Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Oligoarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis (oligo JIA) is defined by limited joint involvement (< 5 joints) in the first 6 months of disease. A subgroup of patients presents with distinct clinical features, including early age at disease onset (< 6 years), female sex, increased risk for uveitis and antinuclear antibody (ANA) positivity. The biological processes that drive clustering of these clinical features in ANA+ oligoarthritis are not understood. The presence of autoantibodies in this oligo JIA subgroup suggests a role for abnormal B cell responses. To better understand interactions between T and B cells in oligo JIA, we characterized CD4+ T cells with a B cell-helper T cell profile in ANA+ and ANA– oligo JIA.
Methods: Synovial fluid (SF) and, where possible, paired peripheral blood (PB) samples were collected from oligo JIA patients, defined by ILAR criteria. PB was obtained from healthy controls (HC). PB and SF mononuclear cells were evaluated with flow cytometry. T effector (CD4+CD25–, Teff) and T regulatory (CD4+CD25+CD127lo) cells were sorted from the SF of 2 patients (one ANA+ and one ANA–), stained with hashing antibodies, pooled together in equal ratio, and processed for single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) coupled with T cell receptor (TCR) repertoire using 10X. Transcriptomic data were analyzed in R using Seurat v3.1.5.
Results: 14 oligo JIA patients and 10 controls were studied. T follicular helper cells (CD4+PD-1hiCXCR5+, Tfh) are found in secondary lymphoid organs and express factors (PD1, ICOS, IL-21, CXCL13) promoting B cell maturation and antibody production. Compared to the PB of controls and patients, Tfh cells were not significantly enriched in the SF of ANA+ or ANA– oligo JIA. In peripheral tissues, B cells are driven to mature and generate autoantibodies by T peripheral helper cells (CD4+PD-1hiCXCR5–, Tph). Flow cytometry studies showed a significant enrichment of Tph cells in the SF of oligo JIA patients. ANA+ patients had the highest proportion of Tph cells, with 50.8% ± 5.5 (mean ± SEM) of Tph among total CD4+ T cells, compared to 32.5% ± 3.4 in ANA– patients. In contrast, Tph cells were rare in the PB of patients and controls (< 6.5% of CD4+ T cells). Tph cells in SF expressed markers of B cell-helper T cells, including ICOS and the B cell chemoattractant CXCL13. scRNA-seq studies of SF CD4+ T cells revealed 2 clusters with Tph features, including cells co-expressing high levels of PDCD1 (gene encoding PD1) and CXCL13 alongside transcription factors previously identified in Tph cells (MAF and BATF). A greater proportion of Teff cells from the ANA+ patient (48%) compared to the ANA– patient (25%) was found in Tph clusters. TCR repertoire analysis showed that clonally expanded T cells (with at least 3 clonal TCR copies) concentrated in Tph clusters and were mostly observed in the ANA+ patient.
Conclusion: Our results show that T cells with features of B cell-helper T cells preferentially accumulate in the joints of children with ANA+ oligo JIA. These results suggest that beyond the clinical features that characterize early-onset, ANA+ oligo JIA, disordered T cell-mediated help to B cells may further define this patient subset. Further studies are needed to delineate the functionality of Tph cells in oligo JIA.
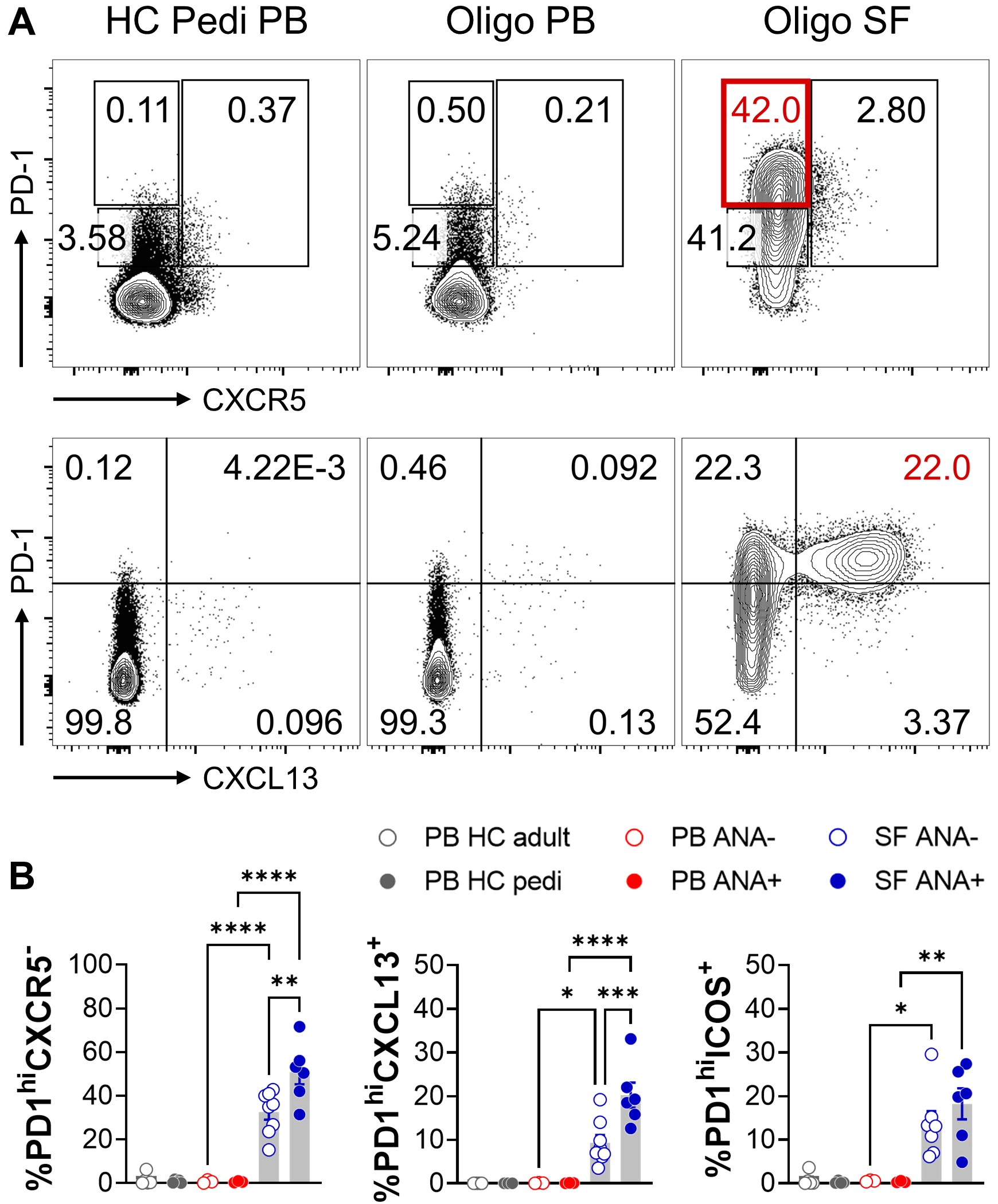 T peripheral helper (Tph) cells are enriched in the synovial fluid (SF) of ANA+ oligo JIA. A) Representative flow cytometry dot plots gated on live CD3+CD4+ T cells. Frequencies of Tph cells (PD1hi, CXCR5-) and of the B-cell chemoattractant CXCL13 in oligo JIA SF are highlighted in red. B) Mean frequency ± SEM of CD3+CD4+ T cells expressing the corresponding markers. Statistical testing: ANOVA with correction for multiple comparisons; p-value < 0.05 *; < 0.01 **, < 0.001 ***, < 0.0001 **** (for readability, not all significant comparisons are shown).
T peripheral helper (Tph) cells are enriched in the synovial fluid (SF) of ANA+ oligo JIA. A) Representative flow cytometry dot plots gated on live CD3+CD4+ T cells. Frequencies of Tph cells (PD1hi, CXCR5-) and of the B-cell chemoattractant CXCL13 in oligo JIA SF are highlighted in red. B) Mean frequency ± SEM of CD3+CD4+ T cells expressing the corresponding markers. Statistical testing: ANOVA with correction for multiple comparisons; p-value < 0.05 *; < 0.01 **, < 0.001 ***, < 0.0001 **** (for readability, not all significant comparisons are shown).
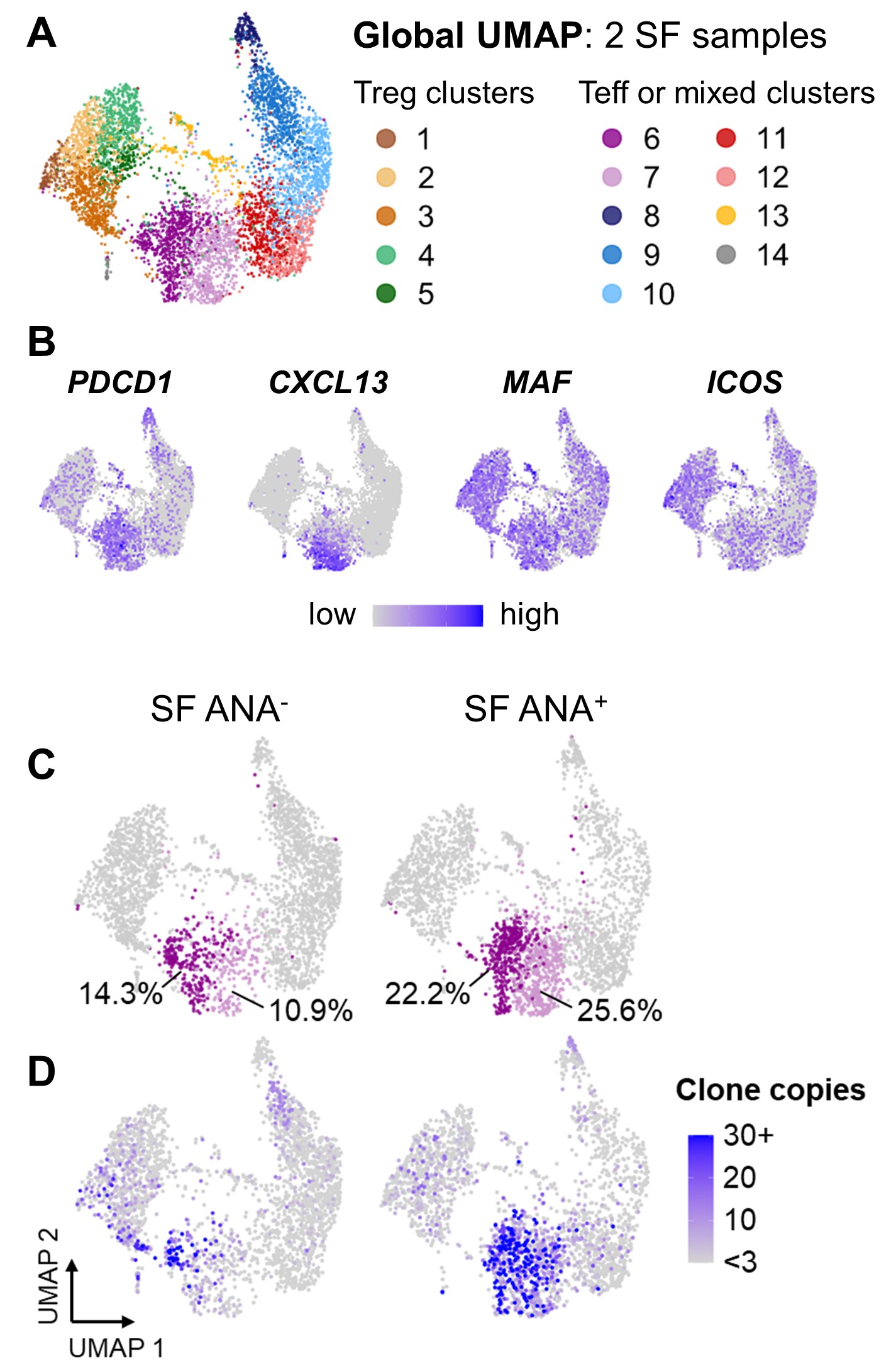 Single-cell RNA sequencing of SF CD4+ T cells reveal clonally expanded cells with features of Tph cells in ANA+ oligo JIA. Sorted Tregs (CD4+CD25+CD127lo) and Teffs (CD4+CD25-) from the SF of 2 oligo JIA patients were studied with 10X. A) Uniform manifold approximation and projection (UMAP) of global dataset (both subjects, 6190 cells), color-coded by cluster. Clusters 6 & 7 contain Tph cells. B) UMAP of global dataset, showing gene expression levels of key Tph cell markers. C) UMAP of dataset, split by patient. The percent of T effector cells found in each Tph cluster for each patient is shown. D) UMAP projection, split by patient, highlighting T cell clones with strictly more than 3 copies across the dataset (expanded clones). A clone is defined by its paired TCRα and TCRβ chain.
Single-cell RNA sequencing of SF CD4+ T cells reveal clonally expanded cells with features of Tph cells in ANA+ oligo JIA. Sorted Tregs (CD4+CD25+CD127lo) and Teffs (CD4+CD25-) from the SF of 2 oligo JIA patients were studied with 10X. A) Uniform manifold approximation and projection (UMAP) of global dataset (both subjects, 6190 cells), color-coded by cluster. Clusters 6 & 7 contain Tph cells. B) UMAP of global dataset, showing gene expression levels of key Tph cell markers. C) UMAP of dataset, split by patient. The percent of T effector cells found in each Tph cluster for each patient is shown. D) UMAP projection, split by patient, highlighting T cell clones with strictly more than 3 copies across the dataset (expanded clones). A clone is defined by its paired TCRα and TCRβ chain.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Jule A, Taylor M, Hoyt K, Wei K, Gutierrez-Arcelus M, Case S, Chandler M, Chang M, Cohen E, Dedeoglu F, Halyabar O, Hausmann J, Hazen M, Janssen E, Lo J, Lo M, Meidan E, Roberts J, Son M, Sundel R, Lee P, Chatila T, Nigrovic P, Rao D, Henderson L. Expanded B Cell-Helper T Cells in ANA+ Oligoarticular Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/expanded-b-cell-helper-t-cells-in-ana-oligoarticular-juvenile-idiopathic-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/expanded-b-cell-helper-t-cells-in-ana-oligoarticular-juvenile-idiopathic-arthritis/
