Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The use of complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) is prevalent in dermatology. Certain CAMs, including Spirulina, Alfalfa, Chlorella, Echinacea, and Blue-Green Algae have been reported to incite an immune response or induce dermatomyositis (DM), cutaneous lupus erythematosus (CLE) or autoimmune blistering diseases (AIBD). Given these potential effects, there is a need to characterize CAM usage in patients.
Methods: We performed a retrospective chart review of prospectively-collected data at the University of Pennsylvania to characterize CAM usage among patients with DM, CLE, AIBD (including pemphigus vulgaris and bullous pemphigoid), and controls without autoimmune disease. Information gathered included demographic information, disease history, and CAM usage and duration (Spirulina, Chlorella, Alfalfa, Green Algae, Echinacea, or other). CAM use was elicited in a stepwise manner, starting with asking patients open-ended questions about CAM use, followed by handing a flyer that lists herbal supplements to aid with recall. Statistical analysis was performed using logistic regression to calculate odds ratios (OR), accounting for race and sex as covariates, at a significance level of 0.05.
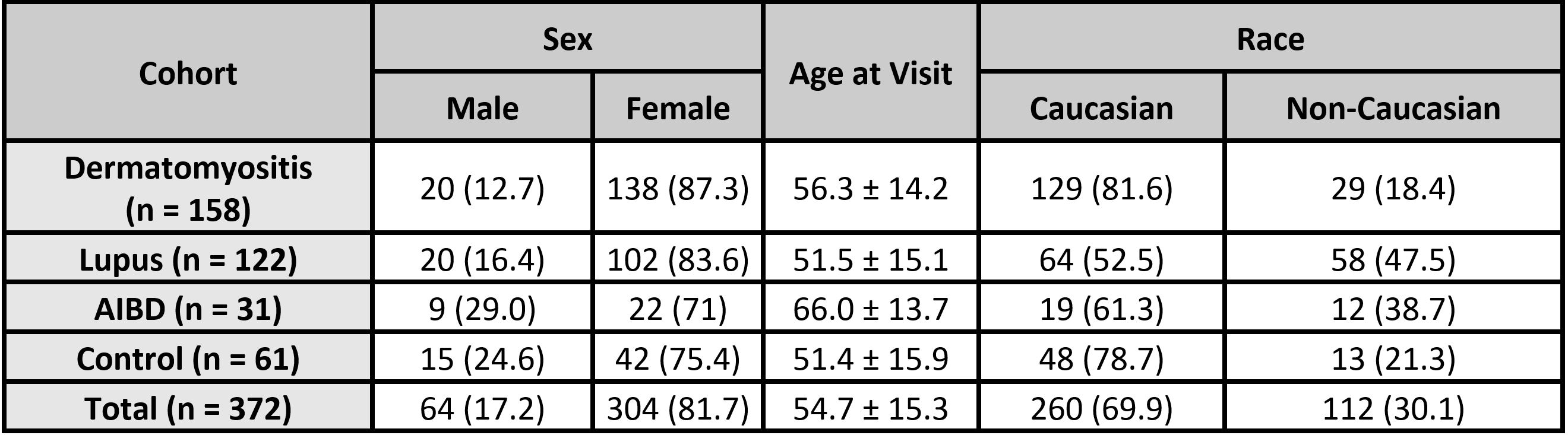
Results: 372 patients were enrolled, including 158 DM (42.5%), 122 CLE (32.8%), 31 AIBD (8.3%), and 61 controls (16.4%). All cohorts were predominantly female and Caucasian. DM had the greatest proportion of Caucasians (81.6%), followed by controls (78.7%), AIBD (61.3%), and CLE (52.5%). CAM use was reported in 12.1% of all patients (19.6% of DM, 5.7% of CLE, 6.5% of AIBD, and 8.2% of controls). Spirulina was the most frequently-used herbal supplement for DM (14.6%), CLE (4.1%), and controls (5.7%), while blue-green algae was the most frequently-used CAM for AIBD (3.2%). Herbal use in DM was greater compared to controls (OR = 2.37, p = 0.0919), and compared to other autoimmune cohorts (OR = 3.47, p = 0.0032). Spirulina use was greater among DM patients compared to both controls (OR = 2.34, p = 0.1345) and to other autoimmune cohorts (OR = 4.92, p = 0.0027). Herbal and spirulina use were not significantly associated with non-DM autoimmune diseases compared to controls.
Conclusion: Our study demonstrates that CAM use, in particular spirulina, is greater among patients with DM. This association is statistically significant for DM compared to CLE or AIBD. This study demonstrates that the use of CAM is of concern among the patients with a history of DM. Patients with DM should be educated regarding the risk of onset or flare from using immunostimulatory CAM such as Spirulina.
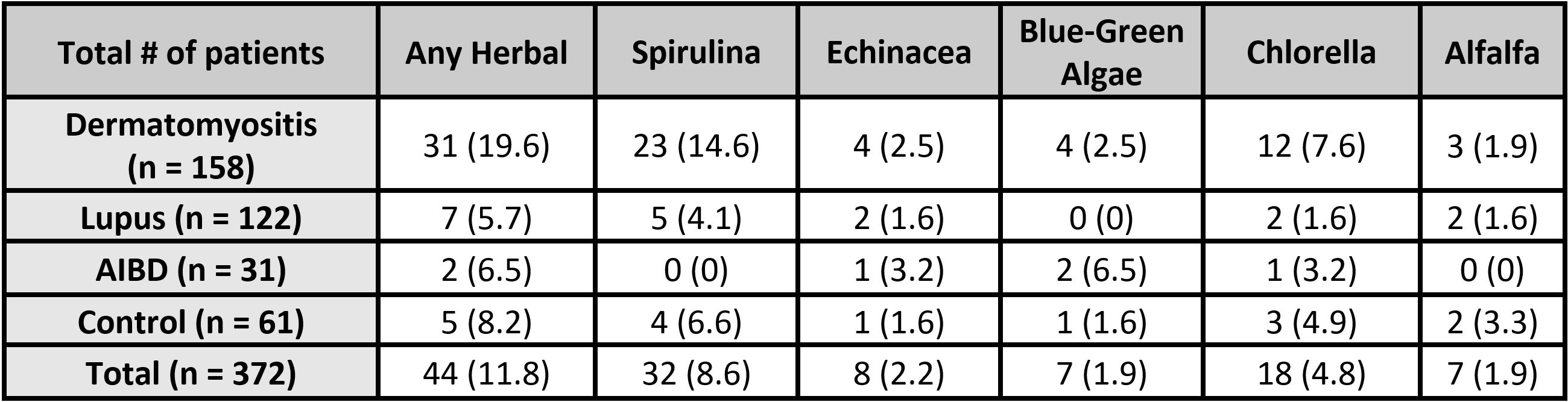 Herbal supplement use for each cohort (%)
Herbal supplement use for each cohort (%)
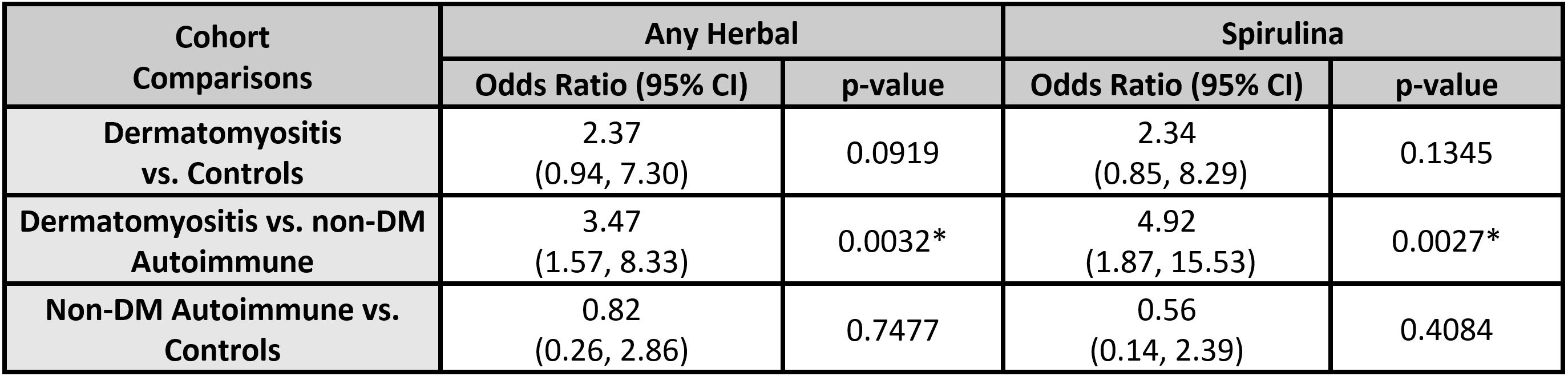 Logistic regression comparison of herbal and spirulina use between cohorts
Logistic regression comparison of herbal and spirulina use between cohorts
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ravishankar A, Yan D, Bax C, Concha J, Shields B, Pappas-Taffer L, Feng R, Okawa J, Werth V. Immunostimulatory Herbal Supplement Use Is More Common Among Patients with Dermatomyositis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/immunostimulatory-herbal-supplement-use-is-more-common-among-patients-with-dermatomyositis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/immunostimulatory-herbal-supplement-use-is-more-common-among-patients-with-dermatomyositis/