Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: 99mTc-maraciclatide (99mTc-M) (Serac Healthcare) is a radio-labelled tracer which binds with high affinity to integrin αvβ3, a cell-adhesion molecule up-regulated on neoangiogenic blood vessels. It therefore has the potential to image synovial inflammation at the whole-body level.
Our group has previously published interim results showing that 99mTc-M uptake correlated with power Doppler ultrasound (PDUS) in 25 patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA)1. This study now explores correlation with PDUS and serum biomarkers in a larger group of patients.
Methods: 50 patients with RA (mean disease duration 12.8 (SD 8.2, 1-35 range) years, mean DAS28-CRP 4.8 (1.2, 1.9-7.1)) fulfilling ACR 2010 classification criteria were recruited. Patients had an ultrasound scan of 40 joints. Each joint was scored on a scale of 0-3 for greyscale and PD with a total score calculated per patient.
Within 3 hours patients were injected with 740 MBq of 99mTc-M. Whole body planar views, and static hand and foot views were taken 2 hours after injection. Acquisition time was 20 minutes for whole body and 20 minutes for hand and foot views. 99mTc-M images were scored as positive or negative uptake for each joint (binary score). A quantitative (geometric mean, GM) score was calculated for each joint where there was uptake with this corrected for background uptake. Total binary and GM scores per patient were calculated.
Sera was taken from each patient on the day of imaging with analysis of 24 biomarkers via multiplex bead assay.
Total PDUS and 99mTc-M scores were tested for correlation using Pearson’s coefficient of determination (r2). Spearman’s rank correlation (rs) was used to evaluate correlation between serum biomarkers and imaging modalities. Significance was set at p< 0.05.
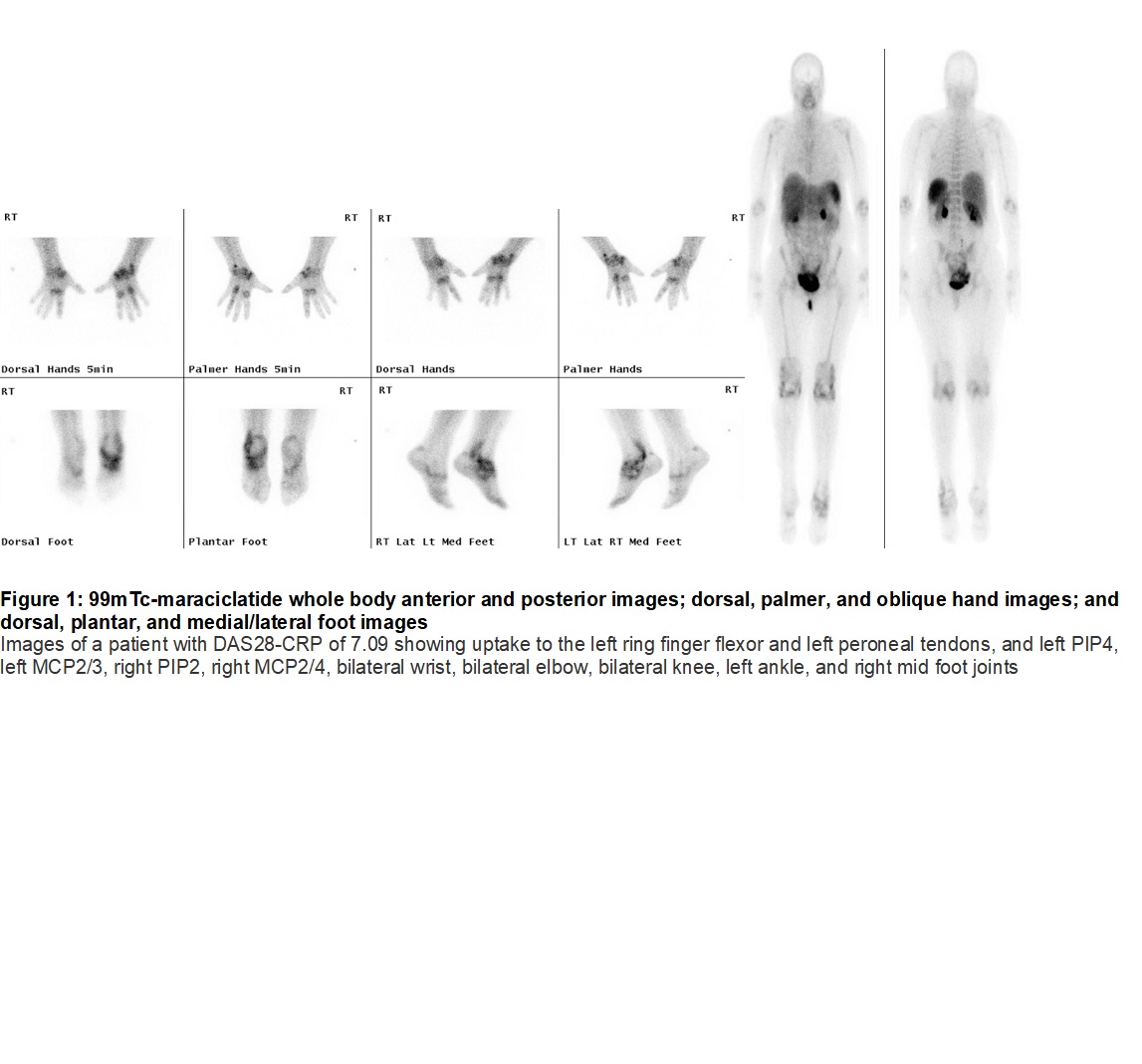
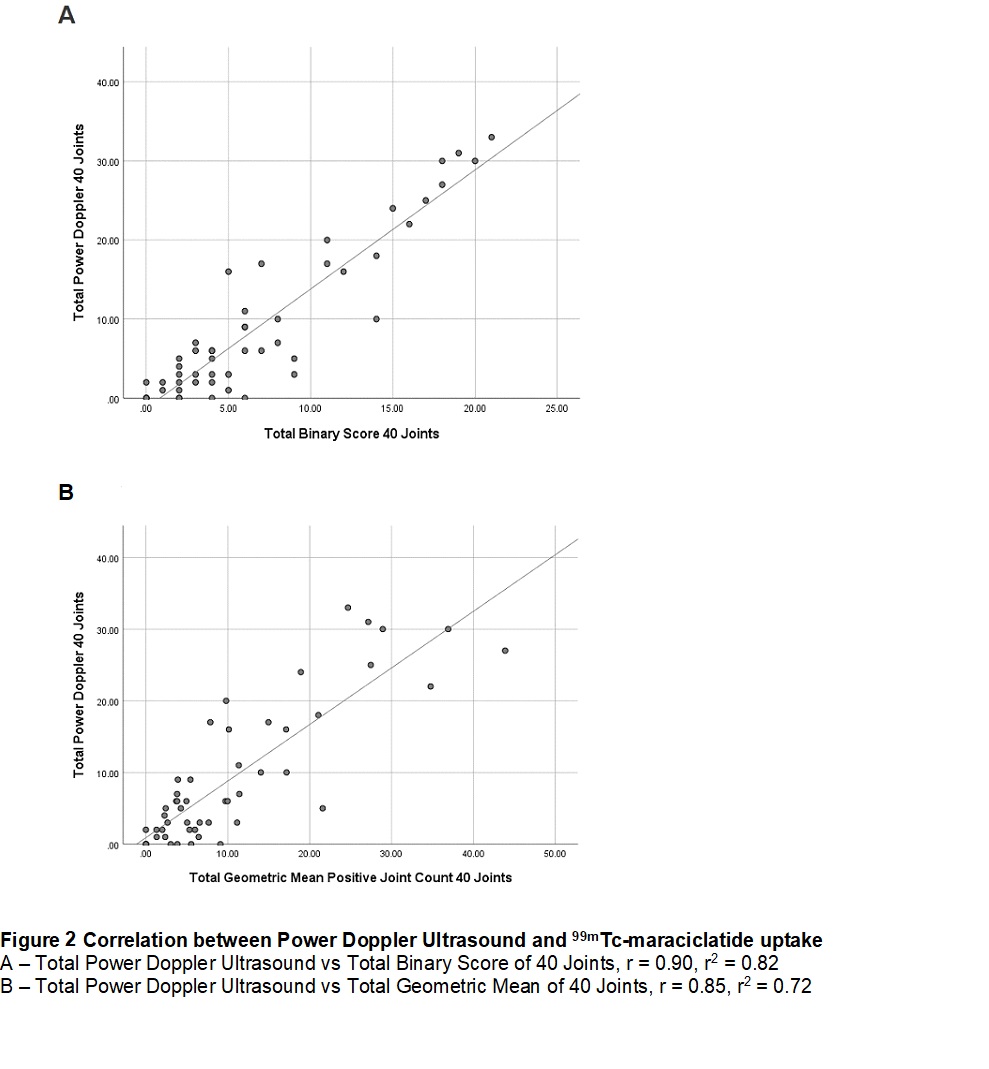
Results: 99mTc-M uptake was clear on visual assessment of small and large joints (Figure 1). Strong correlation was observed when total PDUS was compared to total binary (r2 = 0.82, Figure 2) as compared to total GM 99mTc-M scores (r2 = 0.72). Total GSUS scores also correlated with total binary (r2 = 0.74) and total GM 99mTc-M scores (r2 = 0.60). p was < 0.001 for all values.
There was substantial inter-assessor agreement with a kappa of 0.79 for PDUS, and 0.82 for 99mTc-M scan binary scoring respectively. Concordance correlation coefficient was strong at 0.82 for GM scoring.
99mTc-M uptake at a single joint level had a sensitivity of 78% (95% CI 73-83), specificity of 91% (89-92), positive predictive value (PPV) of 57% (53-61), and negative predictive value (NPV) of 96% (95-97). When assessing small joints alone, sensitivity was 78% (95% CI 72-83), specificity was 94% (93-96), PPV was 72% (67-77), and NPV was 96% (95-97).
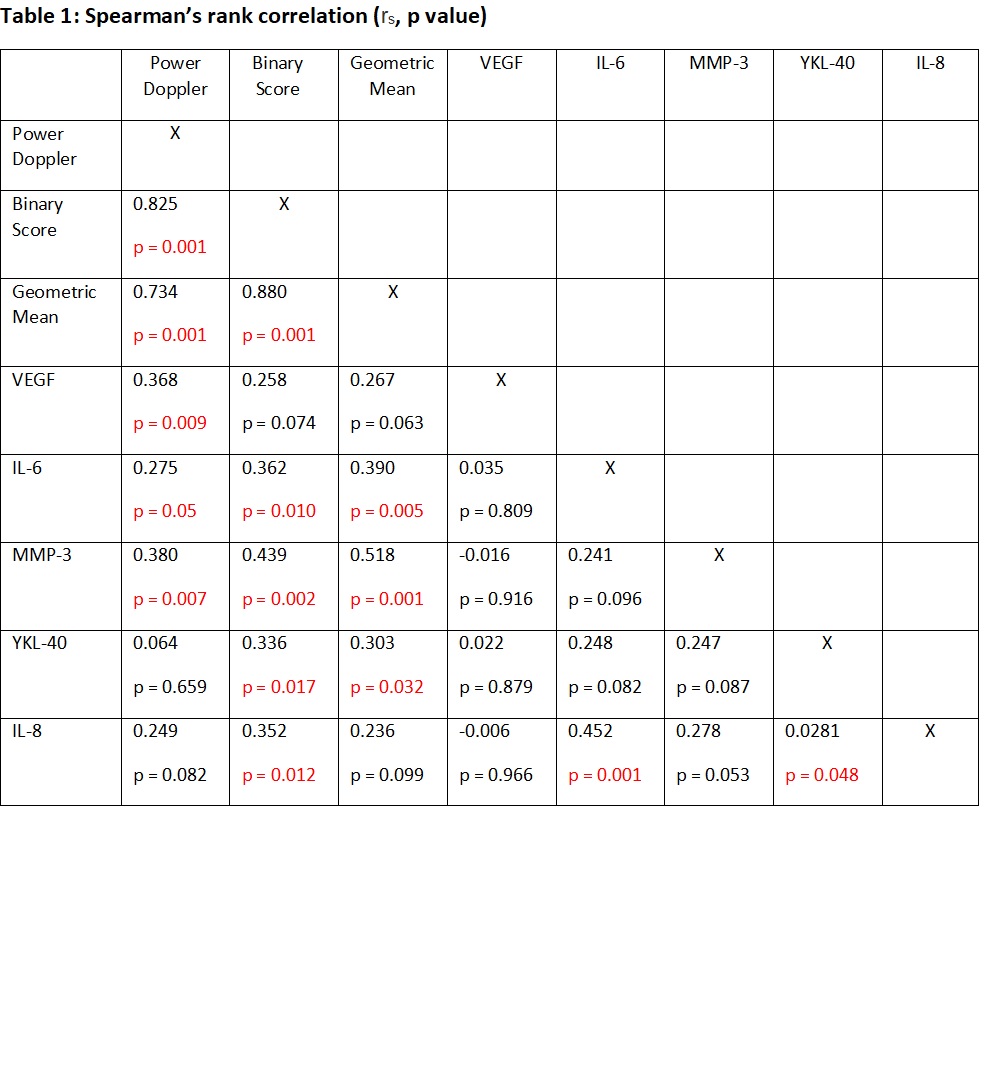
There was moderate correlation between MMP3 and total binary (rs = 0.44, p = 0.002), and GM (rs = 0.52, p = 0.001) scores. There was statistically significant weak correlation between VEGF, IL6, YKL40, IL8 and both imaging modalities (Table 1).
Conclusion: 99mTc-M uptake is highly correlated with PDUS, and weakly to moderately correlated with serum biomarkers highlighting its potential as an alternative imaging modality that captures total synovial inflammatory load. Recruitment is underway to expand the data to a larger group of patients.
1. Attipoe L, Garrood T, Subesinghe S, et al. Imaging Neoangiogenesis in Rheumatoid Arthritis (INIRA): Whole-Body Synovial Uptake of a 99mTc-Labelled RGD Peptide Is Highly Correlated with Power Doppler Ultrasound – ACR Meeting Abstracts. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019;71 (suppl. https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/imaging-neoangiogenesis-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-inira-whole-body-synovial-uptake-of-a-99mtc-labelled-rgd-peptide-is-highly-correlated-with-power-doppler-ultrasound/
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Attipoe L, Subesinghe S, Blanco Gil C, Opena M, Steel K, Ryan S, Norton S, Rosser M, Cook G, Cope A, Garrood T. Imaging Neoangiogenesis in Rheumatoid Arthritis II (INIRA II): Whole-body Synovial Uptake of 99mTc-Maraciclatide Correlates with Power Doppler Ultrasound and Serum Neoangiogenic Biomarkers [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/imaging-neoangiogenesis-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-ii-inira-ii-whole-body-synovial-uptake-of-99mtc-maraciclatide-correlates-with-power-doppler-ultrasound-and-serum-neoangiogenic-biomarkers/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/imaging-neoangiogenesis-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-ii-inira-ii-whole-body-synovial-uptake-of-99mtc-maraciclatide-correlates-with-power-doppler-ultrasound-and-serum-neoangiogenic-biomarkers/