Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: (1155–1182) Muscle Biology, Myositis & Myopathies – Basic & Clinical Science Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Polymyositis/Dermatomyositis (PM/DM) is a chronic inflammatory disease characterized by muscle weakness, and cutaneous manifestations. Although PM/DM exhibits distinct disease phenotypes based on autoantibodies, assessing the severity of muscular symptoms and predicting prognosis solely through autoantibody analysis remains challenging. The aim of this study is to identify potential biomarkers associated with muscle damage in patients with PM/DM.
Methods: This study employed a cross-sectional design to investigate a cohort of patients diagnosed with PM/DM. The initial screening involved a total of 150 PM/DM patients who had visited the Department of Immunology and Rheumatology, and the Department of Respiratory Medicine at Nagasaki University Hospital between August 2008 and June 2021, and had serum samples available for analysis. To assess muscle involvement, bilateral thigh muscles were evaluated using an MRI scoring system described by Andresson et al. Two radiologists independently conducted the scoring process. Serum cytokine levels were measured using a 43-item bead array in both the PM/DM patient group and a control group consisting of 101 healthy subjects from the residents of Saza in Nagasaki prefecture.
Exclusion criteria encompassed cases without disease activity, those complicated by rapidly progressive interstitial pneumonia, or those with underlying malignancies. Ultimately, a total of 43 patients were included in the study, as their femoral MRI images were available for analysis alongside the collected serum samples. Furthermore, an investigation involving immunostaining of muscles obtained from mice with C protein-induced myositis, as previously reported by Sugihara et al., was conducted to identify potential biomarkers.
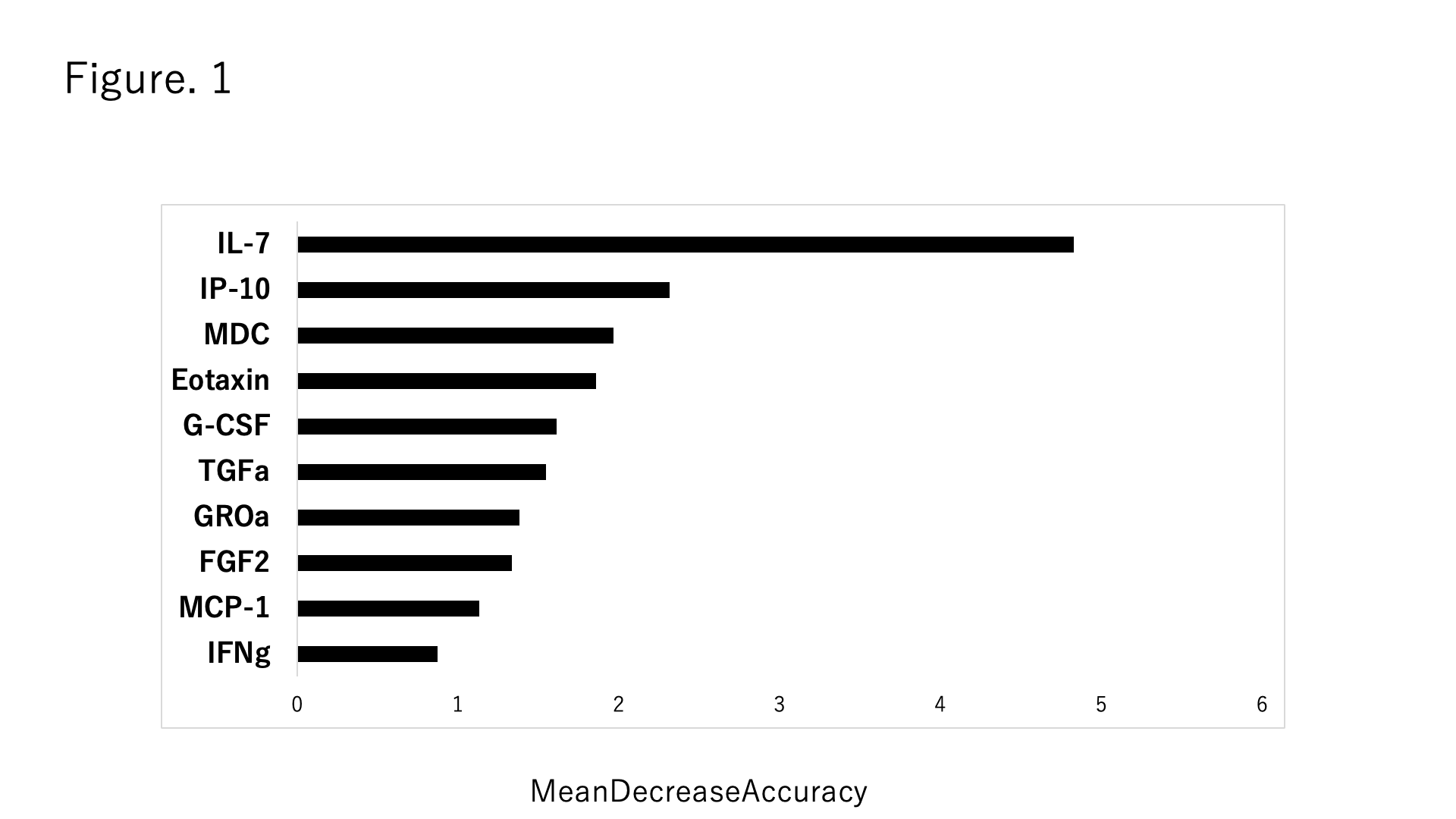
Results: Out of the total of 43 cytokines examined, 38 cytokines were deemed appropriate for further analysis. Through RandomForest analysis, it was determined that Interleukin (IL) -7, among the cytokines studied, exhibited the highest significance in distinguishing between the two groups categorized by median MRI score (Figure 1). Moreover, patients with elevated MRI scores exhibited significantly higher levels of serum IL-7 compared to healthy individuals. Correlation analysis revealed a correlation coefficient of 0.3551 (p=0.019) between MRI score and IL-7. Immunohistochemical assessment of muscle tissues in mice with C protein-induced myositis showed the expression of IL-7 and IL-7 receptor on infiltrating mononuclear cells in the muscles.
Conclusion: Our findings indicate that IL-7 can be as a reliable indicator of muscle damage. Assessing IL-7 levels has the potential to serve as a biomarker for predicting muscle damage in patients with PM/DM, particularly when combined with the measurement of other cytokines.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Matsuo H, Shimizu T, Koga T, Oki N, Kamiya M, Umezawa N, Yasuda S, Uetani M, Kawakami A. Identification of Serum Biomarkers Associated with Muscle Damage Detected on MRI in Polymyositis/dermatomyositis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/identification-of-serum-biomarkers-associated-with-muscle-damage-detected-on-mri-in-polymyositis-dermatomyositis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/identification-of-serum-biomarkers-associated-with-muscle-damage-detected-on-mri-in-polymyositis-dermatomyositis/