Hsu V, Heitmann S, Moroncini G, Iudici M, Henes J, De Langhe E, Herrick A, Montecucco C. Immunosuppression with Targeted Therapies Reduces Morbidity and Mortality in Pre-Capillary Pulmonary Hypertension Associated with Systemic Sclerosis: A EUSTAR Analysis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/immunosuppression-with-targeted-therapies-reduces-morbidity-and-mortality-in-pre-capillary-pulmonary-hypertension-associated-with-systemic-sclerosis-a-eustar-analysis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/immunosuppression-with-targeted-therapies-reduces-morbidity-and-mortality-in-pre-capillary-pulmonary-hypertension-associated-with-systemic-sclerosis-a-eustar-analysis/