Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: Abstracts: SLE – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes II: Omics
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:00PM-5:30PM
Background/Purpose: Navigating the molecular complexity of lupus nephritis (LN), a heterogeneous autoimmune disorder, poses challenges to biomarker discovery. This study addresses these challenges through an integrative approach, combining high-throughput proteomics and curated clinical samples from diverse LN states and subtypes. Our goal is to identify novel biomarkers, enhancing our understanding of LN and informing personalized treatments.
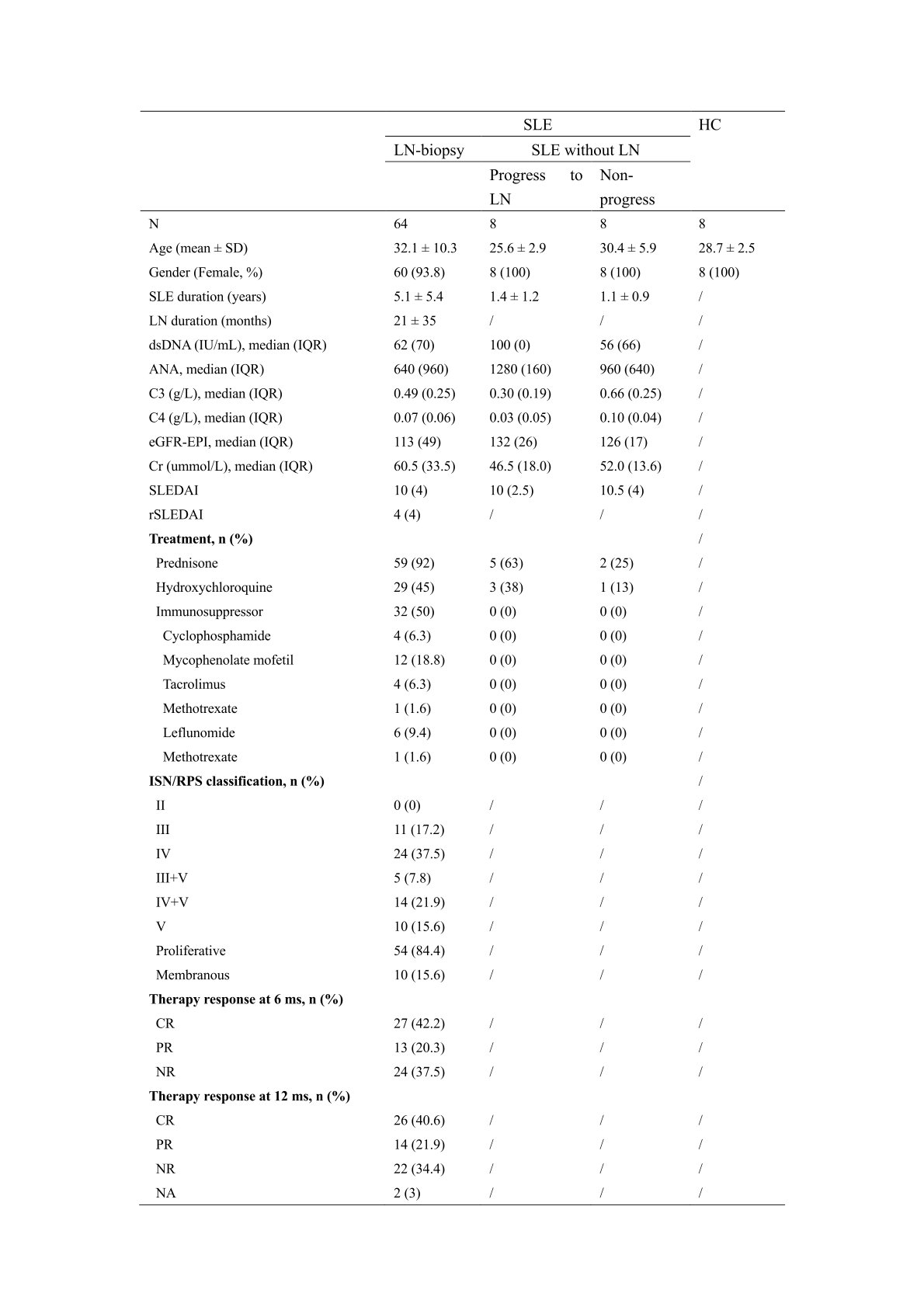
Methods: Proximity extension immunoassay (PEA, Olink) was used to evaluate the serum levels of inflammation related proteins using Explore 384-plex panel in the cohort of 80 SLE patients, including 64 active LN patients with concurrent renal biopsies and 16 active SLE patients without renal involvement at the baseline, as well as 8 age-and sex- matched healthy controls (HCs) (Table 1). Ontological and interrelationship analyses between proteins were performed by GEO, KEGG and String analyses, to interpret the high-throughput proteomic data.
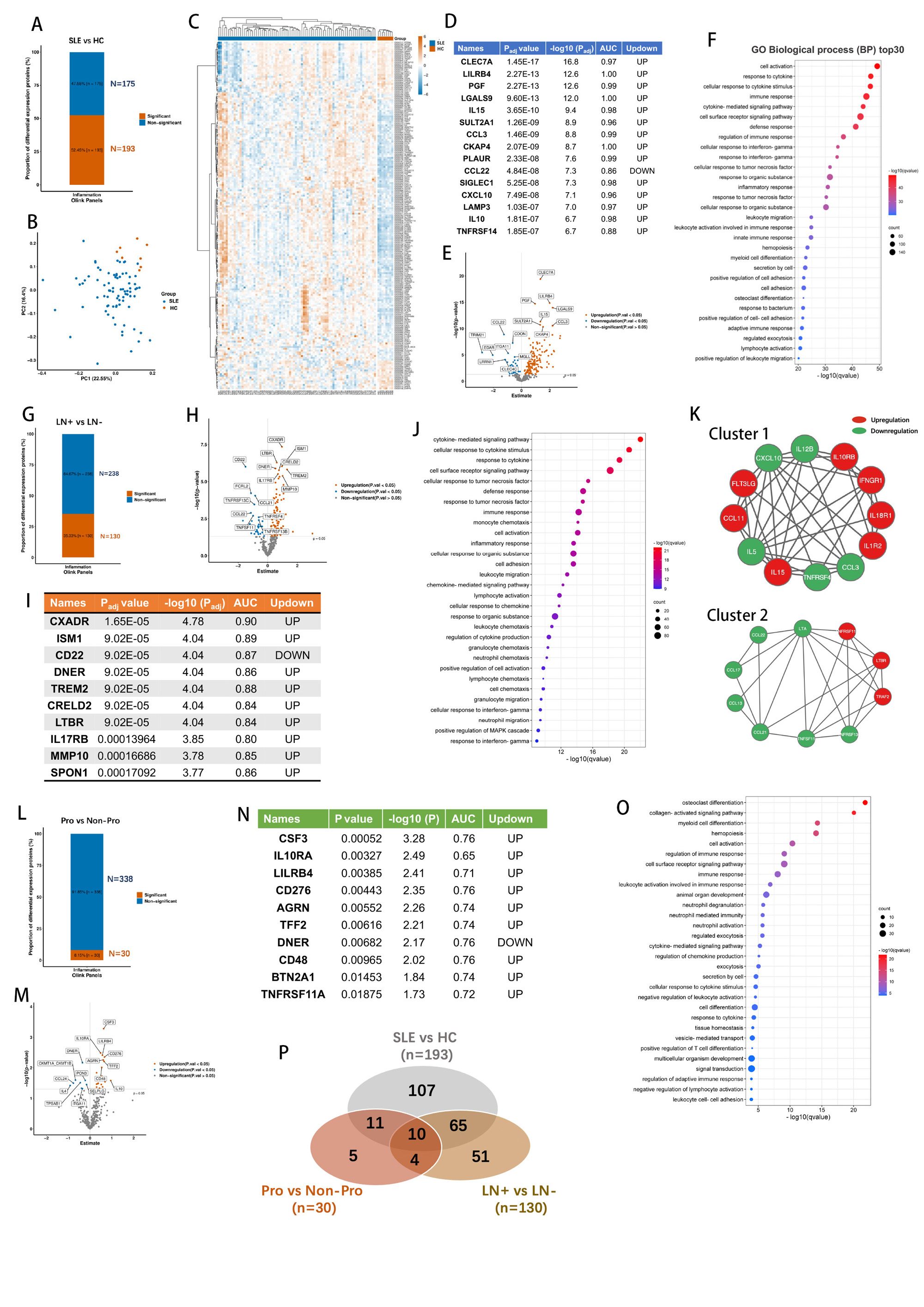
Results: Among the 368 molecules analyzed, 193 differentially expressed serum protein signatures were identified by the comparative analysis between SLE patients and HCs including 144 increased and 49 decreased molecules in SLE patients compared to HCs (Figure 1A-E). The Gene Ontology (GO) analysis was performed to enrich the primary biological processes (Figure 1F). Further comparative analysis was performed in the 80 SLE patients to identify novel biomarkers for kidney damage. There were 130 differentially expressed proteins between LN patients and non-LN SLE patients (Figure 1G-I). The top biological processes were enriched in cytokine-mediated signaling pathway, cellular response to cytokine stimulus, response to cytokine and cell surface receptor signaling pathway (Figure 1J). MCODE module screening using String software identified two clusters among the differential expressed proteins (Figure 1K). Importantly, for the 64 biopsy-proven LN patients, 30 circulating proteins were found significantly altered between proliferative LN (III±V and IV±V) and membranous LN (V) patients (Figure 1L-N). The GO analysis demonstrated osteoclast differentiation, collagen-activated signaling pathway, myeloid cell differentiation and hemopoiesis were enriched in the differential proteins (Figure 1O). Venn diagram was performed to illustrate the distribution of total differential expressed proteins of the three comparasion sets (Figure 1P).
Conclusion: The combination of high-throughput proteomics and well-structured clinical samples provides the foundation to dissect the molecular complexity of LN, potentially leading to the discovery and validation of effective biomarkers for this challenging disease.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ding H, Shen Y, Dai M, Shen N. High-throughput Proteomics Identities a Spectrum of Novel Serum Biomarkers of Lupus Nephritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/high-throughput-proteomics-identities-a-spectrum-of-novel-serum-biomarkers-of-lupus-nephritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/high-throughput-proteomics-identities-a-spectrum-of-novel-serum-biomarkers-of-lupus-nephritis/