Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Treatment-refractory rheumatoid arthritis (RA) represents a major unmet need with substantial societal burden. Targeting RA-associated fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS) may provide a less-immunosuppressive therapeutic option. Recent single cell RNA-sequencing (scRNA-seq) studies of RA synovial tissue have identified distinct fibroblast subsets, including a population of HLA-DR+ FLS that are expanded in RA and express pro-inflammatory cytokines as well as interferon gamma (IFNg) and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFa) response signatures (1). Donors with an expansion of HLA-DR+ FLS have an expansion of inflammatory monocytes, which express interleukin 1 beta (IL-1b), and CD8+ T cells, which express both TNFa and IFNg (1). TNFa stimulated macrophages that produce IL-1b induce key genes expressed by HLA-DR+ FLS, including IL6 (2). Here we explored the ability of distinct combinations of cytokines predominant in RA to impart gene expression features observed in HLA-DR+ FLS and localize these FLS within the inflamed synovium.
Methods: Synovial tissue was obtained from a prospective cohort of RA patients undergoing arthroplasty or synovectomy who are screened for active RA at the time of surgery (HSS IRB no. 2014-233). For cultured FLS, synovial tissue was dissociated and cultured as in (2). FLS were cultured with cytokines for 24 hours. ScRNA-seq was performed on sorted FLS (CD45–, CD31–, PDPN+) from dissociated synovial tissue. Multiparameter immunofluorescence (IF) was carried out using Iterative Bleaching Extends Multiplexity (IBEX) (3).
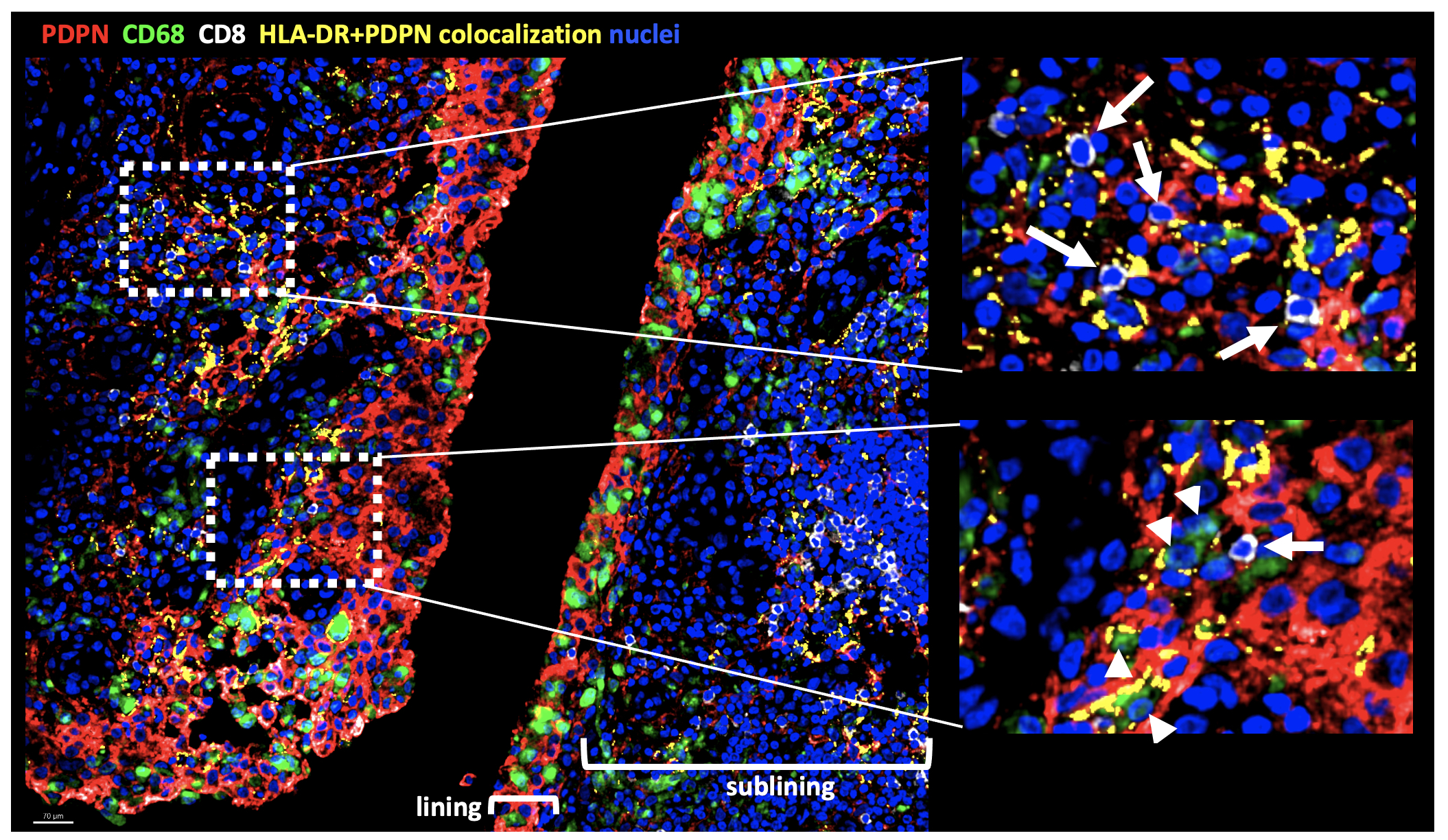
Results: The combination of IFNg, TNFa +/- IL-1b induced FLS expression of genes characteristic of HLA-DR+ FLS such as IL6, CCL2, CXCL9 and ICAM1 (Fig 1A). Differential gene expression analysis of cytokine-stimulated FLS revealed distinct transcriptional features elicited by IFNg + TNFa vs IL-1b (Fig 1B). When used in combination, the cytokines were able to exert a synergistic effect on FLS gene expression with a small set of genes induced by the combination of all three cytokines (IL6, TNFAIP6, MT2A, CCL2, MT1E). Unsupervised clustering analysis of gene expression of freshly dissociated FLS shows heterogeneity of HLA-DR+ FLS with expression in both lining and sublining clusters as well as in clusters with an intermediate lining/sublining phenotype (Fig 2A). Clusters have differential expression of genes driven by TNFa + IFNg (CXCL9), IL-1b (MMP3) or all three cytokines (CCL2) (Fig 2B). IF analysis of inflamed synovium revealed localization of HLA-DR+ FLS to both the lining and sublining areas in proximity to CD68+ macrophages and CD8+ T cells, respectively, (Fig 3).
Conclusion: Pro-inflammatory cytokine exposure of FLS accounts in part for the HLA-DR+ FLS heterogeneity observed in the arthritic synovium in situ. Our analyses suggest that gene expression patterns observed in HLA-DR+ FLS, which we were able to reconstruct with combinatorial cytokine stimulation in vitro, may originate from interacting CD8+ T cells and inflammatory macrophages in the synovium.
References:
1) Zhang F, et al. Nat Immunol. 2019;20(7):928.
2) Kuo D, et al. Sci Transl Med. 2019;11(491):eaau8587.
3) Radtke AJ, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020;117(52):33455.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Smith M, Kochen A, Gao V, Schizas M, DiCarlo E, Goodman S, Leslie C, Donlin L, Rudensky A. Heterogeneity of Inflammatory HLA-DR+ Synovial Fibroblasts in Rheumatoid Arthritis Is Driven by Responses to Leukocyte-Derived Cytokines [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/heterogeneity-of-inflammatory-hla-dr-synovial-fibroblasts-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-is-driven-by-responses-to-leukocyte-derived-cytokines/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/heterogeneity-of-inflammatory-hla-dr-synovial-fibroblasts-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-is-driven-by-responses-to-leukocyte-derived-cytokines/