Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 6, 2021
Title: Abstracts: Immunological Complications of Therapy (0437–0440)
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 9:00AM-9:15AM
Background/Purpose: Rituximab (RTX) has been associated with impaired humoral response to vaccination. This study aim was to identify the predictors for a lack of humoral response to the BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine in patients with autoimmune inflammatory rheumatic diseases (AIIRD) treated with RTX.
Methods: We conducted a sub-analysis of the prospective multicenter study investigating immunogenicity of the two-dose regimen BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine in adult AIIRD patients, including rheumatoid arthritis (RA), systemic lupus erythematosus, systemic vasculitis, and inflammatory myositis treated with RTX compared to controls without rheumatic diseases or immunosuppressants use. Data on the serum IgG level prior to administration of the last course of RTX were collected. Post-vaccination serum IgG levels against SARS-CoV-2 spike S1/S2 proteins were measured 2 – 6 weeks after the 2nd vaccine dose. Seropositivity was defined as IgG ³15 binding antibody units (BAU)/ml.
Statistical analysis included a stepwise backward multiple logistic regression for predicting a seropositive result on AIIRD patients with all data available (n=92), starting with all individual variables showing the significance level < 0.2 between seropositive and seronegative result.
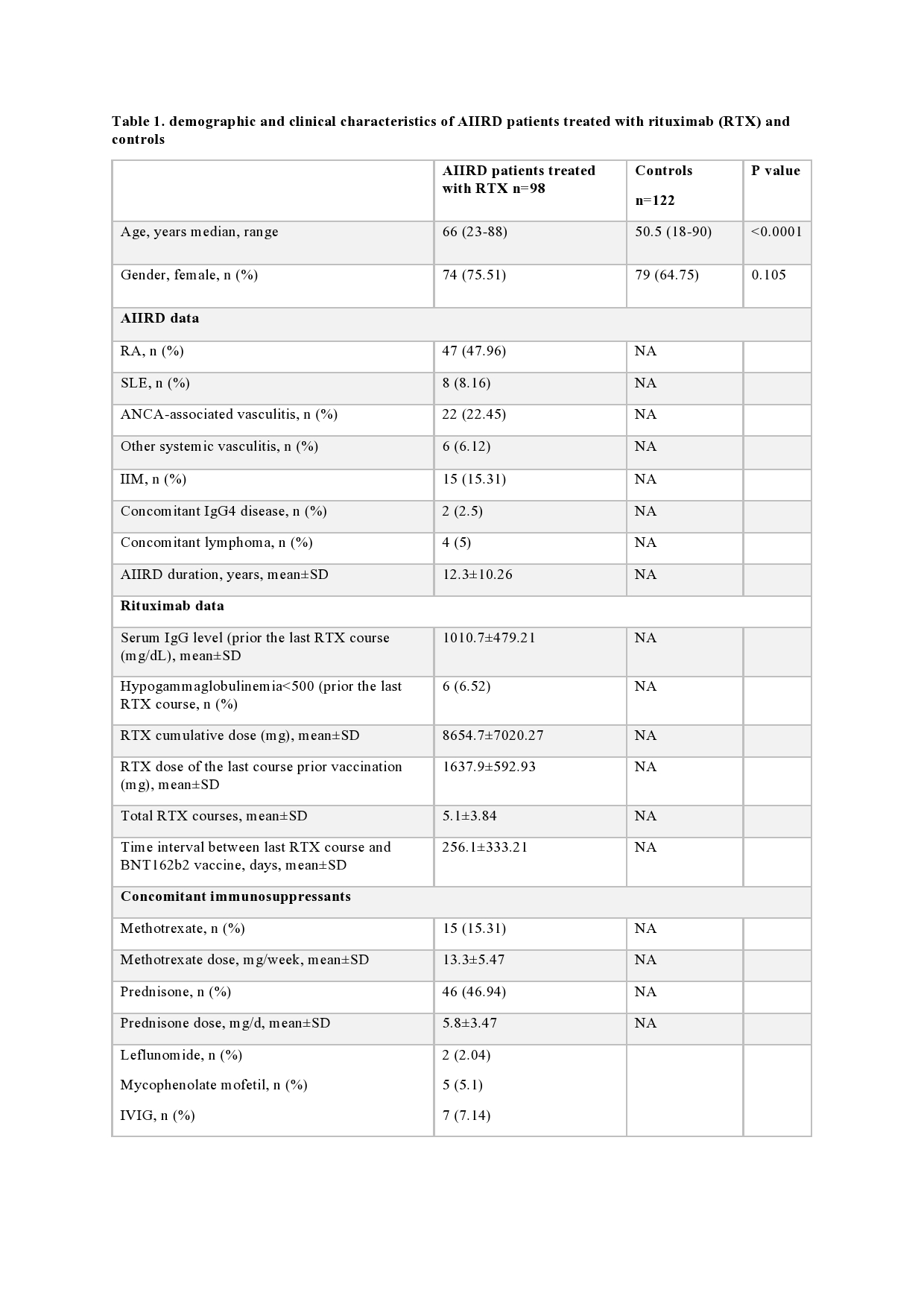
Results: A total of 98 AIIRD patients (75.5% females) and 122 controls (64.8% females) were included in the study (table 1). AIIRD patients were significantly older vs controls, mean±standard deviation (SD) 62.3±14.6 vs 50.8±14.6 years, p>0.0001, respectively. Among AIIRD patients, 4 had a past history of lymphoma. Following vaccination, the seropositivity rate and S1/S2 IgG levels (mean±SD) were significantly lower among AIIRD patients vs controls, 38.8% (n=38) vs 100%, p < 0.0001 and 49.9±81 vs 218.4±81.2 BAU/ml, p < 0.0001, respectively.
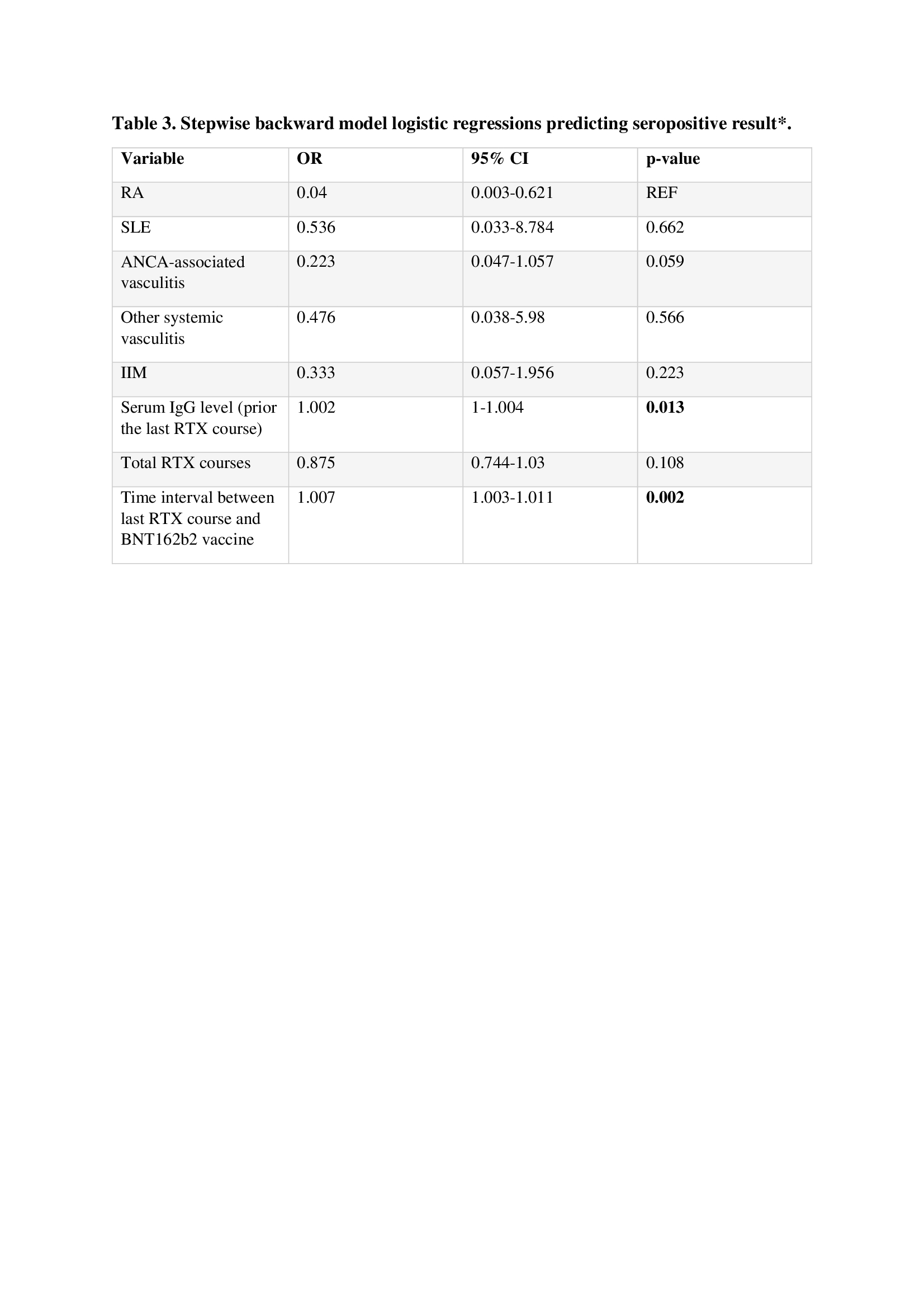
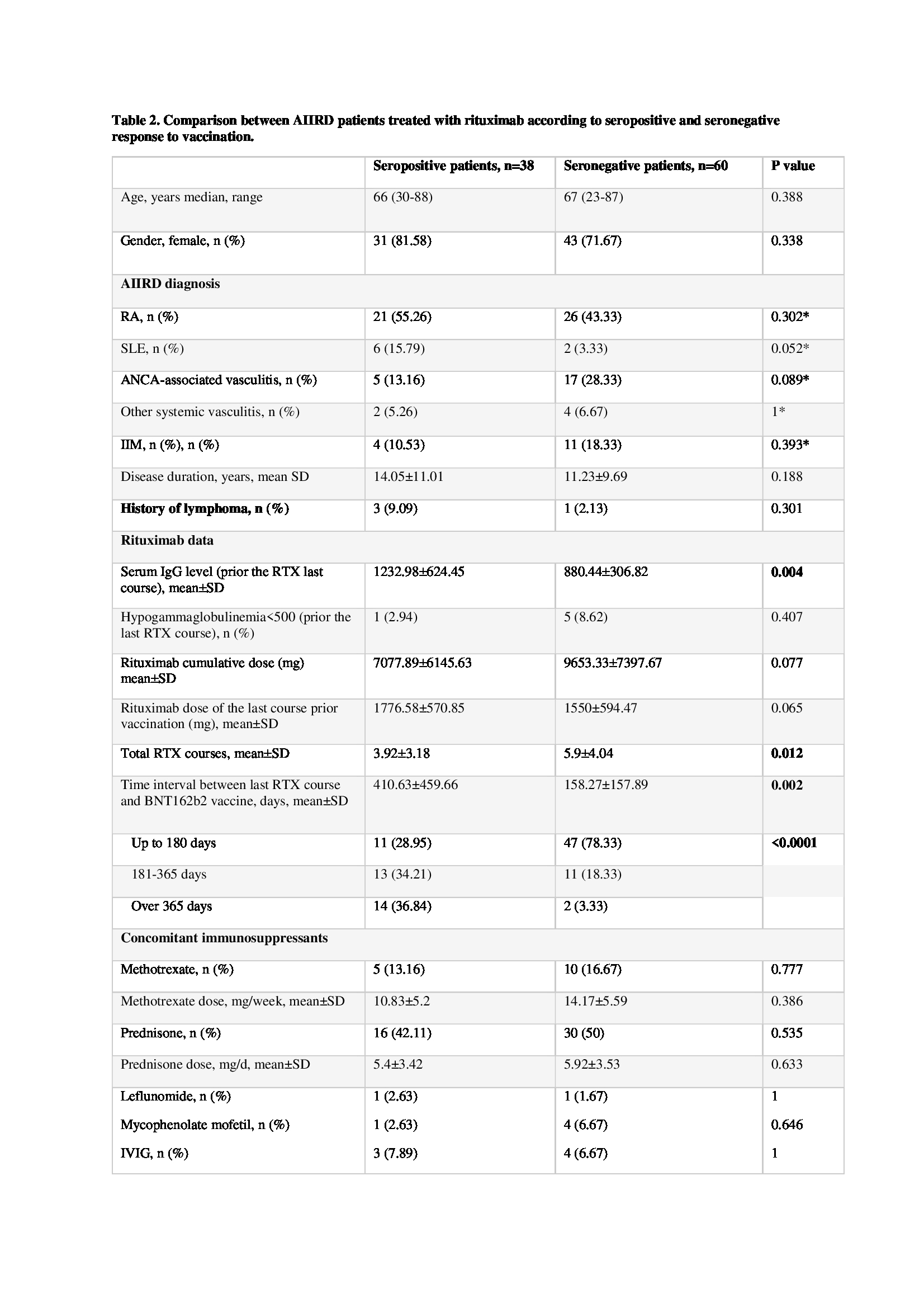
Seronegative and seropositive AIIRD patients treated with RTX significantly differed by the total number of RTX courses, mean 5.9±4.0 vs 3.9±3.2, p=0.012; IgG levels prior to administration of the last course of RTX, 880.4±306.8 vs 1233±624 mg/dl, p=0.0036 and the interval between the last RTX course and vaccination, 158.3±157.9 vs 410.6±459.7 days, p=0.0019 (table 2). Multivariate logistic regression predicting a seropositive response to vaccination in patients treated with RTX showed that RA conferred the highest probability for a positive response, while ANCA-associated vasculitis conferred the lowest probability for a positive response. The odds ratio (OR) of ANCA associated vasculitis was marginally significant (OR = 0.223, p=0.059). Two other variables –IgG level prior the last course of RTX and interval (days) between the last RTX course and vaccination – were associated with a seropositive response: for every 1 mg/dl IgG increment – OR 1.002, 95%CI 1-1.004, p=0.013, and for every day increment – OR 1.007, 95%CI 1.003-1.001, p=0.002, respectively. (table 3)
Conclusion: In AIIRD patients treated with RTX, high exposure to RTX over time, low IgG levels prior to the last RTX course, and a short interval between the last RTX course and BNT162b2 vaccination predicted the absence of a humoral response to vaccination. These data should guide the optimal timing of vaccination in patients treated with RTX.
 RTX-subanalysis_ACR_2021-Table_2.jpeg”
RTX-subanalysis_ACR_2021-Table_2.jpeg”
AIIRD, autoimmune inflammatory rheumatic disease; n, number; RA, rheumatoid arthritis; SLE, systemic lupus erythematosus; ANCA, antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody; IIM, idiopathic inflammatory myopathies; IgG, immune globulin G; SD, standard deviation; RTX, rituximab; IVIG, intravenous immune globulin.
Including and staying criterion was p < 0.2. RA was considered as a reference for diagnosis.
RA, rheumatoid arthritis; SLE, systemic lupus erythematosus; ANCA, antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody; IIM, idiopathic inflammatory myopathies; IgG, immune globulin G; RTX, rituximab.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Furer V, Eviatar T, Zisman D, Peleg H, Paran D, Levartovsky D, Kaufman I, Zisapel M, Elalouf O, Meidan R, Broyde A, Polachek A, Wollman J, Meridor K, Nochomovitz H, Silberman A, Rosenberg D, Feld J, Haddad A, Gazitt T, Elias M, Hijaze N, Kharouf F, Shefer G, Sharon O, Pel S, Nevo S, Elkayam O. Factors Associated with Reduced Immunogenicity of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine in Patients with Autoimmune Inflammatory Rheumatic Diseases (AIIRD) Treated with Rituximab [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/factors-associated-with-reduced-immunogenicity-of-the-bnt162b2-mrna-covid-19-vaccine-in-patients-with-autoimmune-inflammatory-rheumatic-diseases-aiird-treated-with-rituximab/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/factors-associated-with-reduced-immunogenicity-of-the-bnt162b2-mrna-covid-19-vaccine-in-patients-with-autoimmune-inflammatory-rheumatic-diseases-aiird-treated-with-rituximab/