Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 5, 2017
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNFa) is involved in the pathogenesis of RA and is increasingly being studied as a biomarker of cardiovascular disease (CVD). While TNF receptor 2 (TNFR2) and TNFa levels are correlated, TNFR2 is used more frequently as a biomarker in studies because of its stability in stored blood samples. We investigated whether TNF inhibitor (TNFi) use may influence measured TNFR2 levels. Since the mechanism of action for TNFi is binding TNFa, a component of these drugs is a TNF receptor. Thus, we hypothesize that there may be cross-reactivity between specific TNFi’s and the TNFR2 assay.
Methods: All subjects were part of a CVD sub-study performed in a large prospective RA cohort study with blood samples collected annually, data on treatment and C-reactive protein (CRP). TNFR2 was measured using a commercial ELISA kit (R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN). We categorized TNFR2 levels into 3 groups: (1) >46 and £10,000 pg/mL, typical range; (2) >10,000 pg/mL and ≤100,000 pg/mL, samples requiring 200-fold dilution; (3) >100,000 pg/mL, levels exceeding measurable values. We examined the association individual TNFi’s and having a TNFR2 level in group 3. Additionally, we assessed the correlation between natural log transformed CRP and TNFR2.
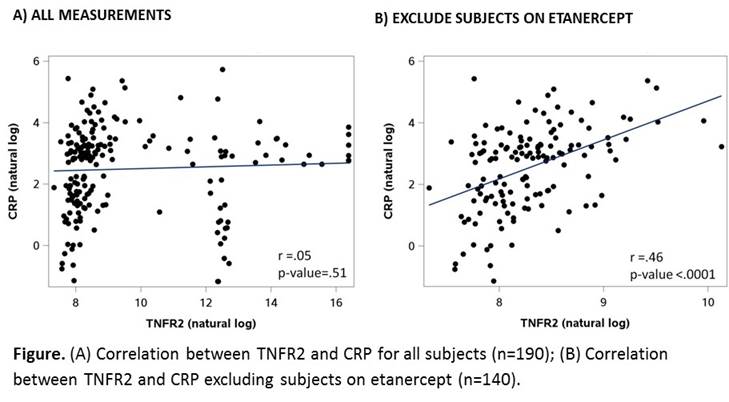
Results: We studied 190 RA subjects, mean age 60 years, 84% female, 73% anti-CCP positive and CRP ranged from 0.31-310 mg/L. Subjects on TNFi comprised 47% of the study: 14% on adalimumab, 26% on etanercept, and 8% on infliximab (no subjects on certolizumab or golimumab). All subjects with TNFR2 exceeding measurable levels (group 3) were on etanercept (Table). Samples that required 200-fold dilution (group 2) not on etanercept therapy had higher levels of CRP compared to those on etanercept (Table). We observed no significant correlation between CRP and TNFR2 for all subjects, r=0.05, p=0.51. After excluding subjects on etanercept, the correlation was significant, r=0.46. p<0.0001 (Figure). We observed no significant changes in the correlation between CRP and TNFR2 after excluding patients on adalimumab or infliximab.
Conclusion: Our data suggest cross-reactivity between etanercept and the TNFR2 assay, as 100% of subjects on etanercept had levels of TNFR2 above measurable levels. Of the TNFi’s, only etanercept has a TNF binding domain modeled after TNFR2. Thus, it is plausible that the TNFR2 assay has a high affinity for the TNFR portion of etanercept. These data should be considered when designing studies using TNFR2 in populations where etanercept is a treatment option.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Frits M, Bradwin G, Shadick NA, Iannaccone C, Weinblatt M, Rifai N, Liao KP. Factors Associated with TNF Receptor 2 Levels Above the Measurable Range in Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/factors-associated-with-tnf-receptor-2-levels-above-the-measurable-range-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/factors-associated-with-tnf-receptor-2-levels-above-the-measurable-range-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/