Session Information
Date: Monday, November 18, 2024
Title: Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Basic Science Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Antibodies (Abs) directed against the angiotensin II type-1 receptor (AT1R) and extracellular vesicles (EVs) derived from systemic sclerosis (SSc) patients have the potential to modulate the function of monocytes, which are key cells in SSc pathogenesis. This study aims to investigate whether AT1R Abs interacts with EVs and to determine the phenotype and function of monocytes, particularly their migration capacity and cytokine secretion.
Methods: Exosomes were isolated from the sera of SSc patients and healthy controls (HC) using sequential centrifugation and precipitation via polyethylene glycol. The size of the EVs was analyzed by nanoparticle tracking analysis. AT1R expression on EVs was analyzed by western blot. To study the phenotype and function of monocytes induced by EVs and AT1R Abs, human peripheral blood (PB) monocytes from HC were stimulated either with a self-engineered activating monoclonal AT1R Abs (AT1R mab) alone or preincubated with EVs from SSc patients or HC. The expression of surface molecules on the monocytes was analyzed by flow cytometry and compared with the monocyte phenotype derived from SSc patients. Monocytic cytokine expression was studied using ELISA and a cytokine array. Monocyte migration was assessed using trans-well and organ-on-a-chip assays.
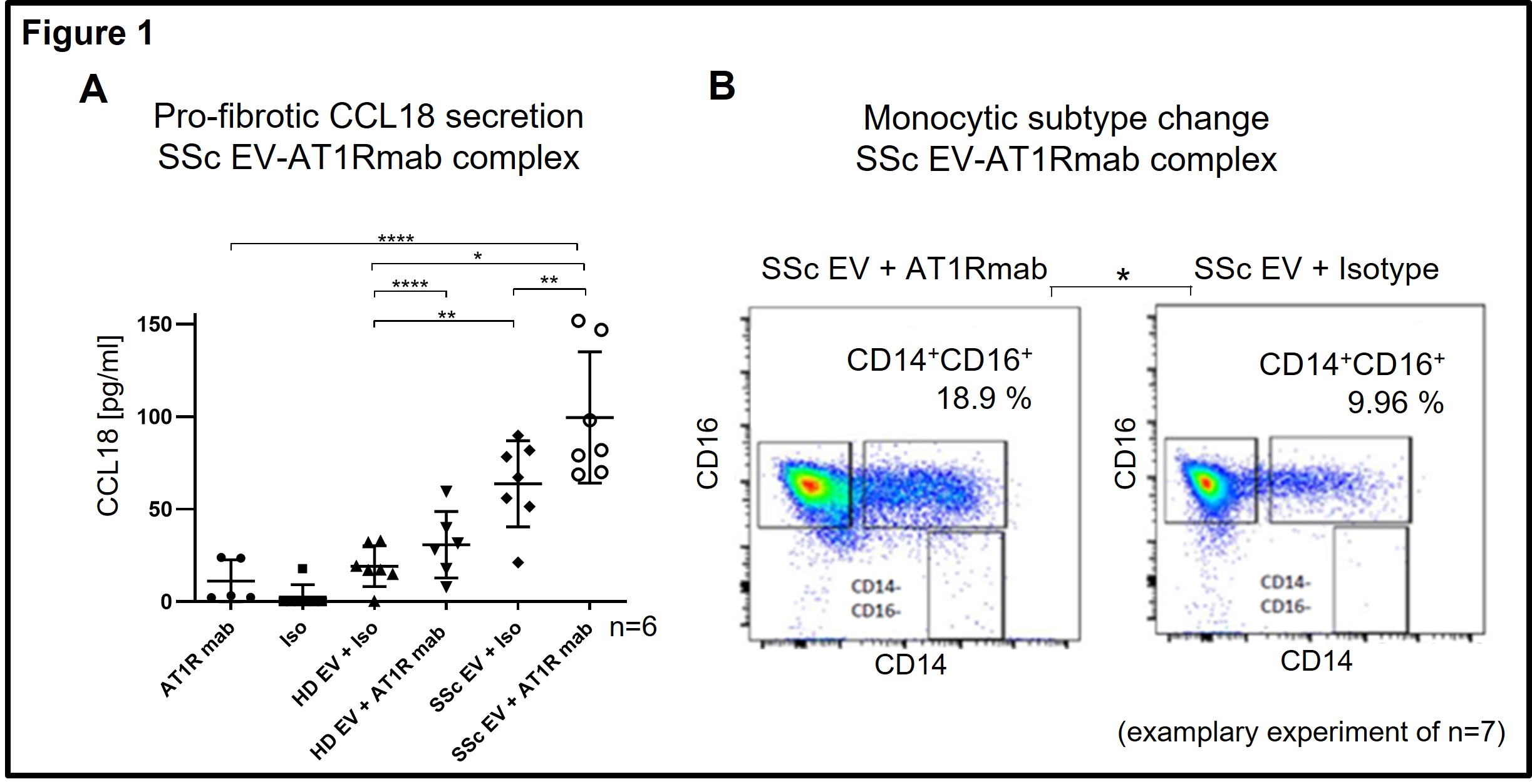
Results: Compared to EVs from HC, those derived from SSc patients showed a higher abundance of AT1R, facilitating antibody binding. In SSc, high AT1R antibody levels go along with reduced EV diameters. Preincubation of SSc-EVs with AT1R mab resulted in pro-inflammatory and pro-fibrotic monocyte activation, as evidenced by secretome analysis and increased secretion of pro-fibrotic CCL18 (Figure 1A). The secretome induced by the combination of EVs and mAT1R Abs was distinct from that induced by either EVs or mAT1R Abs alone. Notably, SSc EVs preincubated with mAT1R Abs induced a significant change in the monocyte cell line phenotype, resulting in an intermediate-like phenotype (Figure 1B). This same phenotype was observed in monocytes from patients with diffuse SSc. Migration of monocytes was significantly increased by both mAT1R Abs and EVs from SSc patients, but not by EVs from HC or by applying an isotype control.
Conclusion: Our study demonstrated that mAT1R ab, EVs, and particularly EV-immune complexes induce a unique phenotype of monocytes. EVs are not only distributing mAT1R abs but also contributing to immune cell migration and induction of fibrosis. This study further supports the specific contribution of AT1R ab-mediated processes in SSc.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hackel A, Leiber M, Winziers M, Riemekasten G, Akbarzadeh R. Immune Complexes of Antibodies Directed to Angiotensin Receptor type-1 and Extracellular Vesicles Are Unique Modulators Contributing to Systemic Sclerosis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/immune-complexes-of-antibodies-directed-to-angiotensin-receptor-type-1-and-extracellular-vesicles-are-unique-modulators-contributing-to-systemic-sclerosis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/immune-complexes-of-antibodies-directed-to-angiotensin-receptor-type-1-and-extracellular-vesicles-are-unique-modulators-contributing-to-systemic-sclerosis/