Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 14, 2023
Title: (2352–2369) Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Clinical Poster III: Translational Science
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Systemic sclerosis-interstitial lung disease (SSc-ILD) is the leading cause of death in SSc patients. There is an unmet need for predictive biomarkers of ILD to identify patients at risk, prior to clinical manifestations. Activated IFN-induced chemokines and proteins are implicated in the early inflammatory phase of SSc-ILD. CXCL10 is an IFN-induced chemokine that is important in the chemoattraction of CXCR3-expressing inflammatory cells in SSc-affected tissue.
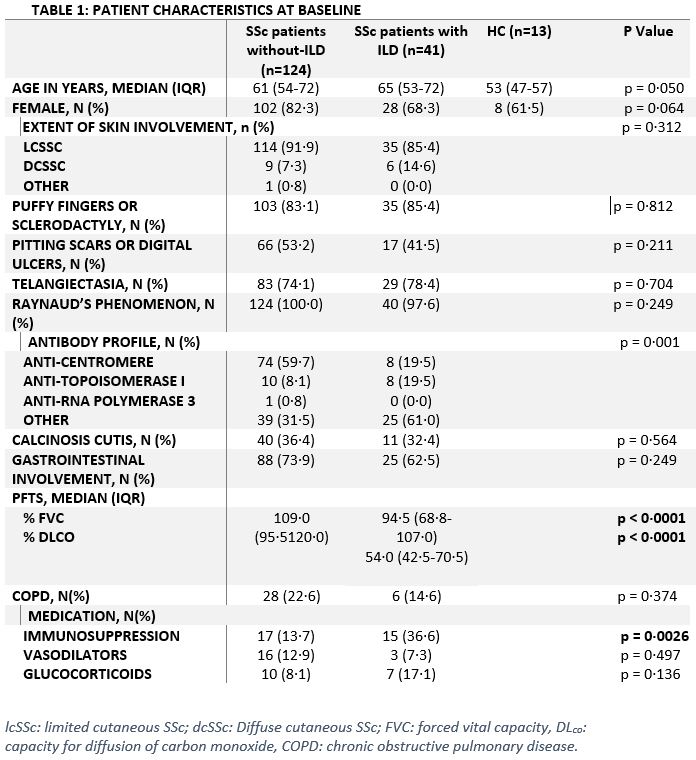
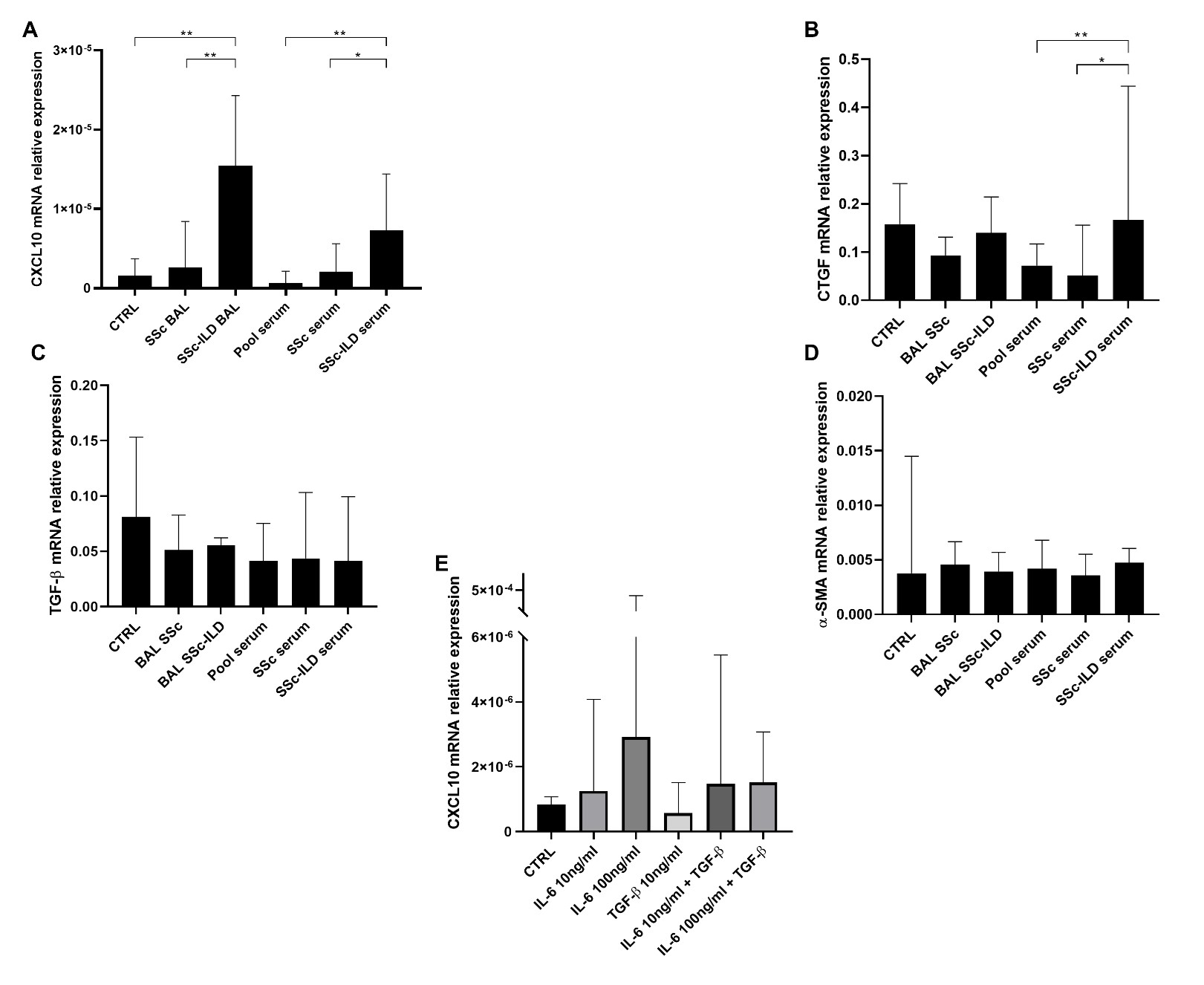
Methods: One-hundred sixty-five SSc patients (SSc-ILD= 41) and 13 age- and sex-matched healthy controls were retrospectively followed for eight years. Furthermore, 15 SSc patients (SSc-ILD= 7) were prospectively recruited for bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) procedure. CXCL10 mRNA and protein levels were measured on various levels (serum, BAL, and SSc-ILD lung tissues) by ELISA and nanoString transcriptomic assay. Spearman’s correlations were performed between CXCL10 levels in serum and lungs. Kaplan-Meier analyses were performed to evaluate predictability of SSc-ILD using CXCL10 levels at baseline. Human primary lung fibroblasts were treated with BAL fluid or serum from SSc without ILD or SSc-ILD patients. After stimulation, inflammatory (IL-6 and CXCL10)/fibrotic (α-SMA and TGF-β) genes were assessed using qPCR.
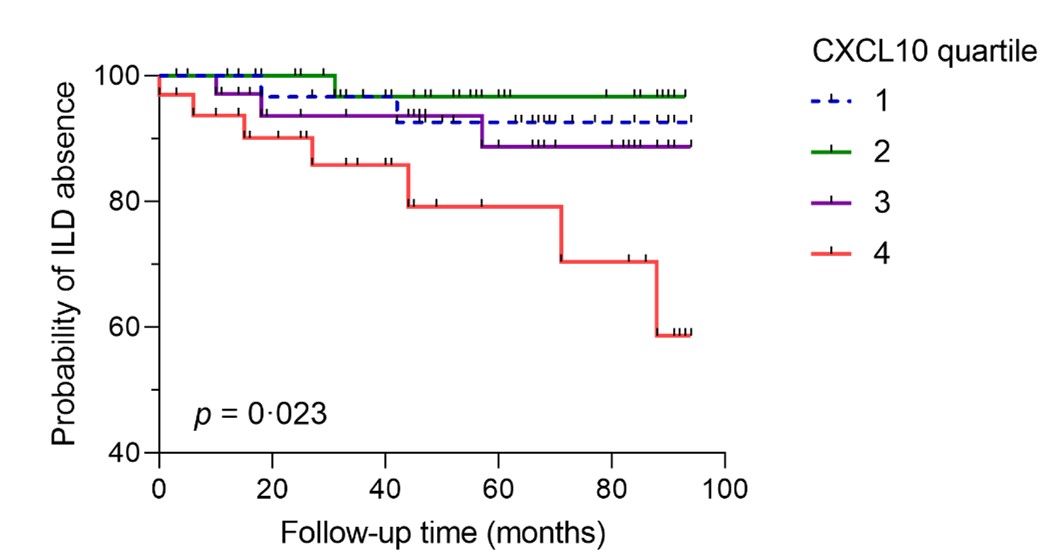
Results: At baseline, serum CXCL10 was significantly higher in SSc-ILD patients compared to SSc without ILD patients [Median (IQR): 126 (66-282) vs 79 (50-122), p=0.004] and healthy controls [Median (IQR): vs. 4 (4-9), p< 0.0001]. BAL fluid CXCL10 levels in SSc-ILD patients were not significantly higher than those in SSc without ILD [Median (IQR): 457 (42-725) vs 134 (72-333), p=0.2). However, BAL fluid CXCL10 levels significantly correlated with serum levels (r=0.7, p=0.007). The nanoString showed that CXCL10 gene expression is significantly higher in inflammatory lung tissue compared to fibrotic tissue (fold change=2.3, p=0.029). Kaplan-Meier survival analysis (figure 1) revealed that CXCL10 levels >3rd quartile at baseline in SSc patients significantly predicted new onset of ILD (p=0.023). The in vitro studies showed that CXCL10 and IL-6 were significantly overexpressed in lung fibroblasts treated with SSc-ILD BAL fluid or serum compared to SSc without ILD [(CXCL10: p=0.0043; p=0.0087), (IL-6: p=0.0022; p=0.0043), respectively) and controls (all: p=0.0022). On the contrary, TGF-β and α-SMA expression did not change after treatment in all groups.
Conclusion: CXCL10 is a potential predictive biomarker for new onset of ILD in SSc patients. Further longitudinal studies with larger sample sizes are needed to verify the capability of CXCL10 to predict ILD. Additionally, our nanoString and in vitro data strongly suggest that CXCL10 may play a significant role in the early development of SSc-ILD which might be amenable to therapeutic interventions.
(E) IL-6 (10ng/ml or 100ng/ml) or TGF-β (10ng/ml) or both were used to stimulate lung fibroblasts for 4h. IL-6 stimulated CXCL10 expression in a concentration-dependent manner. The higher concentration of IL-6 (100 ng/ml) showed increase of CXCL10 expression with a trend towards significance of p value = 0·055 vs CTRL. The results are medians with IQR of three technical experiments (n=3).
CTRL: culture media without stimulant.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Al-Adwi Y, Atzeni I, Doornbos-van der Meer B, van der Leij M, Kroesen B, Stel A, Timens W, Gan C, van Goor H, Westra J, Mulder D. High Serum C-X-C Motif Chemokine Ligand 10 (CXCL10) Potentially Predicts New Onset of Systemic Sclerosis-Interstitial Lung Disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/high-serum-c-x-c-motif-chemokine-ligand-10-cxcl10-potentially-predicts-new-onset-of-systemic-sclerosis-interstitial-lung-disease/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/high-serum-c-x-c-motif-chemokine-ligand-10-cxcl10-potentially-predicts-new-onset-of-systemic-sclerosis-interstitial-lung-disease/