Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: LN is a severe complication of SLE, affecting 21%–48% of patients.1 Development of noninvasive diagnostic tests for LN is ongoing; urinary biomarkers have good tissue proximity with minimal invasivity.2 Anifrolumab, a type I IFN receptor mAb approved for the treatment of moderate to severe SLE,3 is being evaluated in a phase 3 trial for patients with LN.4 We conducted untargeted metabolomics profiling on urine samples from the phase 2 trial to identify markers associated with LN disease activity that were modulated by anifrolumab.
Methods: The phase 2 TULIP-LN (NCT02547922) trial included adults with active LN (+ SLE per ACR 1997 criteria) who were randomized 1:1:1 to receive IV anifrolumab Q4W at standard SLE dosing (basic regimen [BR], 300 mg), intensified regimen (IR, 900 mg x3 doses, 300 mg thereafter), or placebo, in addition to standard therapy (including MMF and/or glucocorticoids). Metabolomics analysis (856 putatively identified metabolites) was conducted on patients with LN and healthy donors without renal involvement using an unbiased liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry-based approach in urine collected at baseline (BL) and Weeks 12, 24, and 48. Differentially modulated metabolites in the anifrolumab IR vs placebo groups were identified using a linear mixed effects model, adjusted for IFN gene signature (IFNGS, high/low) in blood and 24-hour urine protein–creatinine ratio (UPCR >3/≤3 mg/mg). Relationships between metabolite levels and serologic measures of disease activity (anti-dsDNA, complement C3), IFNGS, and UPCR were assessed with repeated measures correlation; nominal P values were adjusted for multiple comparisons (q).
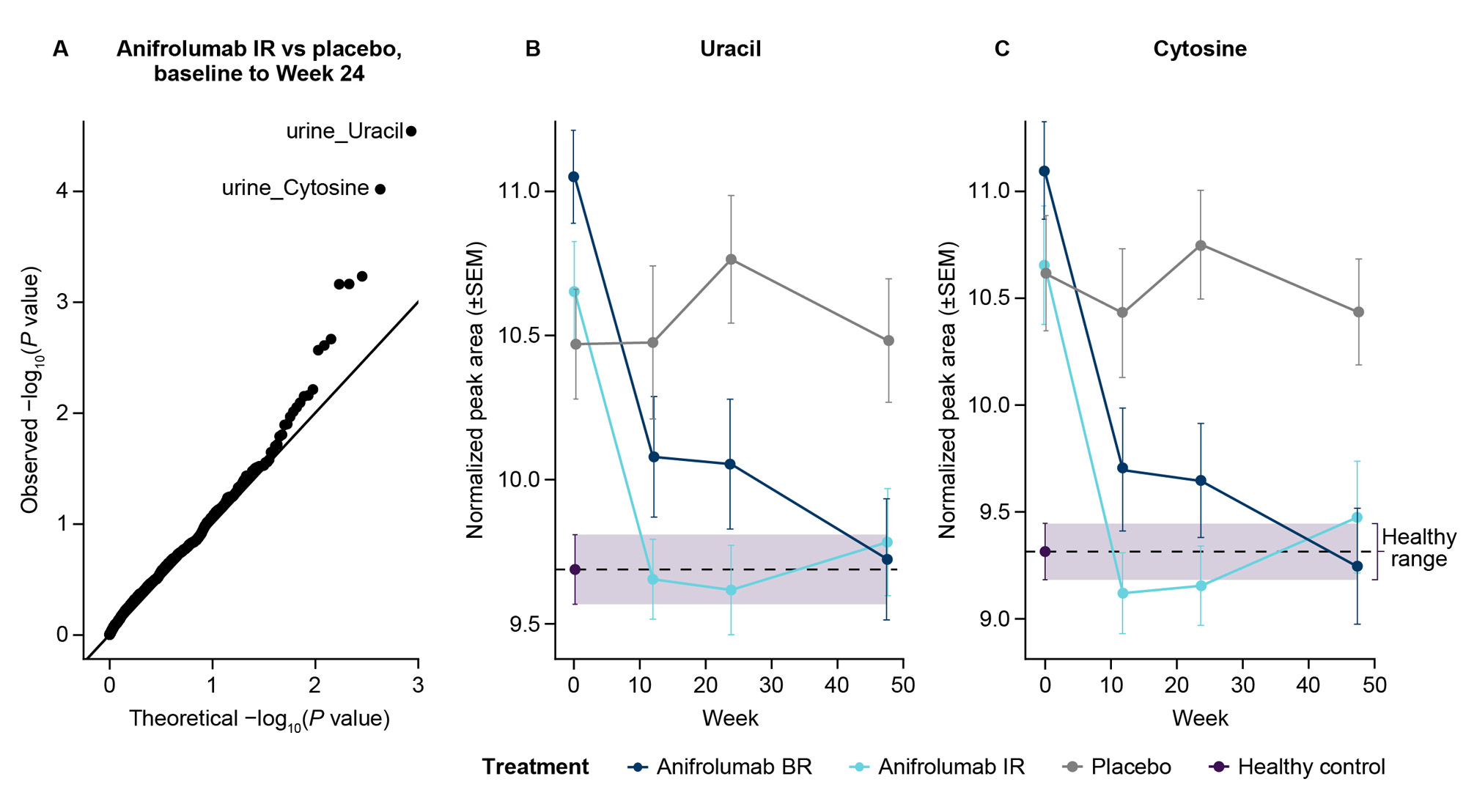
Results: We analyzed urine metabolomics in 117 patients with LN (anifrolumab BR, n=36; IR, n=43; placebo, n=38) and 40 healthy donors. We identified 2 pyrimidine bases, uracil and cytosine, impacted by anifrolumab IR vs placebo from BL to Week 24 (P< 0.05; Figure A). Uracil and cytosine levels at BL were greater in patients with LN compared with healthy donors, and anifrolumab reduced their levels to within healthy ranges (Figures B, C). Within individual patients, uracil and cytosine levels correlated (q< 0.05) with IFNGS (R=0.59; R=0.65), anti-dsDNA levels (R=0.28; R=0.29), complement C3 levels (R=−0.19; R=−0.22), and UPCR (R=0.24; R=0.25).
Conclusion: Urine uracil and cytosine levels were elevated in patients with LN, consistent with studies showing upregulated pyrimidine metabolism in LN.5 Uracil and cytosine levels were associated with IFNGS and measures of disease activity, indicating a previously unrecognized metabolomic link to type I IFN activity. Treatment with anifrolumab, in addition to standard therapy, normalized uracil and cytosine levels. Further studies are required to understand the role of uracil and cytosine in LN pathology, their association with type I IFN, and their potential as noninvasive biomarkers.
References:
1. Wang H, et al. Arch Rheumatol. 2017;33:17–25.
2. Qi S, et al. Lupus. 2018;27:1582–90.
3. AstraZeneca. Saphnelo prescribing information. 2021.
4. ClinicalTrials.gov. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05138133.
5. Panousis N, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78:1079–89.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Jayne D, Mysler E, Amoura Z, Gavin P, Allman E, Di Poto C, Tian X, Hess S, Csomor E, Brohawn P, Muthas D, Platt A, Al-Mossawi H, Lindholm C, Ferrari N. Identification of Urine Metabolites Linked to Disease Activity That Are Modulated by Anifrolumab in a Phase 2 LN Trial Using Untargeted Metabolomics Analysis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/identification-of-urine-metabolites-linked-to-disease-activity-that-are-modulated-by-anifrolumab-in-a-phase-2-ln-trial-using-untargeted-metabolomics-analysis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/identification-of-urine-metabolites-linked-to-disease-activity-that-are-modulated-by-anifrolumab-in-a-phase-2-ln-trial-using-untargeted-metabolomics-analysis/