Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Long-term clinical benefit and patient-reported outcomes (PRO) of subcutaneously-injected abatacept (ABA) in patients with RA in a real-world setting are of therapeutic interest. We conducted a non-interventional, prospective, five-year observational study (ORIGAMI study) to evaluate long-term effectiveness, safety, and PRO of ABA in Japanese patients with RA. We herein report the one-year interim results with the simplified disease activity index (SDAI) remission rate at week 52 as the primary outcome.
Methods: Biologic-naïve patients with RA who showed inadequate responses to conventional synthetic DMARDs (csDMARDs) and had SDAI-moderate disease activity were eligible. A total of 325 patients who started ABA treatment were enrolled at 64 facilities in Japan from June 2016 to October 2018. Clinical outcomes, including SDAI and PRO, were evaluated at weeks 0, 4, 24, and 52. Adverse events (AEs) were assessed during the observational period. Some of the outcomes were compared to those of csDMARDs-treated patients without concomitant biologics therapy and with SDAI-moderate disease activity. These patients were enrolled during the same period in the IORRA registry, which is a prospective, large cohort study for RA in Japan. The propensity score weighting method was used to compare the two groups.
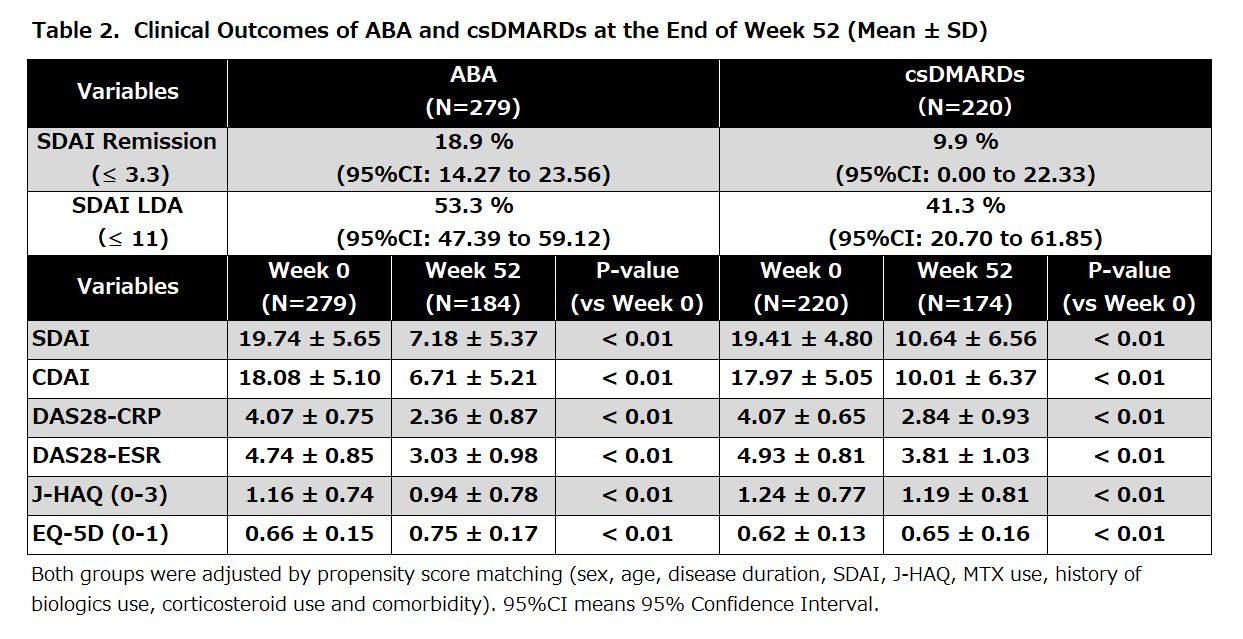
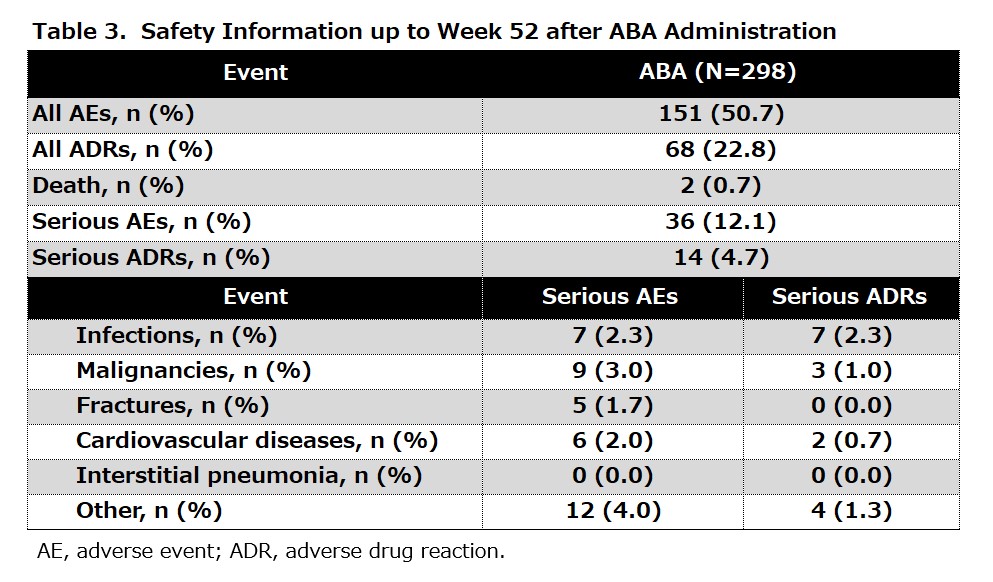
Results: Overall, 279 patients with RA were eligible for effectiveness analyses. The mean age was 66.9 years old and the mean SDAI was 19.7. The proportions of patients with disease durations of < 2, 2 to < 10, and ≥ 10 years were 39.1%, 31.9%, and 29.0%, respectively (Table 1). The proportion of patients with SDAI remission (≤ 3.3) at week 52 was 18.9%. SDAI-low disease activity (LDA, ≤ 11) was achieved in 53.3% of the patients (Table 2). The mean score of SDAI significantly decreased from week 4 and the proportions of LDA at weeks 4, 24, and 52 were 44.6%, 68.6%, and 79.0%, respectively. Similar improvements were observed in other variables such as clinical disease activity index and DAS28-CRP. Treatment with ABA significantly lowered the J-HAQ score. The proportions of patients who achieved HAQ remission (J-HAQ ≤ 0.5) at weeks 4, 24, and 52 were 27.9%, 33.2%, and 36.2%, respectively. These represent a significant increase from 19.4% at baseline. Furthermore, improvement of EuroQol 5 Dimension (EQ-5D) was observed at week 4 and onward. The ABA group showed numerically-higher proportions of patients with SDAI remission and SDAI-LDA, as well as better control of disease activity, J-HAQ score, and EQ-5D score at week 52 than the csDMARDs group (Table 2). The safety of ABA was evaluated in 298 patients. AEs and serious AEs were reported in 151 (50.7%) and 36 (12.4%) patients, respectively. Among patients with serious AEs, malignancy and serious infection were observed in 9 (3.0%) and 7 (2.3%) patients, respectively (Table 3).
Conclusion: ABA significantly improved disease activity, physical disability, and quality of life in as early as 4 weeks of treatment, for up to 52 weeks, in patients with RA in a real-world setting. Moreover, these clinical benefits from ABA, such as improved SDAI and PRO, were apparently better than csDMARDs.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Tamura N, Tanaka E, Inoue E, Yoshizawa Y, Matsumoto S, Yamanaka H, Harigai M. Fifty-Two Week Outcomes of Biologic-Naïve RA Patients Treated with Subcutaneous Abatacept in Japanese Multicenter Investigational Study (ORIGAMI Study) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/fifty-two-week-outcomes-of-biologic-naive-ra-patients-treated-with-subcutaneous-abatacept-in-japanese-multicenter-investigational-study-origami-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/fifty-two-week-outcomes-of-biologic-naive-ra-patients-treated-with-subcutaneous-abatacept-in-japanese-multicenter-investigational-study-origami-study/