Session Information
Date: Friday, November 6, 2020
Title: Patient Outcomes, Preferences, & Attitudes Poster I: RA, Spondyloarthritis, & OA
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: At RA onset, DMARDs are essential to controlling inflammation and preventing disability. In people with established RA, specific beliefs about the necessity of DMARDs and concerns about potential harm influence side effects and adherence. To examine how medication perceptions evolve over time, we evaluated the stability of RA medication beliefs around diagnosis and identified predictors of change 12 months later.
Methods: Data were from Early RA patients enrolled in the Canadian Early Arthritis Cohort (CATCH) March 2017 and January 2020 who completed the Beliefs about Medicines Questionnaire at 0 and 12 months. Necessity and Concerns scales each have 5 statements regarding the need for prescribed medication to control RA and concerns about potential harms of taking them. We used Pearson correlation and multivariable regression to examine associations and predictors of change at 12 months.
Results: The 362 Participants were mostly women (66%), of white racial background (83%), with a mean (SD) age of 56 (15) years, and symptoms of 6 (3) months. Compared with baseline, at 12 months (n=180), mean Necessity beliefs were slightly higher (18.1 vs. 18.9;p=.01) and Concerns were slightly lower (15.2 vs. 14.3; p< .01).
At baseline, weak (r< 0.30) associations were evident between Necessity beliefs and minority status, CDAI, MTX use, and all HRQL domains except sleep. At 12 months, sleep, depression, and pain were positively though weakly related, and participation was inversely and weakly related to Necessity beliefs (Table 1). At baseline, worse CDAI, symptoms, function, and participation were associated with higher Concerns. These relationships were somewhat stronger at 12 months, except physical function was no longer associated with Concerns.
In multivariable regression, when starting treatment Necessity scores were lower in minorities and increased with CDAI, MTX use, and fatigue but decreased as sleep improved (Table 2). No relationships were evident at 12 months. Higher Concerns when starting treatment were predicted by higher education, and greater depression and anxiety. At 12 months, higher Concerns were predicted by minority status and MTX use, higher emotional distress, better function and lower participation in social activities.
Conclusion: Our data suggest that in people with early RA, there is an agreement that medicines are generally necessary, but also significant levels of concerns. Further, medication perceptions appear to be reasonably stable over the first year and are influenced to some degree by some individual characteristics and RA and medication experiences. Findings suggest that specific interventions may be needed to systematically influence medication beliefs and concerns to improve acceptance, tolerance, and long-term adherence.
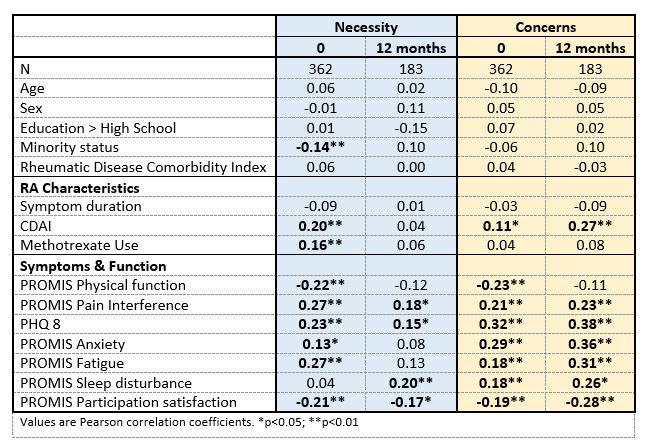 Table 1. Associations between RA medicine necessity and concern beliefs, individual characteristics, and HRQL at baseline and 12 months in early RA.
Table 1. Associations between RA medicine necessity and concern beliefs, individual characteristics, and HRQL at baseline and 12 months in early RA.
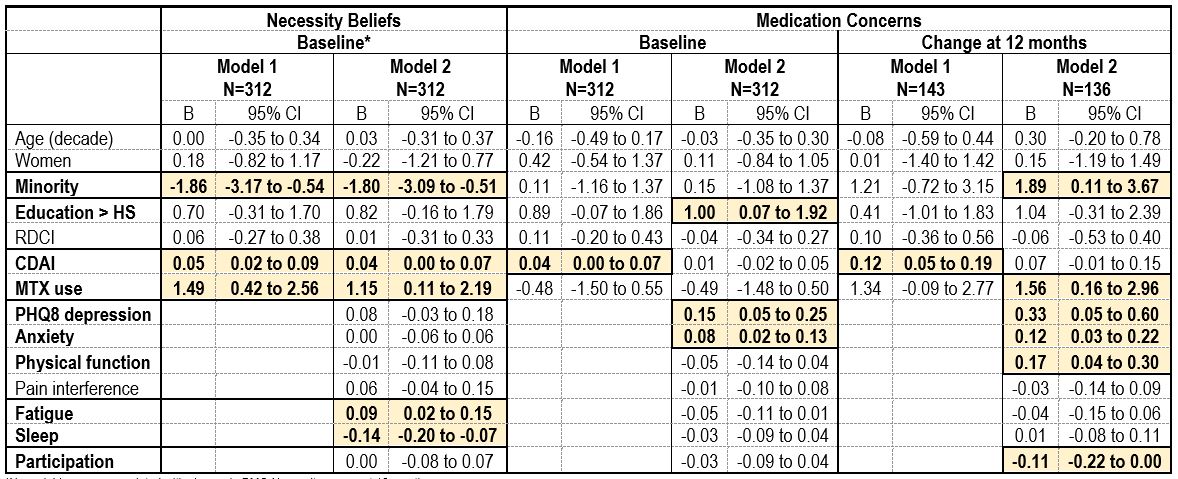 Table 2. Predictors of medicine beliefs and concerns when starting first medications and change at 12 months in early RA.
Table 2. Predictors of medicine beliefs and concerns when starting first medications and change at 12 months in early RA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ta V, Schieir O, Valois M, Bessette L, Boire G, Hazlewood G, Hitchon C, Keystone E, Pope J, Thorne C, Tin D, Andersen N, Bykerk V, Bartlett S, (CATCH) Investigators C. How Stable Are Medication Necessity Beliefs and Safety Concerns in the First Year of RA? [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/how-stable-are-medication-necessity-beliefs-and-safety-concerns-in-the-first-year-of-ra/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/how-stable-are-medication-necessity-beliefs-and-safety-concerns-in-the-first-year-of-ra/
