Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Psoriasis arthritis is known as a subtype of seronegative spondylarthritis. However, autoantibodies against the receptor antagonist at tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 and 2 (TNFR1&2) and death receptor 3 (DR3) Progranulin (PGRN) have been described in psoriatic arthritis.Recently, neutralizing autoantibodies against the interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra) have been described in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus type 2 (SARS-CoV-2)-related diseases, considered to create a pro-inflammatory environment. The interleukin-36 (IL-36) cytokine family is mainly expressed in the skin and, thus, might contribute to the pathogenesis of psoriasis (Ps) and psoriatic arthritis (PsA). In the present study, we screened for hypothetic autoantibodies against the anti-inflammatory mediators IL-36-receptor antagonist (IL-36Ra) and anti-inflammatory IL-38 in PsA, Ps and controls.
Methods: Sera were screened by ELISA for antibodies against IL-36Ra and IL-38. Serum samples of patients with PsA (n=254), Ps (n=102), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE, n=50), rheumatic arthritis (RA, n=100), ulcerative colitis (UC, n=50), Crohn´s disease (CD, n=50), and healthy controls (HC, n=49) were analyzed. Western blot analysis and isoelectric focusing was performed to detect possible atypical IL-36Ra isoforms. Native western blot was done to detect free IL-36-Ra and possible immunocomplexed IL-36Ra. IL-36Ra serum levels were determined by ELISA.
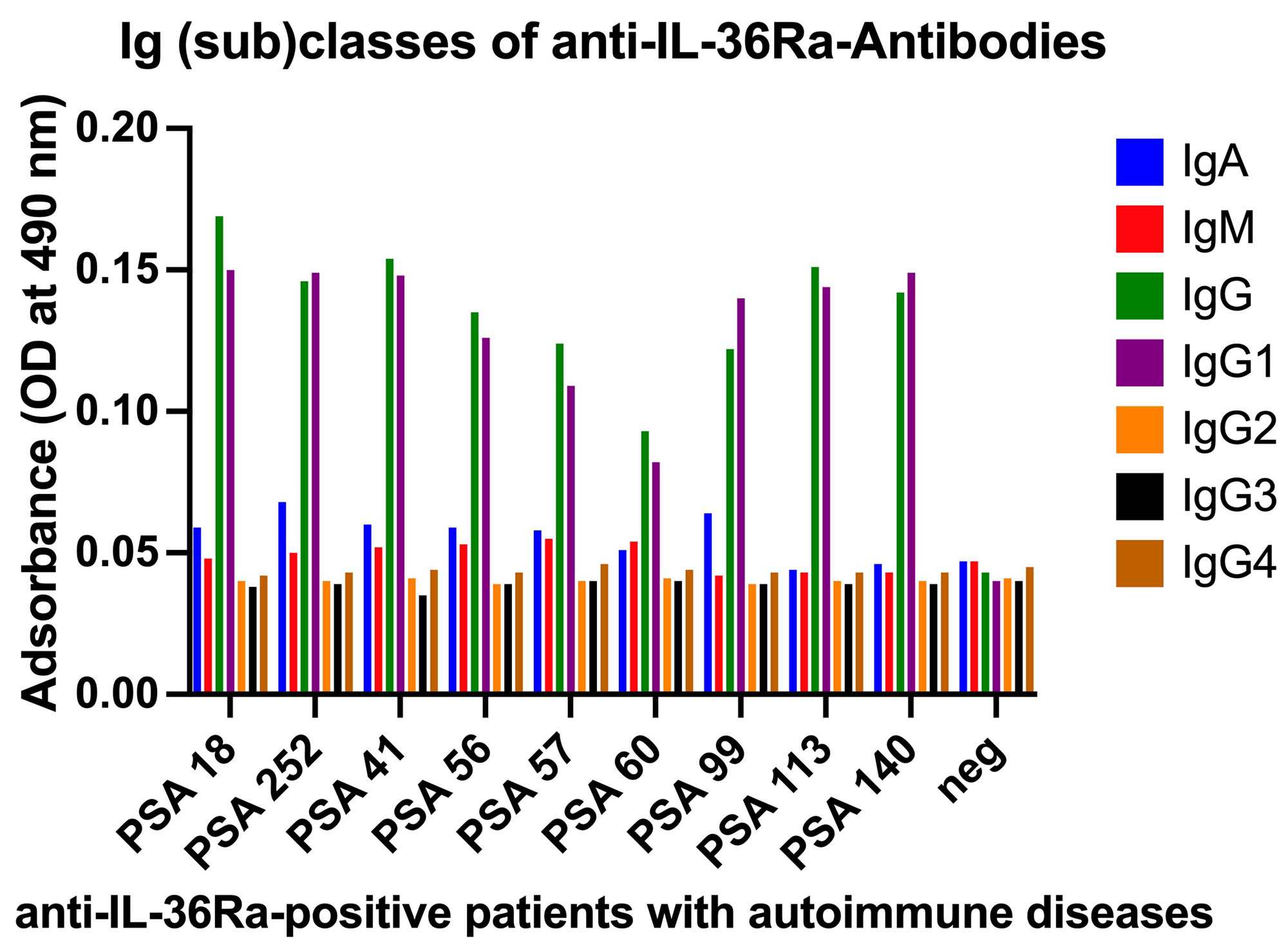
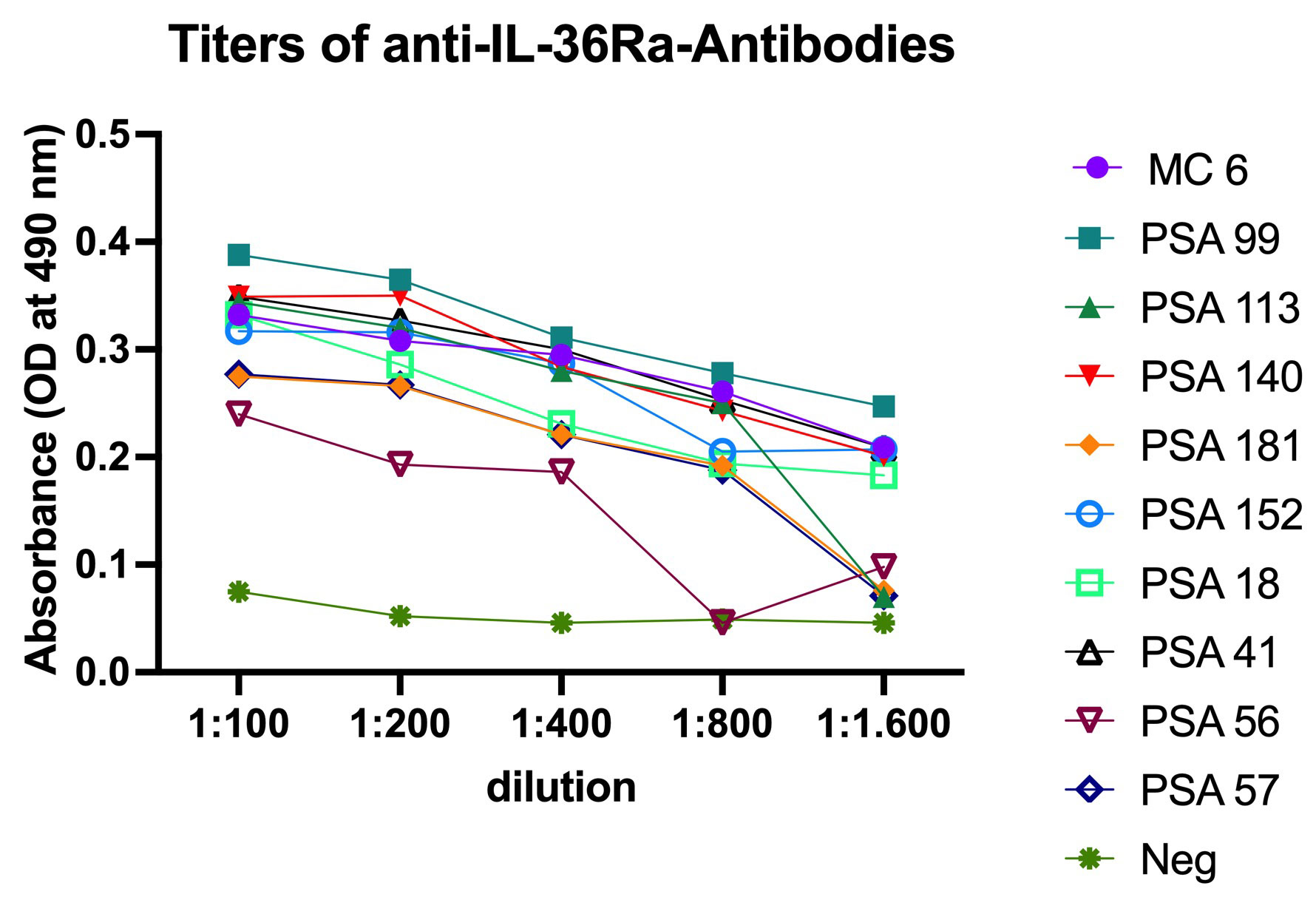
Results: Anti-IL-36Ra antibodies (Abs) were detected in 5 of 102 (4.9%) patients with Ps, in 12 of 254 (4.7%) patients with PsA and in 1 of 50 (2%) patients with CD. There was no detection of anti-IL-36Ra-antibodies in RA individuals. No anti-IL-38-antibodies could be detected. The antibodies against IL-36Ra belonged to IgG subclass 1, and their titers ranged between 1:200 to 1:1.600. No atypically post-translationally modified isoforms of IL-36Ra have been detected in seropositive patients. The native western blot showed that sera with anti-IL-36Ra-antibodies had less strong bands for free IL-36Ra, but additional bands for IgG-immunocomplexed IL-36Ra. In contrast, seronegative serum samples showed only a band for free IL-36Ra. The concentration of IL-36Ra determined by ELISA was significantly reduced in samples of IL-36Ra-Ab seropositive patients.
Conclusion: Apart from anti-PGRN and anti-IL-1Ra Abs, Abs against IL-36Ra represent a further member of the class of autoantibodies neutralizing anti-inflammatory receptor antagonists. They were found in small subsets of patients with Ps and PsA, where IL-36 imbalances are known for their pathophysiologic impact. Beside PGRN-Abs this is a second proinflammatory autoantibody in PsA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hoffmann M, Fadle N, Regitz E, Preuss K, Zaks M, Stöger E, Zimmer V, Klemm P, Assmann G, Thurner B, Pföhler C, Bittenbring J, Kessel C, Thurner L. IL-36-receptor Antagonist-Antibodies in Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/il-36-receptor-antagonist-antibodies-in-psoriasis-and-psoriatic-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/il-36-receptor-antagonist-antibodies-in-psoriasis-and-psoriatic-arthritis/