Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Over the past decade, genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have identified TRAF1/C5 locus as a risk locus for rheumatoid diseases including RA and JIA(Plenge, Seielstad et al. 2007, Behrens, Finkel et al. 2008), and TRAF1 negatively regulates Toll-like receptor signaling(Abdul-Sater, Edilova et al. 2017). However, the exact risk variant within that locus and its underlying mechanism regulating TRAF1 expression are still not known. We aim to identify non-coding variant in TRAF1/C5 locus governing the expression of TRAF1 gene and its regulatory pathway.
Methods: Single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in linkage disequilibrium (LD) with the most disease-associated SNP in TRAF1/C5 locus from immunochip data (5 thousand JIA patients and 14 thousand health controls) were high-throughput screened by SNP-seq(Li, Martinez-Bonet et al. 2018). Top candidates’ regulatory function were further validated by electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) and luciferase reporter assay. Then the transcriptional factor that might bind to the functional variant after validation was tested by CHIP-qPCR, oligo pulldown assay as well as supershift assay. Finally, the association between this transcriptional factor and TRAF1 gene expression was analyzed by RNAi knockdown experiment.
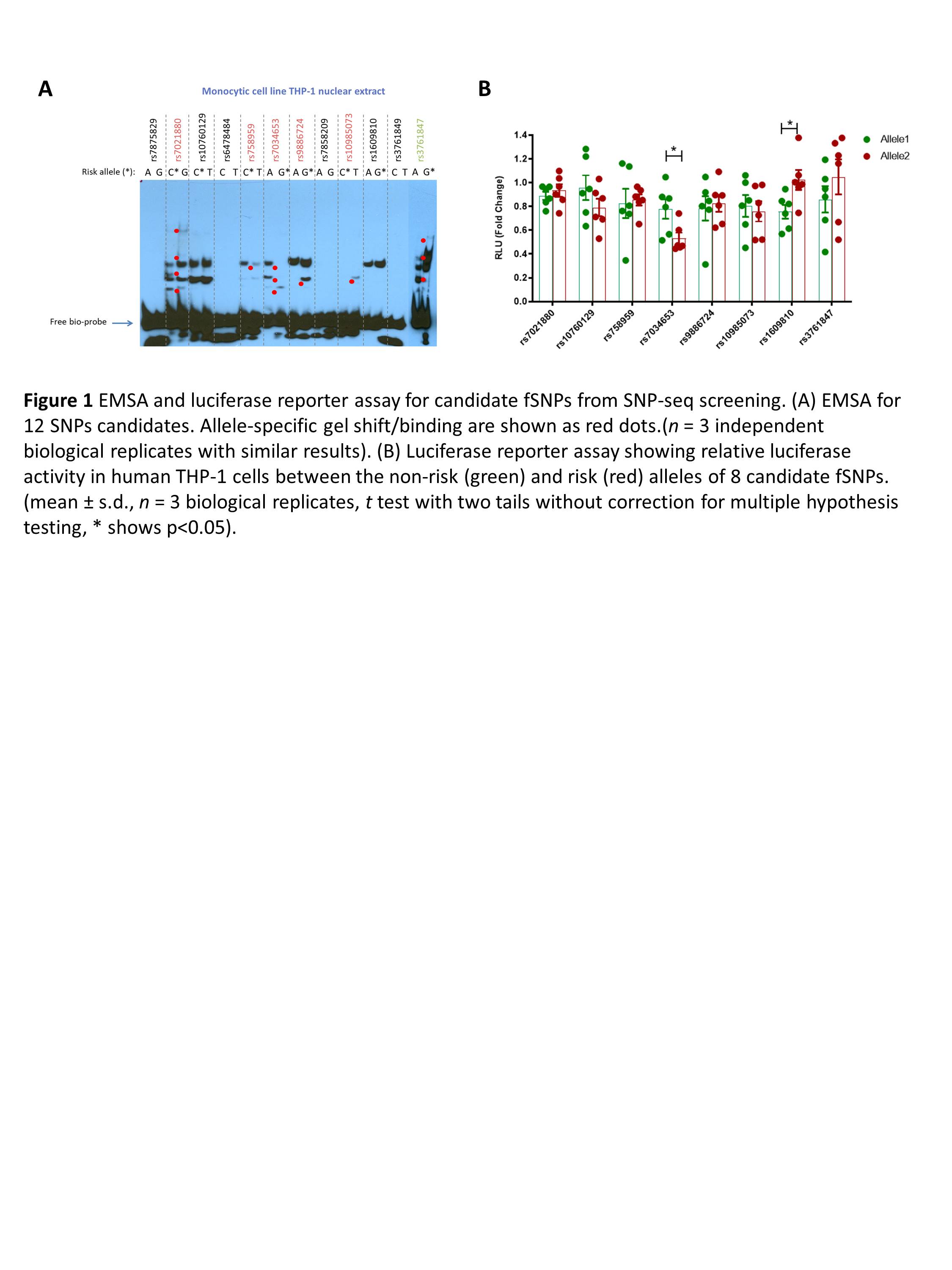
Results: After screening by SNP-seq, EMSA, and luciferase reporter assay, rs7034653 was found to be the best functional non-coding variant in TRAF1/C5 locus that is associated with JIA. EMSA shows that protein from monocyte nuclear extract has a preferential binding to protective allele A than the risk allele G of rs7034653, and that binding preference likely regulates higher gene expression as shown by luciferase reporter assay, which is consistent of existing eQTL data that shows higher expression of TRAF1 in protective allele A than risk allele G in human monocytes. Furthermore, this variant is found to be able to bind to AP1 transcriptional factor FRA2. Suppressed expression of FRA2 by RNAi leads to lower expression of TRAF1 after LPS stimulation in the THP-1 monocytic cell line.
Conclusion: Non-coding variant rs7034653 in TRAF1/C5 locus likely regulates TRAF1 gene expression in monocytes through binding to transcriptional factor FRA2.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Wang Q, Martínez M, Weirauch M, Nigrovic P. Identification of a Regulatory Pathway Governing Expression of TRAF1 via a JIA-associated Non-coding Variant [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/identification-of-a-regulatory-pathway-governing-expression-of-traf1-via-a-jia-associated-non-coding-variant/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/identification-of-a-regulatory-pathway-governing-expression-of-traf1-via-a-jia-associated-non-coding-variant/