Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: S100A4, a member of the S100 protein family, is implicated in various cellular processes. In systemic sclerosis (SSc), S100A4 is believed to contribute to disease pathogenesis through interaction with key signaling pathways of fibroblast activation, inflammation and angiogenesis. Previous studies have linked circulating S100A4 with fibrotic and vasculopathic manifestations such as interstitial lung disease (ILD), and renal crisis [1]. However, associations with other common vasculopathic manifestations and inflammation have not been explored so far. A comprehensive understanding of S100A4’s role in SSc could reveal its therapeutic potential, not only in targeting fibrosis but also in addressing inflammation and vasculopathy, thereby influencing patient recruitment and study outcomes.
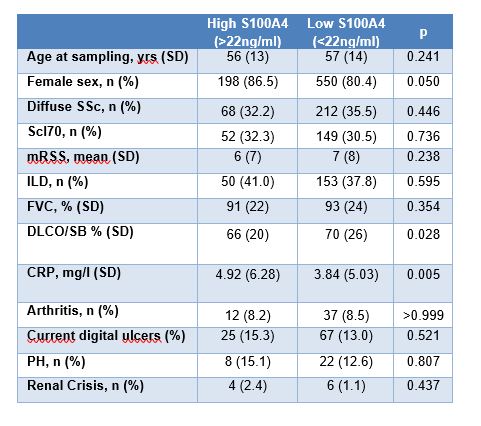
Methods: S100A4 protein concentration was measured in the serum of SSc patients (n=1048) from four SSc expert centers (Oslo, Zurich, Prague, Paris) and healthy controls (HC) (n=100) using ELISA. Prospectively collected clinical data were available for analysis. Inflammation was defined by elevated CRP levels or the presence of arthritis judged by the treating physician. Vasculopathy was defined by the presence of digital ulcers, renal crisis, or pulmonary hypertension (PH) confirmed by right heart catheterization, and diffusion capacity of the lung for carbon oxide (DLCO) in the absence of ILD. S100A4 levels were categorized as “high” or “low” based on the third quartile value of S100A4 in SSc patients, with an upper quartile value of 22 ng/ml. Descriptive statistics were performed; logistic regression analysis with odds ratios (OR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) tested association between inflammation, vasculopathy and S100A4.
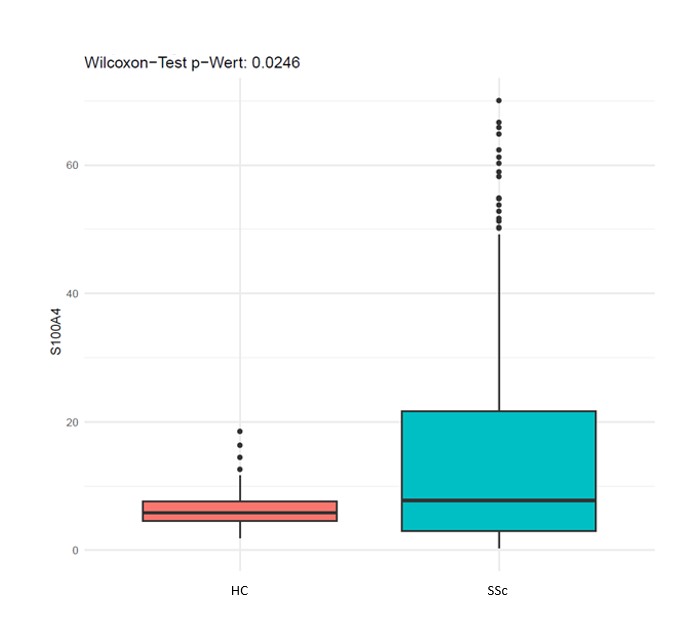
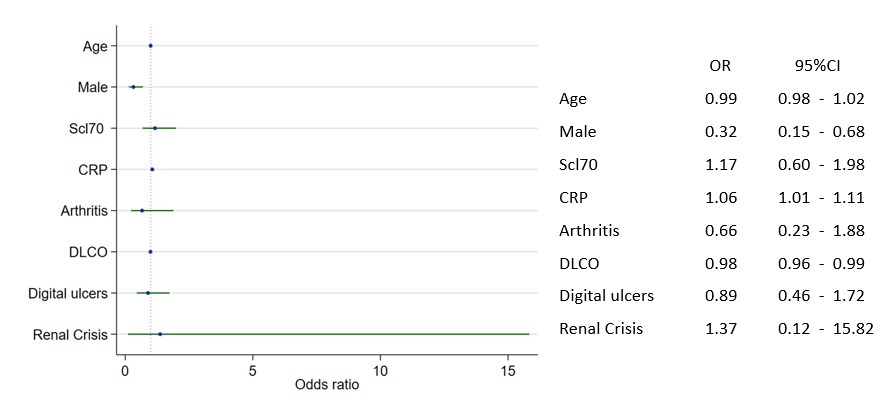
Results: The SSc cohort included (15%) males and 280 (27%) patients with diffuse cutaneous SSc (Table). Serum levels of S100A4 were significantly higher in SSc patients compared to healthy controls (HC (Fig 1). When assessing the association of S100A4 with inflammation, we found significantly higher CRP levels in patients with high S100A4. Regarding vasculopathy, high S100A4 was significantly associated with low DLCO and showed a numerical higher prevalence of current digital ulcers, renal crisis, and pulmonary hypertension (PH) (Table). In multivariable logistic regression, both elevated CRP and low DLCO remained significantly associated with high S100A4 when adjusted for age, sex and other inflammatory and vasculopathic manifestations (Fig 2).
Conclusion: Our results suggest additional associations of inflammation and vasculopathy with higher S100A4 in SSc. These findings encourage the assessment of S100A4 as a biomarker reflecting all 3 pathogenic processes in SSc, and as a therapeutic target for multiple organ manifestations in SSc.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sarbu A, Fretheim H, Šenolt L, Didriksen H, Bruni C, Sprecher M, Ueland T, Hallén J, Hussain R, Klingelhöfer J, Tomcik M, Allanore Y, Distler O, Hoffmann-Vold A. High S100A4 Levels Associate with Inflammation and Vasculopathy in Systemic Sclerosis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/high-s100a4-levels-associate-with-inflammation-and-vasculopathy-in-systemic-sclerosis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/high-s100a4-levels-associate-with-inflammation-and-vasculopathy-in-systemic-sclerosis/