Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 7, 2021
Title: Abstracts: Sjögren's Syndrome – Basic & Clinical Science (0984–0987)
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:00PM-4:15PM
Background/Purpose: Sjögren’s syndrome (SS) is an autoimmune disease affecting excretory glands and characterized by B-cell hyperactivity. Ianalumab (VAY736) is a human monoclonal antibody to B-cell activating factor receptor, engineered for direct ADCC-mediated B-cell depletion. A Phase 2b study evaluated the dose-response of VAY736 vs placebo (PBO) in EULAR SS Disease Activity Index (ESSDAI) change from baseline (CHB) and other secondary endpoints. Primary results at Week (Wk) 24 were reported previously1. Here we report 52 Wks safety and efficacy from extended blinded treatment period 2 (TP2).
Methods: 190 patients were randomized equally to receive s.c. doses of VAY736 (5, 50, 300 mg) or PBO every 4 Wks (q4w). Eligible patients fulfilled American European Consensus Group (AECG) criteria, were anti-Ro/SSA+, had ESSDAI ≥6 and EULAR SS Patient Reported Index (ESSPRI) ≥5. At Wk 24, after completion of the first blinded TP (TP1), PBO-treated patients were switched to VAY736 150 mg, and patients on 300 mg were re-randomized to continue 300 mg or PBO for 28 Wks in TP2. Patients were followed post-treatment for ≥20 Wks. Safety was assessed for all periods. Due to lack of PBO-control in TP2, descriptive efficacy analysis was performed for ESSDAI, ESSPRI, Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy Fatigue (FACIT-F), Physician’s (PhGA) and Patient’s Global Assessments (PaGA), 36-Item Short Form Survey (SF-36), and SS symptom diary (SSSD).
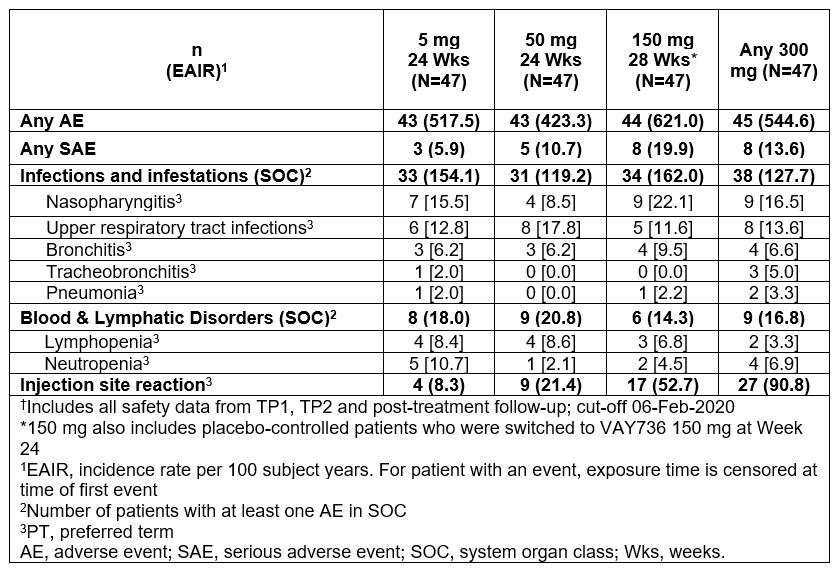
Results: Overall, there was no dose dependency of treatment emergent adverse events (TEAEs) except for injection site reactions, which were mostly mild to moderate in severity. Lymphopenia and neutropenia were mostly grade (G)1 and G2, and none G4. Most common TEAEs were infections and infestations in exposure-adjusted analysis of incidence rates. Nasopharyngitis and upper respiratory tract infections were the most common TEAEs, with no dose response (Table). Tracheobronchitis and pneumonia, were mild to moderate severity, not associated with absolute neutrophil count G3, and none led to treatment withdrawal.
At Wk 52, efficacy was sustained for patients who continued 300 mg in TP2 (ESSDAI, ESSPRI, PaGA, PhGA CHB: –9.06, –1.91, –22.03, and –35.80, respectively). Efficacy was partially lost for patients who switched to PBO at Wk 24 (Figure). Improvement was noted for PBO patients who switched to 150 mg. Stimulated whole salivary flow at Wk 24 was improved for 300 mg (PBO-adjusted CHB 0.20 ml/min; P=0·037); last measurement at Wk 48 was 0.45 and 0.22 ml/min CHB in patients who continued 300 mg or PBO in TP2, respectively.
Conclusion: Ianalumab 300 mg was well tolerated up to 52 Wks. Exploratory efficacy measures showed that continuous dosing of 300 mg s.c. q4w provided sustained clinical benefit. PaGA was the outcome that showed the most prominent change following switch to PBO or VAY736.
Reference:
- Dörner T, et al. [OP0302]. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;79(suppl 1):187.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Dörner T, Bowman S, Fox R, Mariette X, Papas A, Grader-Beck T, A Fisher B, Barcelos F, De Vita S, Schulze-Koops H, Moots R, Junge G, Woznicki J, Sopala M, Luo W, Hueber W. Ianalumab (VAY736) Safety and Efficacy in Patients with Sjögren’s Syndrome: 52 Week Results from a Randomized, Placebo-controlled, Phase 2b Dose-ranging Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/ianalumab-vay736-safety-and-efficacy-in-patients-with-sjogrens-syndrome-52-week-results-from-a-randomized-placebo-controlled-phase-2b-dose-ranging-trial/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/ianalumab-vay736-safety-and-efficacy-in-patients-with-sjogrens-syndrome-52-week-results-from-a-randomized-placebo-controlled-phase-2b-dose-ranging-trial/