Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 6, 2021
Title: Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Clinical Poster I (0387–0413)
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
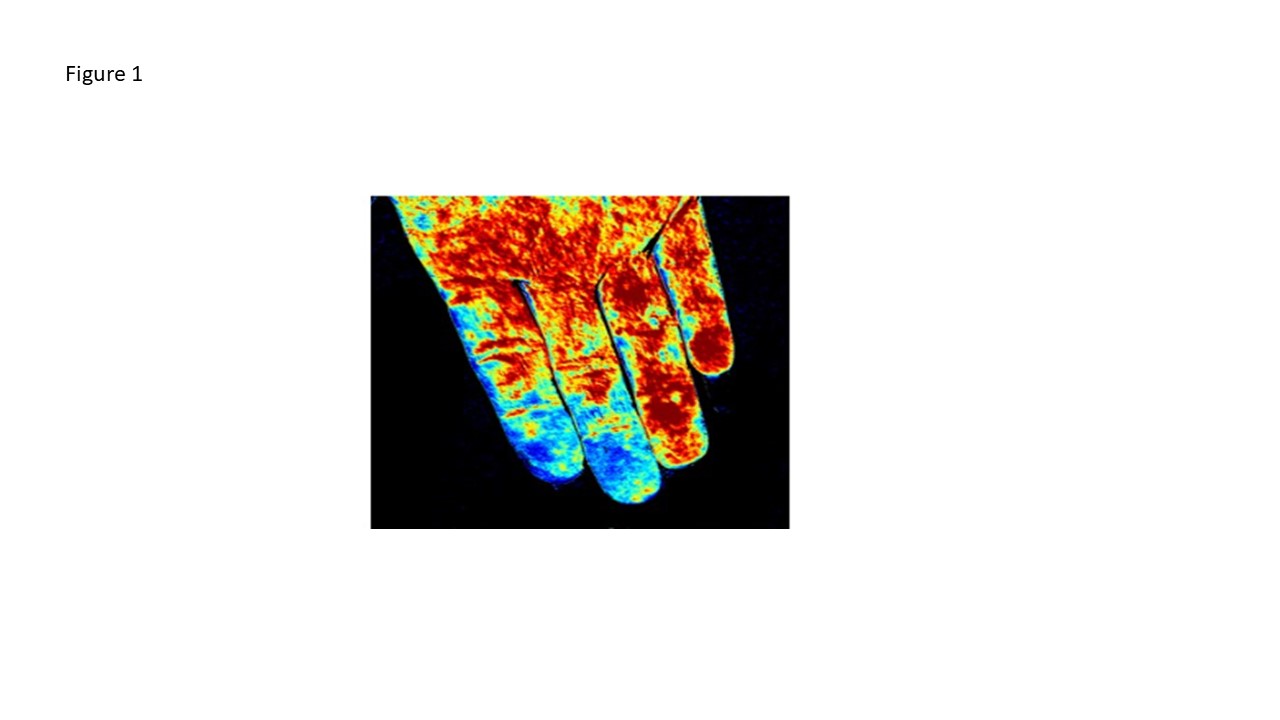
Background/Purpose: Raynaud phenomenon (RP), a microcirculatory, vasospastic disorder, may be primary or secondary to an autoimmune disease [e.g., an early indicator of systemic sclerosis (SSc)]. Raynaud phenomenon clinical trials have been hampered by the lack of a robust, feasible, and quantitative methodology for assessing change over time. Hyperspectral imaging (HSI) noninvasively measures oxygenated hemoglobin (oxyHb) and deoxygenated hemoglobin (deoxyHb) concentrations, and oxygen saturation (O2 sat) in the skin microcirculation by visible spectroscopy (a spectrometer quantifies hemoglobin light absorption). Data are depicted as an oxygenation heatmap (Fig. 1). The study goal is to explore the potential role of HSI in quantifying SSc-RP hand microcirculation.
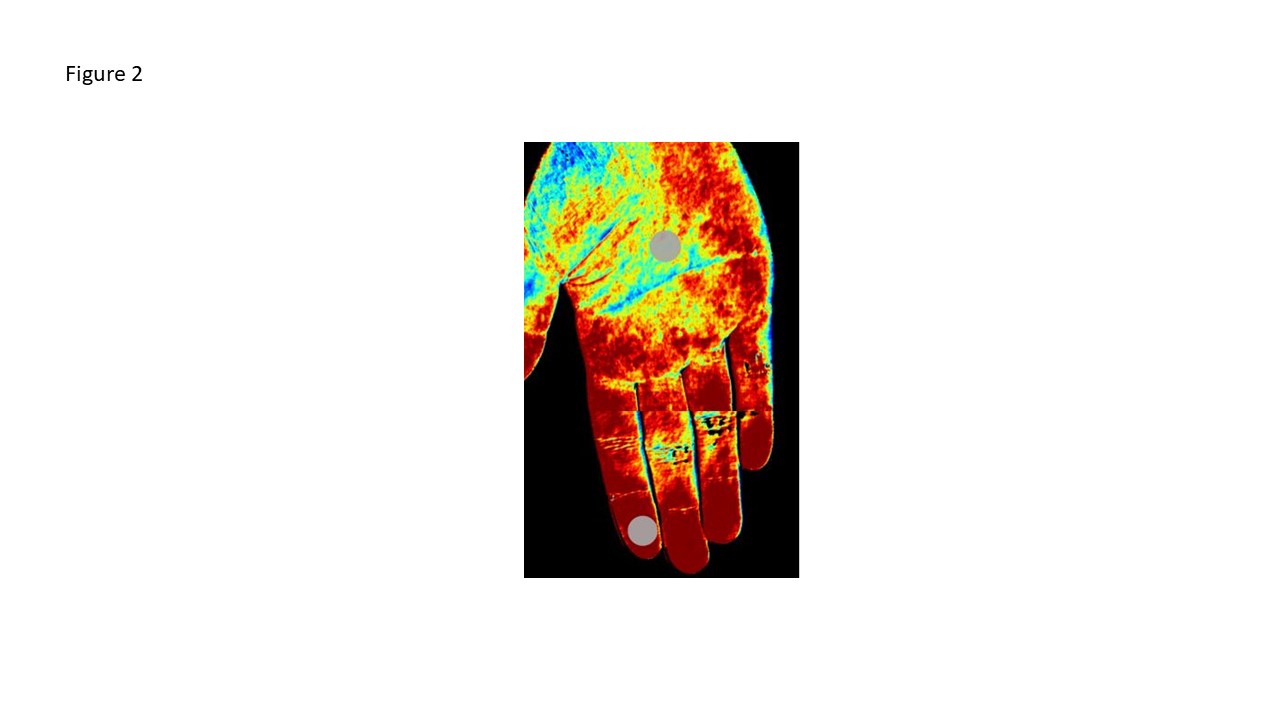
Methods: The Yale University Human Investigation Committee approved this prospective study (HIC# 2000026608) of Yale Scleroderma Program patients and healthy control participants (HC). Patients with SSc completed two patient-reported outcome (PRO) instruments: the Raynaud Condition Score (RCS) and the Cochin Hand Function Scale (CHFS) to assess symptom burden. Then, bilateral palmar HSI (HyperMed™, Waltham, MA) was obtained in a temperature-controlled room (22°C). OxyHb, deoxyHb and O2 sat values were calculated using a default region of interest (ROI) measuring 78 mm2 on the palmar side of the fingertips and palm (for normalization) (Fig. 2). Subjects then underwent a cold provocation challenge whereby hands were submerged in 15°C for one minute, and HSI was subsequently repeated at 0, 10, and 20 minutes (min.). Statistical analysis was performed using the mixed effects model (Stata, College Station, TX).
Results: The mean and standard deviation (SD) age and % female for SSc (n=13) and HC (n=13) participants were 49±22 and 40±13 years (y), and 92% and 94% female, respectively. The mean (SD) SSc duration was 10.9 ± 10.4 y with 69% having limited cutaneous SSc. Thirty eight percent of SSc subjects had prior digital ulcers; none were current. Sixty-two% and 38% of SSc patients were prescribed a calcium channel blocker and statin, respectively. Baseline oxyHb, deoxyHb and O2 sat maps did not significantly differ between SSc and HC participants. However, after cold provocation, images from baseline to 0 min revealed significant reductions in mean slopes of oxyHb and O2 sat for SSc (-0.71, -0.33) compared to HC (-0.22, -0.11; p=0.005, 0.014, respectively). There were no differences in deoxyHb maps between SSc patients and HC immediately post cold challenge. From 0 to 20 min, SSc subjects had more change in oxyHb (p=0.001), deoxyHb (p=0.003), and O2 sat (p< 0.001) compared to HC (Fig. 3).
Conclusion: We showed that HSI is a feasible approach for microcirculation measurement in the hands of SSc patients and HC participants. SSc subjects had a greater decline in oxyHb and O2 sat images from baseline to time 0 (after cold provocation) with significant change in oxyHb, O2 sat, and deoxyHb compared to HC subjects thereafter. These data suggest that HSI technology to assess RP vascular dysfunction is a potential quantitative measure for SSc-RP severity and activity in clinical trials.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gupta A, Teaw S, Williams A, Wilson F, Sumpio B, Sumpio B, Hinchcliff M. Hyperspectral Imaging in Systemic Sclerosis-Raynaud Phenomenon [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/hyperspectral-imaging-in-systemic-sclerosis-raynaud-phenomenon/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/hyperspectral-imaging-in-systemic-sclerosis-raynaud-phenomenon/