Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Changes in capillaroscopy nailfold image are a valuable element in the diagnostic procedure and monitoring of systemic sclerosis as well as other systemic diseases. However, manual image assessment is time consuming and the classification of observed changes is subjective. This makes it difficult to compare the results of tests evaluated by different physician, as well as to thoroughly analyse the progression that occurs between repeated tests. The aim of the study is to validate an automated software for classification of nailfold capillary image as normal or disturbed
Methods: From among the available resources, 100 normal capillaroscopy images and 100 with varying severity of pathological changes were selected. manual image analysis was performed twice. In the teaching program prepared for this purpose (Figure 1), region of interest (ROI) was determined and individual capillaries were marked, images were classified as correct and changed. The neural network was trained using the fast.ai library (based on PyTorch). The ResNet-34 deep residual neural network was chosen, as it is widely known to perform image recognition and classification. The dataset was split on training, validation and test sets, using a proportion 70/20/10. Due to a small number of images, 10-fold cross-validation with validation and test set was performed.
Results: The manual annotations (normal/disturbed) of images were treated as ground truth. Sensitivity and the specificity of validation set (the 20% subset of images used for validation during the neural network training process) were, respectively, 89.0% and 89.4%, while for test set, these metrics were reported as 89.0% and 86.9%, respectively
Conclusion: Pilot software for the fully automatic assessment of capillaroscopic image can be a useful tool for quick classification of correct and changed capillaroscopy pattern. In the course of further work on the software, additional functionalities allowing for capillary counting, shape and clinical pattern classification will be developed
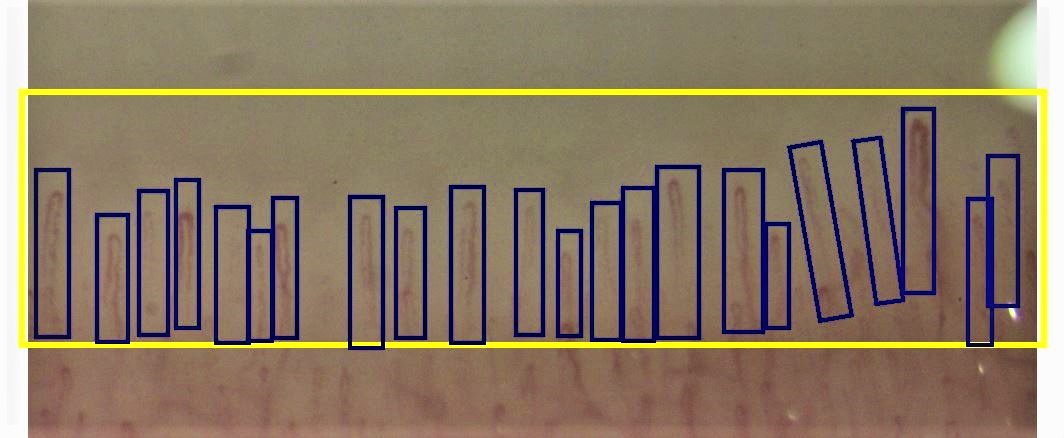 Figure. 1 Screen from training capillaroscopy software with manually marked region of interest (ROI) and individual capillaries
Figure. 1 Screen from training capillaroscopy software with manually marked region of interest (ROI) and individual capillaries
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Brzezińska O, Rychlicki-Kicior K, Makowska J. Fully Automatic Assessment of Nail Fold Capillaroscopy Software – Early Results [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/fully-automatic-assessment-of-nail-fold-capillaroscopy-software-early-results/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/fully-automatic-assessment-of-nail-fold-capillaroscopy-software-early-results/
