Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 17, 2024
Title: Abstracts: Muscle Biology, Myositis & Myopathies – Basic & Clinical Science I
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 3:00PM-4:30PM
Background/Purpose: Exercise is a recognized adjunctive therapy for patients with idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIM), enhancing physical capacity and reducing inflammation. Hitherto, moderate-to-intensive exercise has been investigated in established, low-active IIM, hence, effects of intensive exercise in recent-onset, active IIM is less known. This study aimed to evaluate tolerance and efficacy of High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) compared to clinical standard moderate-intensity home-based training (CON) in patients with recent onset IIM.
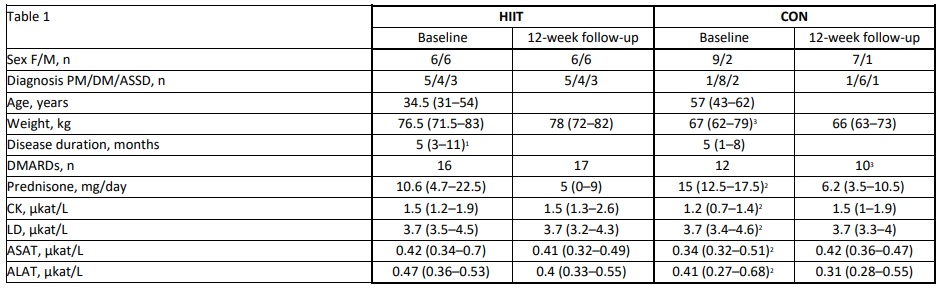
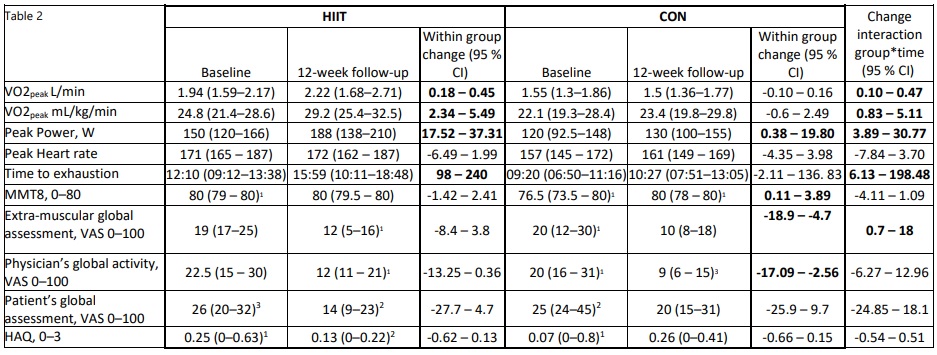
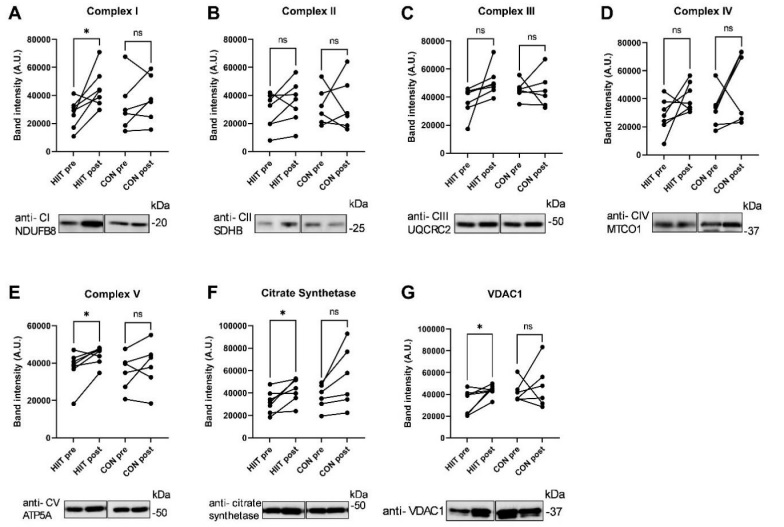
Methods: Between 2017-2023, patients with adult IIM (≤ 12 months of diagnosis), fulfilling EULAR/ACR classification criteria for myositis, excluding IBM, aged < 70 years, and capable of performing HIIT were recruited. Patients deemed unfit for participation (e.g., severe lung-involvement or active myocarditis) were excluded. Participants underwent pre- and post-intervention investigations to assess disease activity using the International Myositis Assessment Clinical Studies (IMACS) disease core set. This included the physician’s global activity (PhGA), patient’s global assessment (PtGA), HAQ, muscle enzymes, Manual Muscle Test 80 (MMT8), and extra-muscular global assessment. Additionally, exercise effects were measured by maximal exercise tests on a stationary bike, including measure of peak oxygen uptake (peakVO2), peak power, and time-to-exhaustion (TTE). Limb muscle biopsies were performed at diagnosis and post-intervention. HIIT included supervised 30-45-second stationary bike intervals (≥ 85% of maximal heart rate), thrice weekly. The controls followed a home-based exercise regimen (< 70% of maximal heart rate) with five sessions weekly. Intensity and resistance were tailored to individual limitations and heart rate was monitored during exercise. To study muscle adaptations to aerobic capacity muscle biopsies were analyzed for expression of key mitochondrial proteins by Western Blot.
Results: Twenty-three patients, with a median disease duration of 5 months, were randomized into HIIT (n=12) or CON (n=11, 8 finishing). There were non-significant differences in sex, age, and type of IIM between the groups (Table 1). Patients in the HIIT protocol demonstrated a significant improvement in exercise capacity with higher peakVO2 (16.2 % vs 1.8 %), peak power (18.4 % vs 8.2 %), and TTE (23.1 % vs 11.5 %) compared to CON (Table 2). In the HIIT group, an increase in muscle mitochondria protein expression was recorded after training compared to before (p< 0.05) (Figure 1). No significant changes were seen among the blood biomarkers for adverse reactions (CK, ASAT, ALAT and LD) or for PtGA and extra-muscular global assessment. However, CON improved significantly in MMT8 and PhGA (Table 2).
Conclusion: Supervised HIIT was safe and provided superior enhancement of exercise capacity compared to CON. Furthermore HIIT, but not CON, led to increased expression mitochondrial proteins showing adaptation in aerobic metabolism within the myositis muscle that links to aerobic capacity and clinical improvement. This study offers novel insights into using intensive exercise for recent onset IIM, suggesting potential changes in future exercise recommendations.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Andreasson K, Leijding C, Dastmalchi M, Notarnicola A, Gastaldello S, Sandlund H, Andersson D, Lundberg I, Alexanderson H. High-Intensity Interval Training Outperforms Moderate Exercise in Aerobic Capacity for Recent-Onset Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies: A Randomized Controlled Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/high-intensity-interval-training-outperforms-moderate-exercise-in-aerobic-capacity-for-recent-onset-idiopathic-inflammatory-myopathies-a-randomized-controlled-trial/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/high-intensity-interval-training-outperforms-moderate-exercise-in-aerobic-capacity-for-recent-onset-idiopathic-inflammatory-myopathies-a-randomized-controlled-trial/