Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Abatacept (ABT) is a soluble fusion protein, which links cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 to the modified Fc portion of IgG1. Seropositivity and a shorter disease duration are well known to be associated with response to ABT in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), however, discrimination of seropositive patients who will respond to ABT is still challenging. The aim of this study is to identify predictive biomarkers for remission achievement with ABT in patients with seropositive RA.
Methods: We enrolled patients with seropositive RA (rheumatoid factor and/or anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody [anti-CCP] positive) who had started ABT from 2010 through 2018 in Keio University Hospital. Early RA was defined as ABT initiation within two years from diagnosis with erosion score less than three in hand X-rays. Laboratory tests and immunophenotyping were conducted before ABT initiation and at 6 months, and compared between patients in remission and non-remission group according to clinical disease activity index (CDAI) at 6 months.
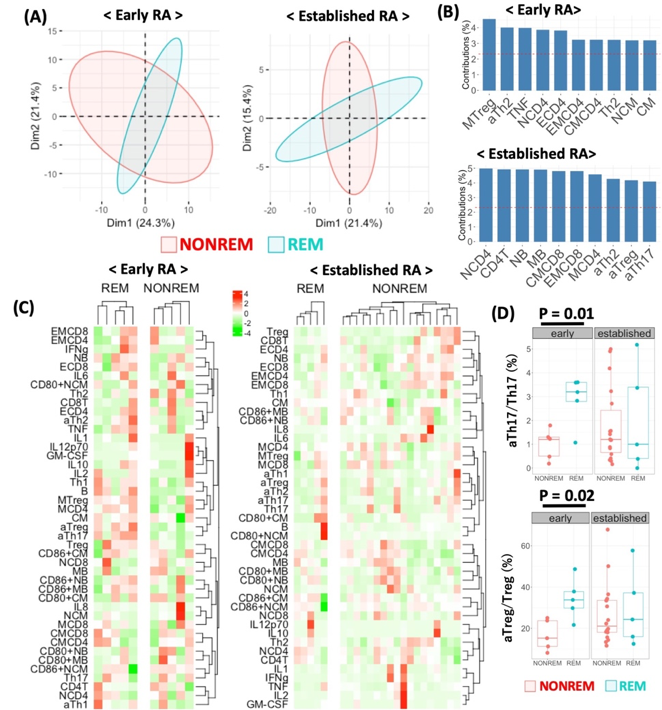
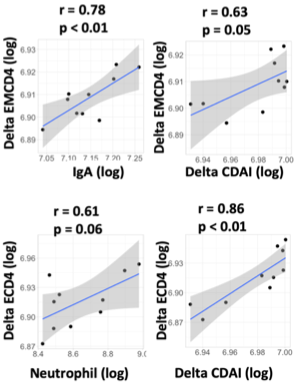
Results: One hundred and three seropositive RA patients who were treated with ABT were enrolled. Among them, 24 and 79 patients were classified into early and established RA, respectively. While in early RA, patients in remission showed higher serum IgA levels, anti-CCP titre and neutrophil count than patients in non-remission (351 mg/dL vs 289 mg/dL, p=0.12; 304 IU/mL vs 156 IU/mL p=0.06 and 6437/uL vs 4751/uL, p=0.10, respectively), no specific laboratory finding was identified in established patients. Receiver operating analysis demonstrated an optimal cut-off value of baseline serum IgA levels, anti-CCP titre, and neutrophil count to predict CDAI remission achievement in early RA as 342 mg/dL with sensitivity of 66.7%, specificity of 86.7%, and area under the curve (AUC) of 0.659, 330 IU/mL with sensitivity of 44.4%, specificity of 86.7%, and AUC of 0.741, 6200/uL with sensitivity of 55.6%, specificity of 86.7% and AUC of 0.704, respectively. In immunophenotyping analysis of peripheral blood of 33 patients (10 early and 23 established patients), primary component analysis demonstrated that the early patients and the established patients in remission made different clusters (Figure 1A-C). The proportion of activated Th17 (aTh17) cells and activated Treg (aTreg) cells were significantly higher in the early patients in remission compared to those in non-remission (aTh17/Th17, 2.86 % vs 1.0 %, p=0.01; aTreg/Treg, 34.3% vs 16.6%, p=0.02), while this difference was not seen in established RA (Figure 1D). Serum IgA at baseline and change in the proportion of effector memory CD4 T cells, and the count of neutrophil at baseline and change in the proportion of effector CD4 T cells were significantly correlated in early RA (Figure 2). Furthermore, the changes were also significantly correlated with changes in CDAI.
Conclusion: We identified serum IgA titer and the count of neutrophil were predictive biomarkers for response to ABT in patients with seropositive and early RA. Immunophenotyping analysis suggested they might reflect upregulation of effector helper T cell subsets, which could be inhibited by ABT.
A, Primary component analysis using immunophenotyping data. B, Top 10 of variables which contributed to make clusters in figure 2A. C, Hierarchical clustering analysis with heatmap using cell subpopulations. D, Comparison of the proportion of activated Th17 -above- and activated Treg -below- between remission and nor-remission group in patients with early RA and established RA.
aTh1, activated Th1; aTh2, activated Th2; aTh17, activated Th17; aTreg, activated regulatory T cell; B, B cell; CM, classical monocyte; CMCD4, central memory CD4 T cell; CMCD8, central memory CD8 T cell; ECD4, effector CD4 T cell; ECD8, effector CD8 T cell; EMCD4, effector memory CD4 T cell; EMCD8, effector memory CD8 T cell; GM-CSF, granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor; IL, interleukin; MB; memory B cell; MTreg, memory regulatory T cell; NB, naive B cell; NCD4, naive CD4 T cell; NCD8, naive CD8 T cell; NCM, non-classical monocyte; NONREM, non-remission; REM, remission; Treg, regulatory T cell.
Scatter plot of IgA and change of the proportion of effector memory CD4 T cells -top left-, change of CDAI and the proportion of effector memory CD4 T cells -top right-, neutrophil count and change of the proportion of effector CD4 T cells -bottom left- and change of CDAI and the proportion of effector CD4 T cells -bottom right-. CDAI, clinical disease activity index; ECD4, effector CD4 T cell; EMCD4, effector memory CD4 T cell.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Inamo J, Kaneko Y, Kikuchi J, Takeuchi T. High Serum IgA and High Proportion of Activated Th17 and Activated Treg Cells Are Predictive Biomarkers for Remission Achievement with Abatacept in Patients with Early, Seropositive Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/high-serum-iga-and-high-proportion-of-activated-th17-and-activated-treg-cells-are-predictive-biomarkers-for-remission-achievement-with-abatacept-in-patients-with-early-seropositive-rheumatoid-arthrit/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/high-serum-iga-and-high-proportion-of-activated-th17-and-activated-treg-cells-are-predictive-biomarkers-for-remission-achievement-with-abatacept-in-patients-with-early-seropositive-rheumatoid-arthrit/