Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 12, 2022
Title: RA – Treatment Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Upadacitinib (UPA) is an oral Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor approved for the treatment of moderately-to-severely active rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Previous investigations demonstrated UPA modulates innate and adaptive immune systems in RA via direct and indirect inhibition of the critical pathogenic pathways.1,2 Despite significant exposure-response (ER) relationships between plasma UPA exposure and clinical efficacy endpoints, the relationships between UPA plasma exposures and the modulated pathway biomarkers have not been fully investigated. The objective of the current study is to identify biomarkers, and associated pathways, that demonstrate a significant relationship with UPA plasma exposures in RA patients.
Methods: A subset of patients with available plasma samples at baseline, Week 2, and Week 12/14 visits were randomly selected from three UPA Phase 3 studies (SELECT-NEXT, SELECT-BEYOND, and SELECT-MONO) for biomarker assessment. Among the selected patients, 267, 300, and 100 received placebo, UPA 15 mg QD, and UPA 30 mg QD, respectively. The plasma levels of 92 proteins were analyzed using the Olink Target 96 Inflammation Panel. The data for 78 quantifiable proteins were matched by the individual-level UPA steady-state average plasma concentration over a dosing interval (Cave) obtained as the post-hoc estimates from a previously developed population pharmacokinetics model3. ER analyses were conducted by linear regression using UPA exposure as a predictor of the log2 fold change from baseline at both Week 2 and Week 12/14 for each protein. Multiplicity was adjusted using the Benjamini-Hochberg procedure controlling false discovery rate at the level 0.1. The biomarkers were ranked based on the effect size of the ER relationship at Week 12/14.
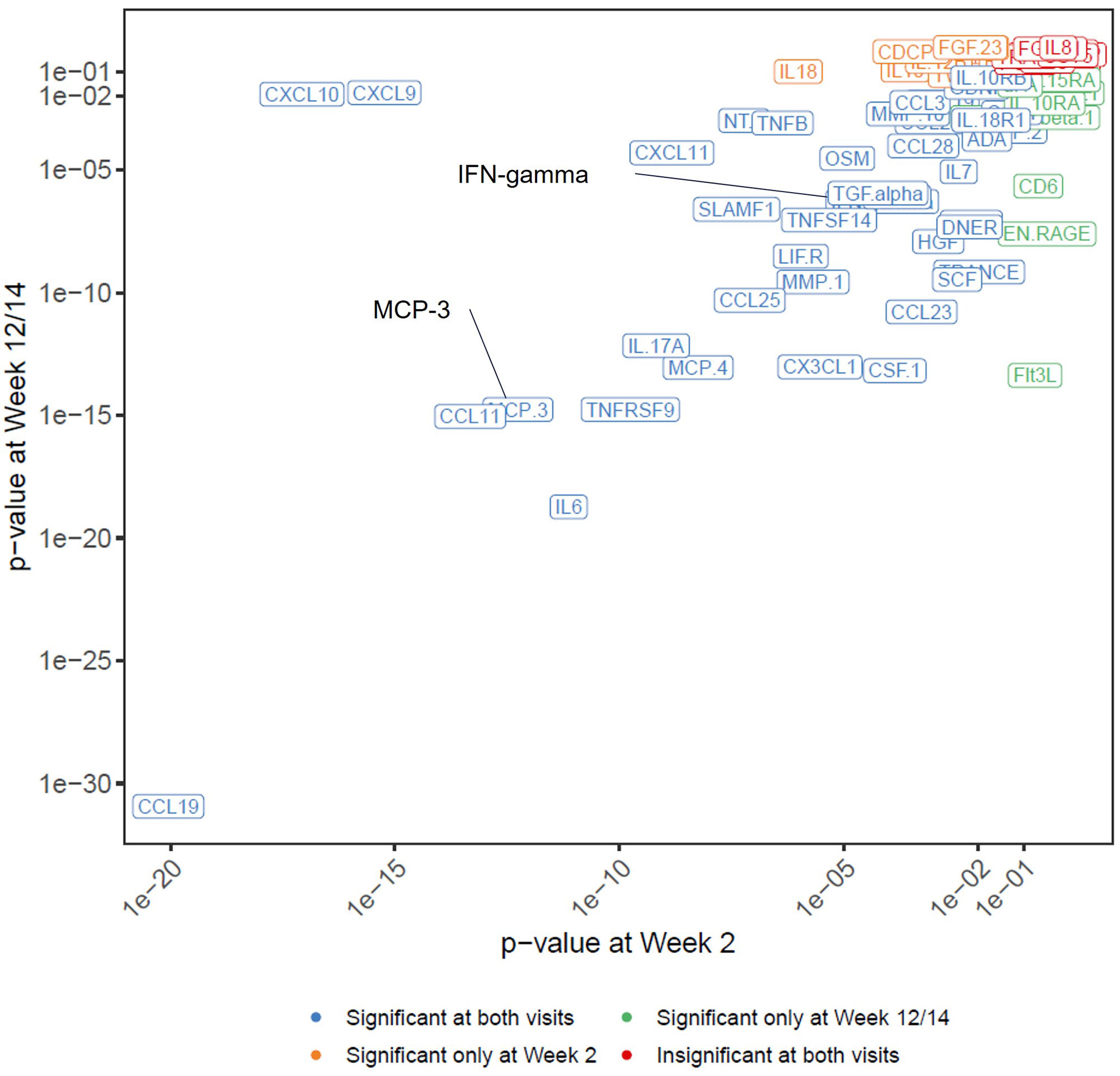
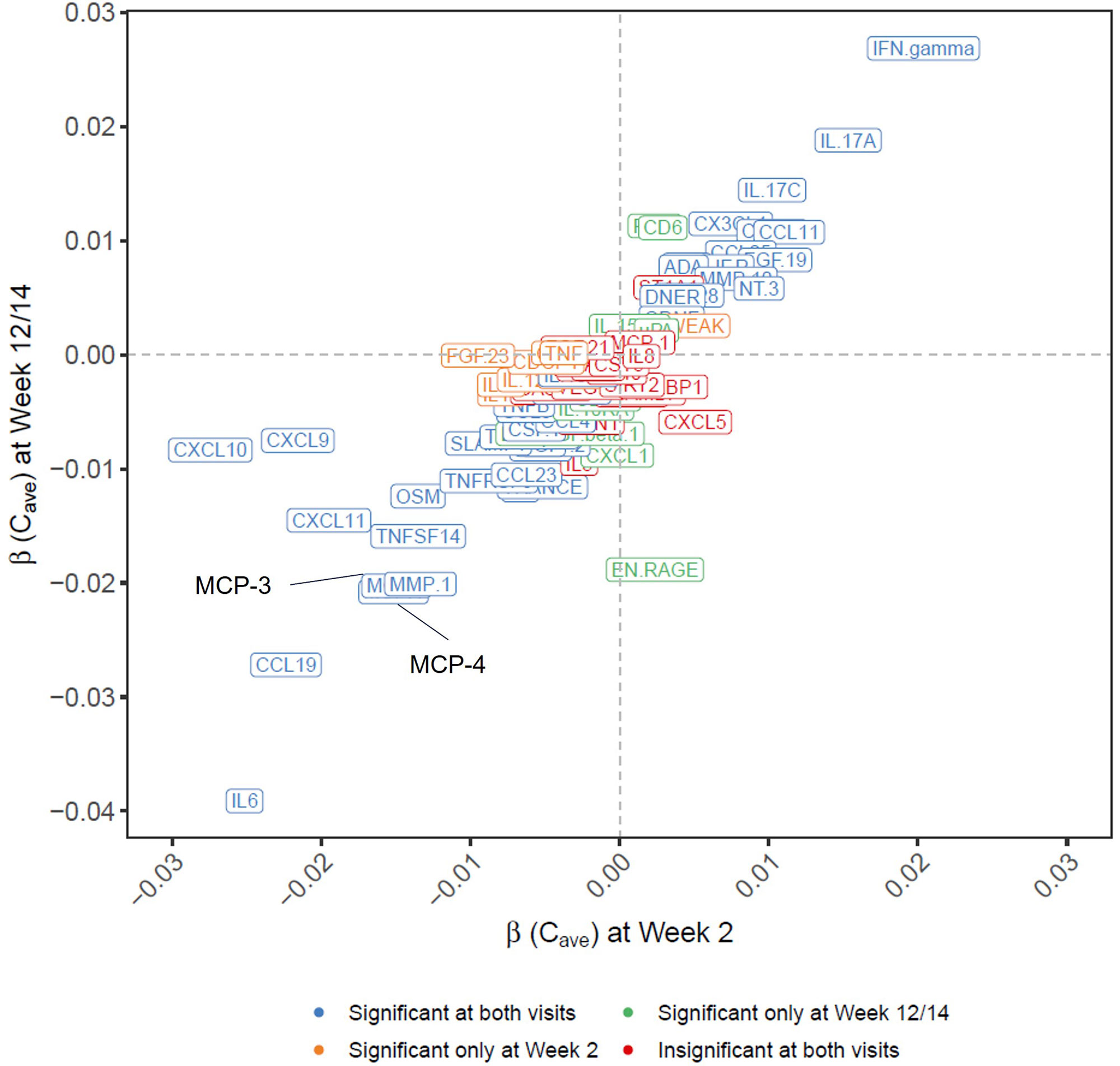
Results: Among the 78 measurable proteins (Figures 1 and 2), 41 exhibited significant ER relationships with UPA exposure at both visits, while nine having a significant ER relat at either Week 2 (IL-10, IL-18, TWEAK, IL-12B, PD-L1, CDCP1, CD5, TNF, FGF-23) or Week 12/14 (EN-RAGE, Flt3L, CD6, CXCL1, Lap-TGF-beta1, IL-10RA, CD244, IL-15RA, uPA). A negative correlation with UPA exposure were observed for IL-6, CCL19, MCP-4, MCP-3, MMP-1, EN-RAGE, TNFSF14, CXCL11, CXCL9, and CXCL10 while a positive ER correlation was observed for IFN-gamma and IL-17A.
Conclusion: The identified biomarkers provide quantitative evidence for our existing knowledge about the inhibitory effects of UPA on pathogenic pathways in the RA patients, including crucial inflammatory mediators (IL-6, interferon-related biomarkers, TNFSF11, and ENRAGE), myeloid cell chemotaxis (CCL19, MCP-3, and MCP-4), and cartilage destruction (MMP1). These results provide additional insights into UPA mechanism of action in RA.
References
1. Sornasse T, et al. Arthritis Rheumatol 2019; 71 (suppl 10).
2. Sornasse T, et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 10)
3. Klünder B, et al. Clin Pharmacokinet 2019; 58(8):1045-1058.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Qian Y, Cai F, Sornasse T, Shen J, Camp H, Mohamed M. Exposure-Response Analyses of Upadacitinib Effects on Plasma Biomarkers in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/exposure-response-analyses-of-upadacitinib-effects-on-plasma-biomarkers-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/exposure-response-analyses-of-upadacitinib-effects-on-plasma-biomarkers-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients/