Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 12, 2023
Title: (0252–0282) Miscellaneous Rheumatic & Inflammatory Diseases Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
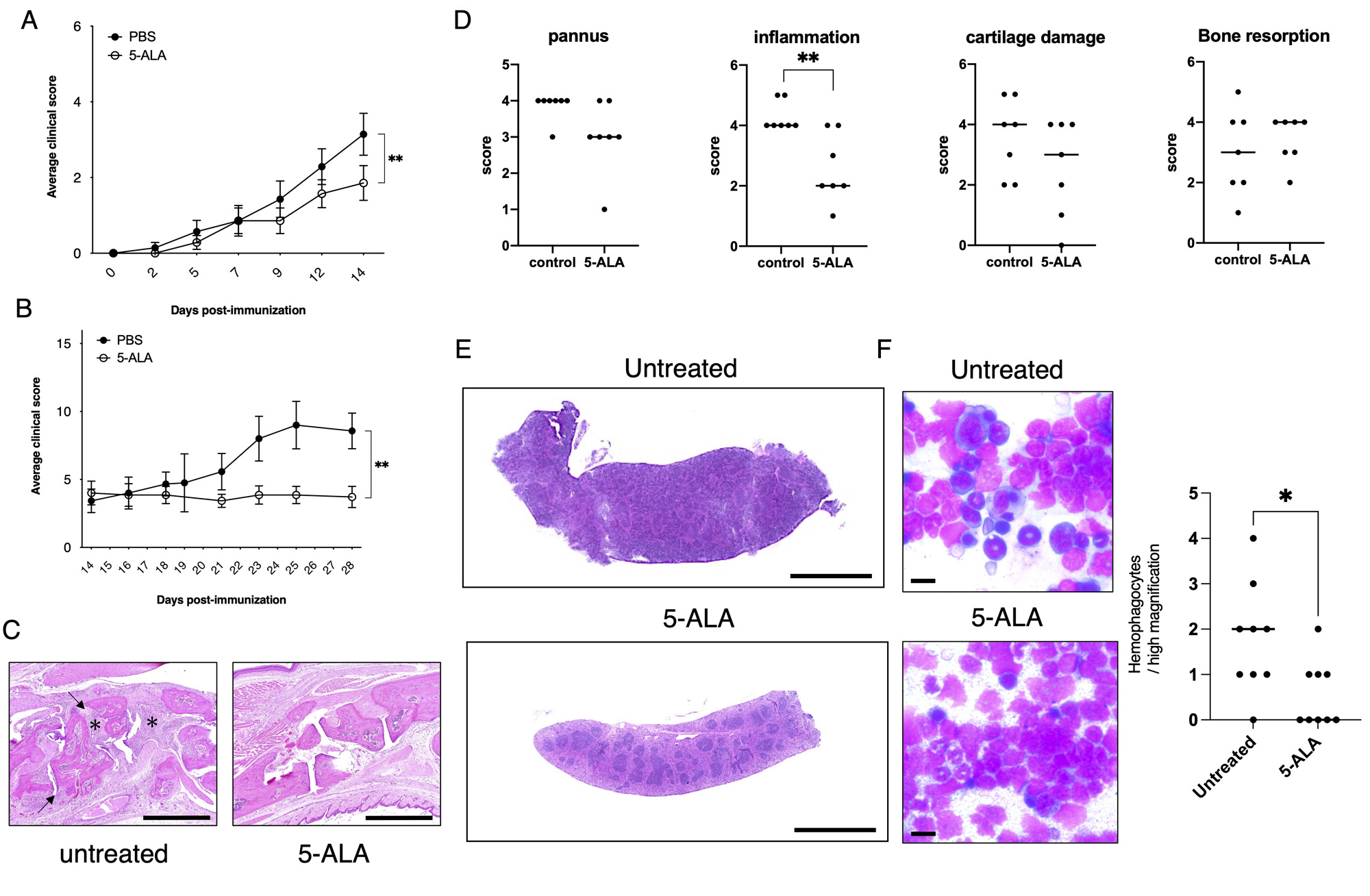
Background/Purpose: The primary objective of this study is to elucidate the therapeutic potential of 5-aminolevulinic acid/sodium ferrous citrate (5-ALA/SFC) in ameliorating the pathological manifestations associated with adult-onset Still’s disease (AOSD), with a specific focus on arthritis and macrophage activation syndrome (MAS). This investigation entails the utilization of mouse models to examine the impact of 5-ALA/SFC on the aforementioned pathologies in AOSD. Additionally, a pilot study involving patients diagnosed with AOSD was conducted to further assess the therapeutic efficacy and safety of 5-ALA/SFC in a clinical setting.
Methods: In this study, mice were subjected to collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) by immunization with type II collagen, and to MAS by repeated administration of stimulating synthetic oligonucleotides containing CpG motifs (CpG-S-ODN) via drinking water. The objective of this investigation was to assess the preventive and therapeutic effects of 5-ALA/SFC on arthritis in CIA mice, as well as its potential to ameliorate hemophagocytosis observed in bone marrow smears of CpG-S-ODN-treated mice. AOSD patients undergoing prednisolone (PSL) treatment were enrolled in an open-label trial, wherein oral administration of 5-ALA/SFC was conducted. The efficacy and safety of 5-ALA/SFC in facilitating prednisolone tapering were subsequently evaluated.
Results: In both experimental models for arthritis prevention and treatment, the group receiving 5- 5-ALA/SFC exhibited significantly reduced joint scores compared to the control group. Furthermore, in mice treated with CpG-S-ODN, the 5-ALA/SFC group demonstrated a decrease in hemophagocytosis (phagocytosis of red blood cells by immune cells) and splenomegaly (enlarged spleen). The anti-inflammatory properties of 5-ALA/SFC are attributed to its ability to suppress the production of CCL4 and CXCL10 in monocytes and macrophages, while also promoting the induction of M2 macrophages (a type of anti-inflammatory macrophage). These cellular responses contribute to the observed therapeutic effects. In the clinical study, four out of five participants completed the prescribed drug administration, and all patients successfully maintained a tapering regimen of PSL without experiencing any serious adverse events or worsening of symptoms throughout the study duration.
Conclusion: The administration of 5-ALA/SFC holds promise as a viable therapeutic intervention for inflammatory disorders, specifically AOSD. The utilization of 5-ALA/SFC may impart a multifaceted therapeutic impact, encompassing the regulation of arthritis symptoms and the suppression of MAS. Furthermore, our findings provide supporting evidence regarding the safety profile associated with 5-ALA/SFC treatment in individuals diagnosed with AOSD. However, further investigations are warranted to elucidate the underlying mechanisms and evaluate the clinical efficacy of 5-ALA/SFC, which should be pursued in future scientific inquiries.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Koga T, Sumiyoshi R, Tsuji Y, Kodama K, Furukawa K, Endo Y, Kawakami A. Exploring the Potential of Oral Administration of 5-aminolevulinic Acid/sodium Ferrous Citrate in Adult-onset Still’s Disease: Preclinical Study in Mice and Pilot Investigation in Humans to Assess Efficacy and Safety [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/exploring-the-potential-of-oral-administration-of-5-aminolevulinic-acid-sodium-ferrous-citrate-in-adult-onset-stills-disease-preclinical-study-in-mice-and-pilot-investigation-in-humans-to-assess-ef/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/exploring-the-potential-of-oral-administration-of-5-aminolevulinic-acid-sodium-ferrous-citrate-in-adult-onset-stills-disease-preclinical-study-in-mice-and-pilot-investigation-in-humans-to-assess-ef/