Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Controlling inflammation with tumour necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients is hypothesized to reduce their cardiovascular risk. Arterial wall thickness (carotid intima media thickness (IMT)) and arterial stiffness (pulse wave velocity (PWV) and augmentation index (AIx)) are well established markers for subclinical cardiovascular disease and can be used as surrogate endpoints. A systematic review and meta-analysis on the effects of TNF inhibitors on arterial stiffness and carotid IMT in RA was performed.
Methods: MEDLINE, EMBASE, clinicaltrials.gov and WHO Clinical Trials Registry were searched for studies evaluating the effects of TNF inhibitors on PWV, AIx and IMT in RA.
Only controlled trials and prospective cohort studies were included. Principal study measures were baseline, follow-up and mean difference of the primary outcome measures IMT, PWV and AIx after TNF inhibiting treatment. A meta-analysis was performed to assess changes of these measures after therapy during different follow-up periods.
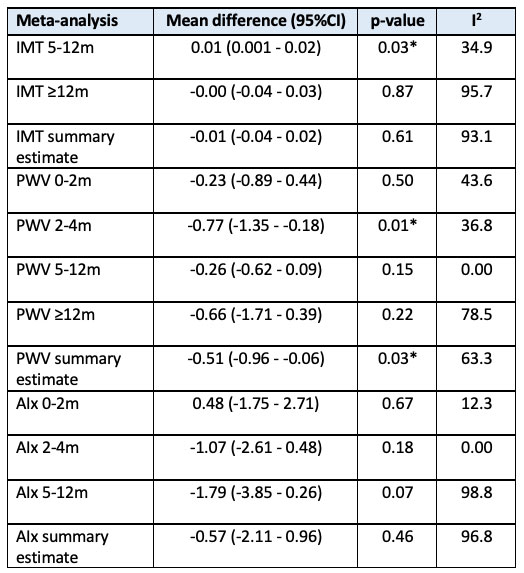
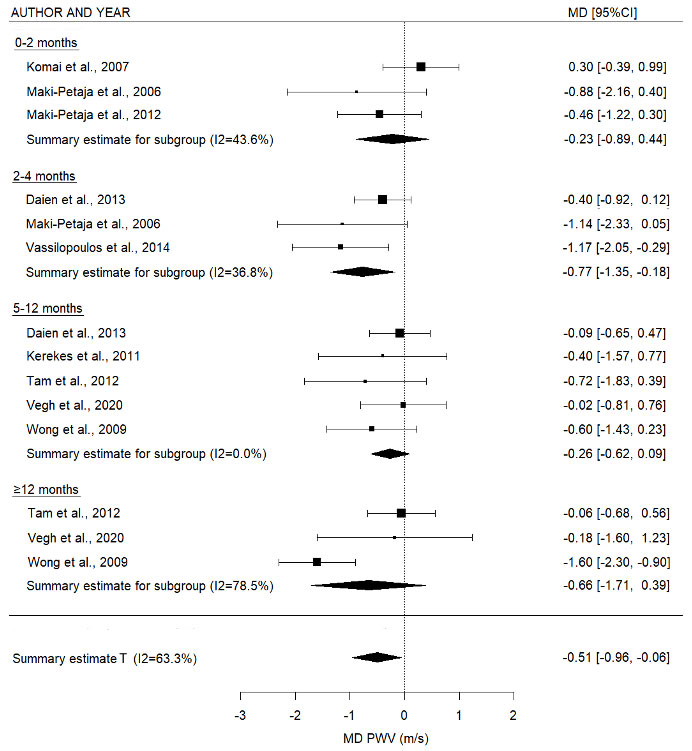
Results: 30 studies were identified from 1436 records, of which 23 were included in the meta-analysis. For IMT, there was a slight increase in the first months of follow-up, however the long-term follow-up revealed no progression (mean difference (MD) overall timepoints 0.01 mm (95%CI -0.04 – 0.02), p=0.61). PWV and AIx showed a decrease after treatment (PWV: MD -0.51 m/s (95%CI -0.96 – -0.06), p=0.03; AIx: MD -0.57 % (95%CI -2.11 – 0.96), p=0.46). Heterogeneity was high in the overall analyses and subgroups with long follow-up periods (≥12 months).
Conclusion: This meta-analysis showed mixed results of the effects of TNF inhibitors on the surrogate markers. The results suggest that TNF inhibiting therapy in RA patients does not deteriorate intima media thickness and decreases PWV and AIx. This indicates favorable effects of TNF inhibitors on the cardiovascular disease risk. Whether this ultimately leads to less clinically overt cardiovascular events in comparison to other antirheumatic therapies needs further investigation.
Results of meta-analyses for IMT, PWV and Aix for different time intervals, given in mean difference over time with 95% confidence interval, p-value and I2. *: P-value is significant. The mean difference for IMT is given as millimeter, for PWV as meter/second and for AIx as percentage. I2 is given as percentage.
Summary estimate: the model includes all timepoints, except when in one study the same patients were measured multiple times, the longest follow-up time was used.
IMT: inter media thickness; PWV: pulse wave velocity; AIx: augmentation index, m: months, 95%CI: 95% confidence interval.
Data are presented as mean difference over time in meter/second with 95% confidence interval.
Summary estimate T: the model includes all timepoints, except when in one study the same patients were measured multiple times, the longest follow-up time was used.
PWV: pulse wave velocity; MD: mean difference; m/s: meter/second; 95%CI, 95% confidence interval.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
van Geel E, Abdulmajid B, Blanken A, Nurmohamed M. Favorable Effects of TNF Inhibitors on Intima Media Thickness and Arterial Stiffness in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/favorable-effects-of-tnf-inhibitors-on-intima-media-thickness-and-arterial-stiffness-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-systematic-review-and-meta-analysis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/favorable-effects-of-tnf-inhibitors-on-intima-media-thickness-and-arterial-stiffness-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-systematic-review-and-meta-analysis/