Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 10, 2015
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis - Human Etiology and Pathogenesis Poster III
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: RA is an autoimmune,
inflammatory and chronic disease which aetiology is unknown. It presents
different autoantibodies such as RF and ACPA. A population of CD4 T cells
expressing CXCR5, Bcl6, PD-1, ICOS, CD40L and IL-21, named Follicular helper T
cells (Tfh), collaborates with B cells to produce antibodies. Increased levels
of peripheral blood Tfh cells have been implicated in the development of
systemic autoimmunity. Differential expression of CXCR3 and CCR6 whitin CD4+CXCR5+
T cells defines three mayor subset: CXCR3+CCR6– (Tfh1),
CXCR3–CCR6– (Tfh2) and CXCR3–CCR6+
(Tfh17). The aim is to ascertain if differents subsets of CD4+CXCR5+
T cells are alterated in RA patients and if their percentages correlate with
disease activity.
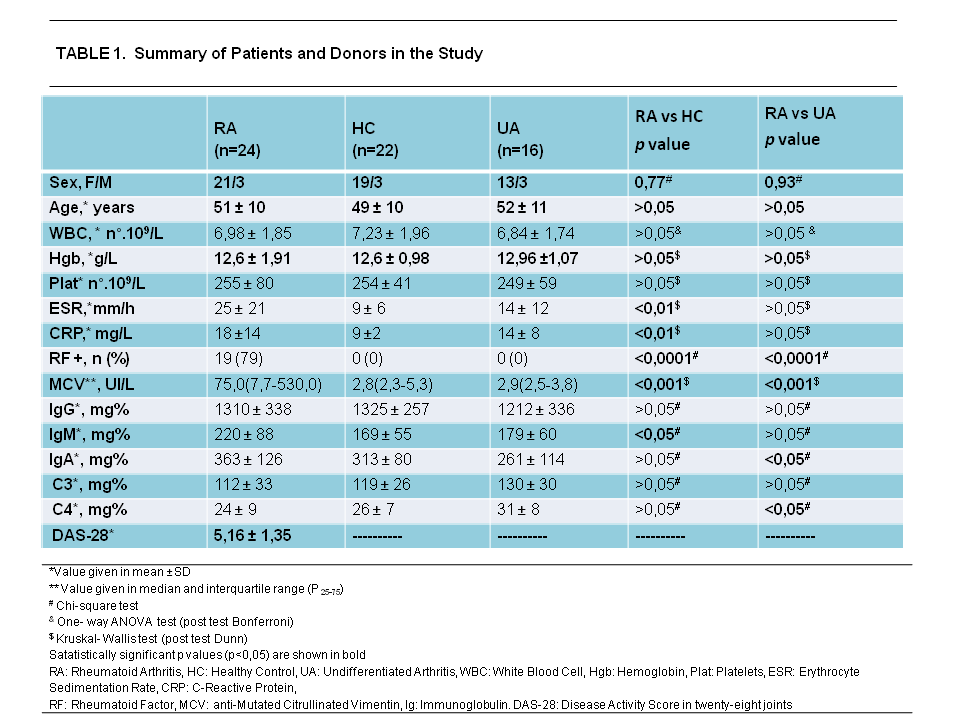
Methods: In this study participated RA patients
(n=24), healthy controls (HC) (n=22) and undifferentiated arthritis (UA)
patients (n=16) (Table 1). Percentage of CD4+CXCR5+ T
cells and their subsets CXCR3+CCR6–, CXCR3–CCR6–
and CXCR3– CCR6+ from PBMCs were analysed by flow
cytometry. Pearson or Spearman correlation
coefficients were used for statistics.
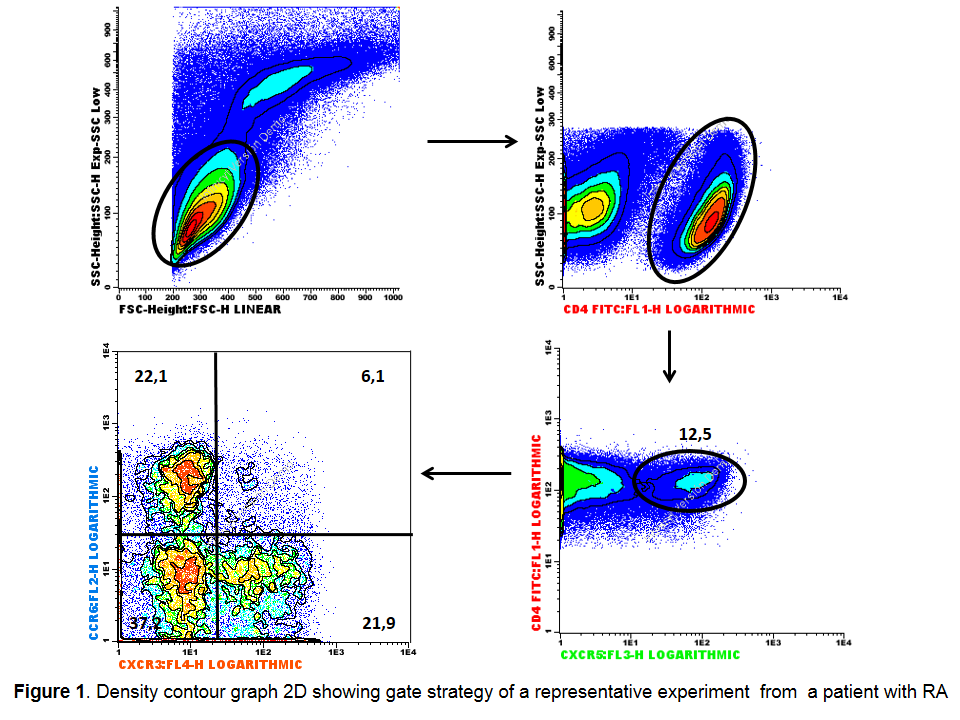
Results: Figure 1 shows flow cytometry
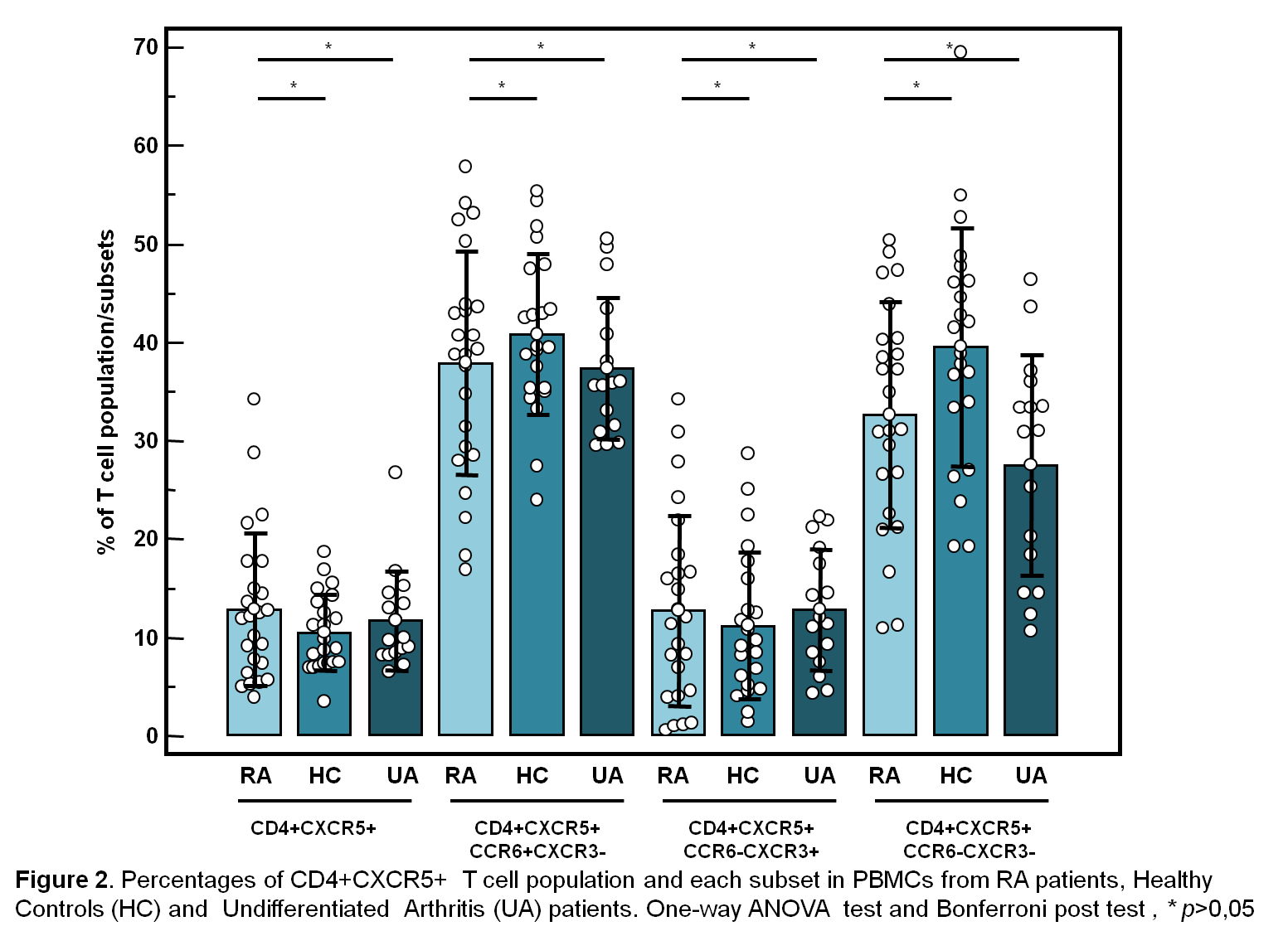
analysis. No differences were found in the % of CD4+CXCR5+
T cells between RA vs HC or RA vs UA (mean±SD, RA 12,89±7,73; HC 10,48±3,9; UA
11,71±5,04). Either in the % of Tfh1 (12,75 ±
9,72; 11,22 ± 7,48; 12,81 ± 6,13), or Tfh2 (32,66 ± 11,46; 39,53 ± 12,12; 27,56
± 11,25), or Tfh17 subsets (37,94 ± 11,34; 40,79
± 8,17; 37,34 ± 7,16) between previous groups (Figure 2). There was not
correlation between CD4+CXCR5+ T cells (r=-0,19 p=0,37
), or Tfh1 (r=0,09 p=0,68 ), or Tfh2 (r=0,36 p=0,09 ), or Tfh17
(r=-0,20 p=0,35 ) vs DAS-28, like either between each subset and ESR (
r=-0,18 p=0,39, r=-0,08 p=0,71,
r=-0,01 p=0,97, r=-0,25 p=0,23,
respectively). Unexpectedly, there was positive correlation between Tfh17 cells
and CRP r=0,47 p=0,021. Finally, there was not correlation between CD4+CXCR5+
T cells vs mutated citrullinated vimentin (MCV) r= 0,38 p=0,07, either
between Tfh1, Tfh2 and Tfh17 subsets vs MCV( r=-0,04 p=0,84, r=-0,14 p=0,51,
r=-0,19 p=0,37, respectively) or all of them vs RF (r=0,30 p=0,15,
r=-0,18 p=0,39, r= -0,15 p=0,46, r=0,01 p=0,98,
respectively).
Conclusion: In concordance with our
results, CD4+CXCR5+ T cells and their subsets would not
be involved in the RA development.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Costantino AB, Onetti L, Cloquell MDV, Acosta CDV, Mussano E, Cadile II, Rodriguez CM, Santo S, Ferrero PV. Follicular Helper T Cells in Peripheral Blood of Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/follicular-helper-t-cells-in-peripheral-blood-of-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/follicular-helper-t-cells-in-peripheral-blood-of-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/