Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 12, 2022
Title: RA – Treatment Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Activation of T cells plays a key role in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), which is characterized by inflammation of the synovial tissue and autoantibody production. Abatacept, a CTLA-4-Ig fusion protein that targets CD80/CD86 and CD28 interaction and therefore interferes with T cell activation, is widely used as a treatment of RA. However, the response rates to abatacept are variable in heterogeneous RA patients and there are limited data on biomarkers associated with therapeutic response. We conducted this study to assess the therapeutic effects of abatacept on different T cell and B cell subsets in peripheral blood and to identify predictive biomarkers of the therapeutic efficacy of abatacept in patients with moderate to severe RA.
Methods: A total of 20 patients with RA were enrolled in this study. All participants fulfilled the 1987 ACR criteria or 2010 ACR/EULAR criteria, with clinical disease activity index (CDAI) ≥16. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were isolated and analyzed by flow cytometry at baseline, week 14 and week 24. Responders were defined as subjects who achieved ACR50 Response at week 24. Percentages of different T cell and B cell subsets were compared between the responder and non-responder groups.
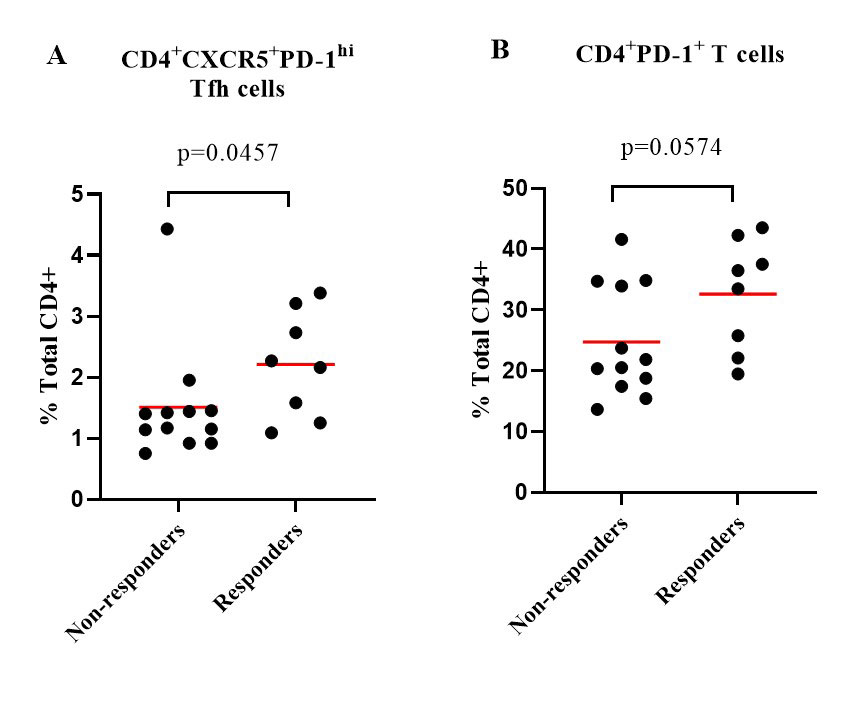
Results: At week 24, subjects treated with abatacept had a significant decline in the frequencies of circulating CD4+CXCR5+PD-1hi follicular helper T (Tfh) cells (p< 0.0001), CD4+CXCR5–PD-1hi peripheral helper T (Tph) cells (p< 0.0001) and CD4+PD-1+ T cells (p=0.0001). Abatacept dramatically reduced the expression of inducible costimulatory molecule (ICOS) in Tfh cells and Tph cells (p< 0.0001). Only the frequencies of CD4+CXCR5+CXCR3+CCR6– Tfh-Th1 cells were decreased (p< 0.01) among the Tfh subsets. There was also reduction in other T cell subsets, including CD4+CD25+CD127– regulatory T (Treg) cells (p< 0.0001) and CD4+CD45RA–CCR7– effector memory T cells (p< 0.01). Abatacept also reduced the frequencies of circulating CD19+IgD–CD27+ class-switched memory B cells and CD19+IgD–CD27– double negative B cells (p=0.0128 and p=0.0184, respectively) after 24-week treatment. Eight patients (40%) achieved ACR 50 response with abatacept at week 24. Compared to the non-responders, the responders had numerically higher percentage of anti-CCP antibodies (88% vs 58%, p=0.325) and rheumatoid factor (88% vs 50%, p=0.158). Baseline frequencies of Tfh cells (p=0.0457) and CD4+PD1+ T cells (p=0.0574) were higher in responders compared to non-responders (Figure 1).
Conclusion: These findings identify CD4+CXCR5+PD-1hi Tfh cells as a potential biomarker in predicting the therapeutic efficacy of abatacept in RA patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
WANG T, Giltiay N, Lood C, Han B. Higher Baseline Circulating CD4+CXCR5+PD-1hi Follicular Helper T Cells Predict Therapeutic Efficacy of Abatacept in Moderate to Severe Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/higher-baseline-circulating-cd4cxcr5pd-1hi-follicular-helper-t-cells-predict-therapeutic-efficacy-of-abatacept-in-moderate-to-severe-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/higher-baseline-circulating-cd4cxcr5pd-1hi-follicular-helper-t-cells-predict-therapeutic-efficacy-of-abatacept-in-moderate-to-severe-rheumatoid-arthritis/