Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 17, 2024
Title: Metabolic & Crystal Arthropathies – Basic & Clinical Science Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
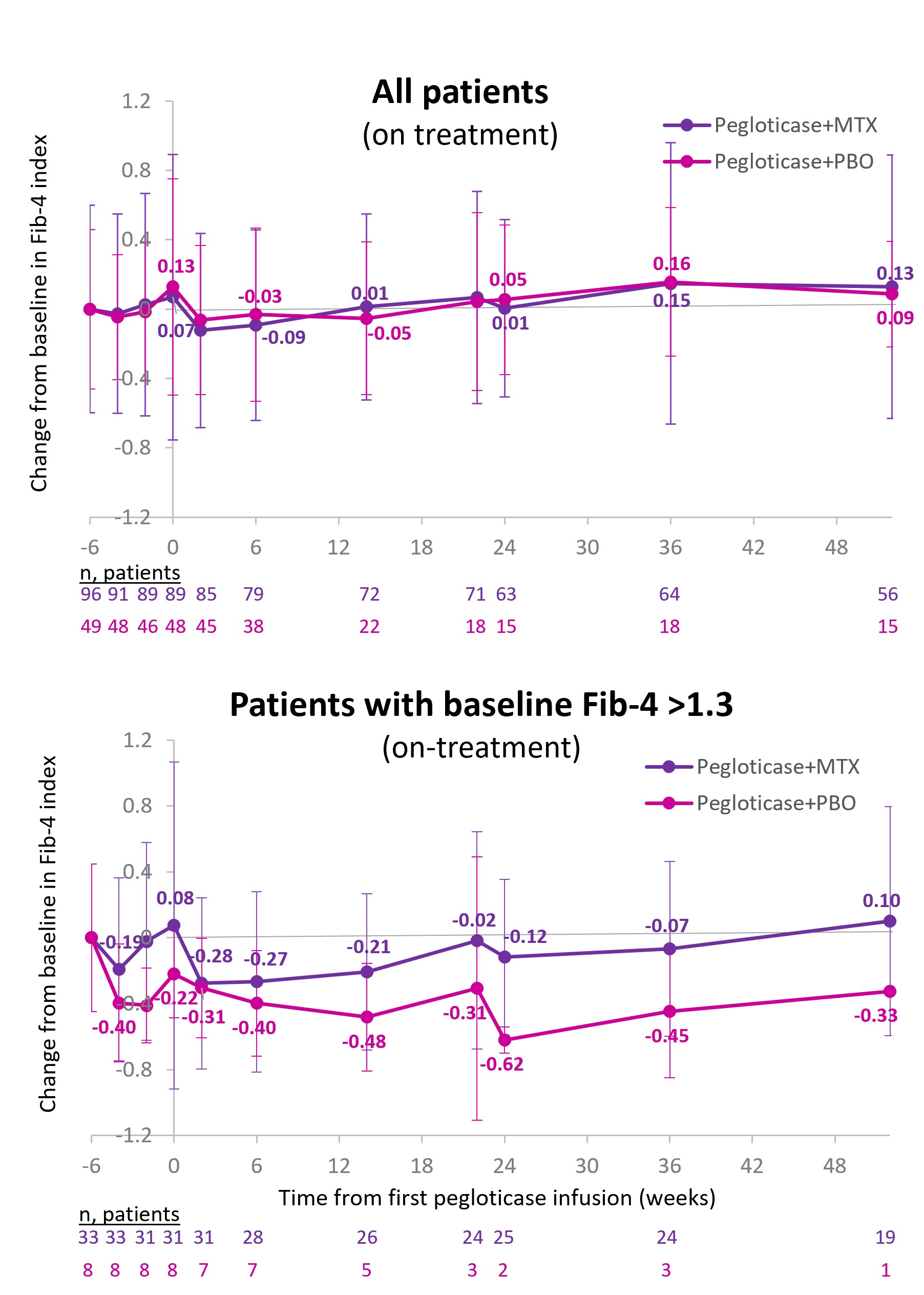
Background/Purpose: Gout is associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD),1 with elevated serum urate (SU) and high flare frequency (≥3 flares/yr) contributing.2 The Fib-4 index, calculated from liver enzyme levels, platelet count, and age,3 assesses liver fibrosis risk (Low: 0-1.3, Moderate: >1.3 to < 2.67, High: ≥2.674). Sustained SU-lowering with pegloticase monotherapy significantly reduced Fib-4 scores, implying a possible effect on NAFLD progression.5 Methotrexate (MTX) is now recommended as co-therapy to pegloticase6 to increase response rate and decrease infusion reaction risk (MIRROR RCT, NCT03994731).7 However, MTX can have liver-related adverse effects.8 Here, we examine Fib-4 during pegloticase therapy with and without MTX co-therapy.
Methods: MIRROR RCT participants with ≥1 pegloticase infusion and sufficient laboratory data were included. All had uncontrolled gout (SU ≥7 mg/dL, oral ULT failure/intolerance, and tophi, ≥2 flares/yr, and/or gouty arthritis) and up to 52 wks of pegloticase (8 mg infusion every 2 wks) with either 15 mg oral MTX/wk or placebo. First infusion (Day 1) occurred after a 2-wk MTX Tolerance period and a 4-wk MTX/placebo (PBO) Run-in. Baseline was prior to MTX exposure (Wk -6). Laboratory measures were obtained at Screening (≤6 wks before baseline) and predefined points during Tolerance (Wk -6), Run-in (Wks -4, -2), and Treatment (Day 1; Wks 6, 14, 22, 24, 36, 52). Only on-therapy data were included in analysis.
Results: 96 received pegloticase+MTX (92% men, 56.0±12.5 yrs, BMI: 32.8±5.6 kg/m2, gout duration: 13.7±10.7 yrs); 49 pegloticase+PBO (86% men, 52.6±12.3 yrs, BMI: 33.0±7.9 kg/m2, gout duration: 14.4±10.9 yrs). At baseline, Fib-4 was 1.1±0.6 in the MTX group and 0.9±0.5 in the PBO group. Fib-4 did not meaningfully change from baseline in either group through Wk 24 (mean change MTX: +0.01±0.35, PBO: +0.05±0.44) or Wk 52 (+0.13±0.63, +0.09±0.30), but PBO group numbers were small later in therapy (Figure). At baseline, 28.3% (41/145) had Fib-4 >1.3. Similar findings were observed in these patients at risk for liver fibrosis (mean change: Wk 24, MTX: ‑0.12±0.46 [n=25], PBO: -0.62±0.51 [n=2]; Wk 52: +0.10±0.75 [n=19], -0.33 [n=1]).
Conclusion: In agreement with prior data,5 sustained SU lowering with pegloticase showed Fib-4 stability through Wk 24 of therapy. In MIRROR RCT, stability persisted through Month 12 with and without MTX co-therapy. Importantly, 28.3% of patients had elevated Fib-4 at baseline; these subjects also had Fib-4 stability through Wk 52 of treatment. Consistent with overall MIRROR RCT findings,9 these data suggest MTX hepatic tolerance through Month 12 of pegloticase therapy with or without MTX co-therapy.
References
1. Kuo CF et al. Scand J Rheumatol 2010;39:466-71
2. Si K et al. Clin Rheumatol 2023;42:1389-95
3. Vallet-Pichard A et al. Hepatology 2007;46:32-6
4. Vieira Barbosa J et al. Hepatol Commun 2022;6:765-79
5. Schlesinger N et al. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2023;41:60-6
6. Pegloticase [package insert] Horizon Therapeutics USA, 2022
7. Botson JK et al. Arthritis Rheumatol 2023;75:293-304
8. Methotrexate tablets [package insert] EXCELLA GmbH, 2009
9. Botson JK et al. ACR Open Rheumatol 2023;5:407-18
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Schlesinger N, Obermeyer K, Padnick-Silver L, LaMoreaux B, Lipsky P. Hepatic Fibrosis Before and During Intensive Urate-lowering with Pegloticase in the Presence and Absence of Methotrexate Co-therapy [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/hepatic-fibrosis-before-and-during-intensive-urate-lowering-with-pegloticase-in-the-presence-and-absence-of-methotrexate-co-therapy/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/hepatic-fibrosis-before-and-during-intensive-urate-lowering-with-pegloticase-in-the-presence-and-absence-of-methotrexate-co-therapy/