Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: To better understand the complex relationships between treatment and pain and physical function (PF) outcomes, we investigated a set of mediation models of osteoarthritis (OA) patients’ responses to tanezumab, an antibody against nerve growth factor that is in development for the treatment of OA.
Methods: Data came from two randomized clinical trials of tanezumab (Study 1: NCT02697773, JAMA. 2019;322:37-48 and Study 2: NCT02709486, Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;79:800-810); in both trials tanezumab provided greater pain relief and improvements in PF than placebo in patients with OA (all patients satisfied the American College of Rheumatology criteria for OA). A set of mediation models was used to explore the interrelationships among treatment, PF as measured by the Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC*) PF scores, and pain (WOMAC Pain scores) as a mediator of the effect of treatment on PF: (a) cross-sectional mediation models, (b) longitudinal mediation models, and (c) pseudo steady-state longitudinal mediation models. The cross-sectional mediation models include the following variables: treatment (tanezumab vs placebo), pain and PF scores (models were assessed separately at weeks 2, 4, 8, 12, 16, or 24). The longitudinal mediation models estimate relationships using data from all weeks simultaneously and include treatment, pain and PF scores at weeks 2, 4, 8, 12, 16, and 24. The longitudinal steady-state mediation model also uses all available data at weeks 2, 4, 8, 12, 16, and 24 with the assumption that relationships among variables in the model are the same at all time points.
*© 1996 Nicholas Bellamy. WOMAC® is a registered trademark of Nicholas Bellamy (CDN, EU, USA).
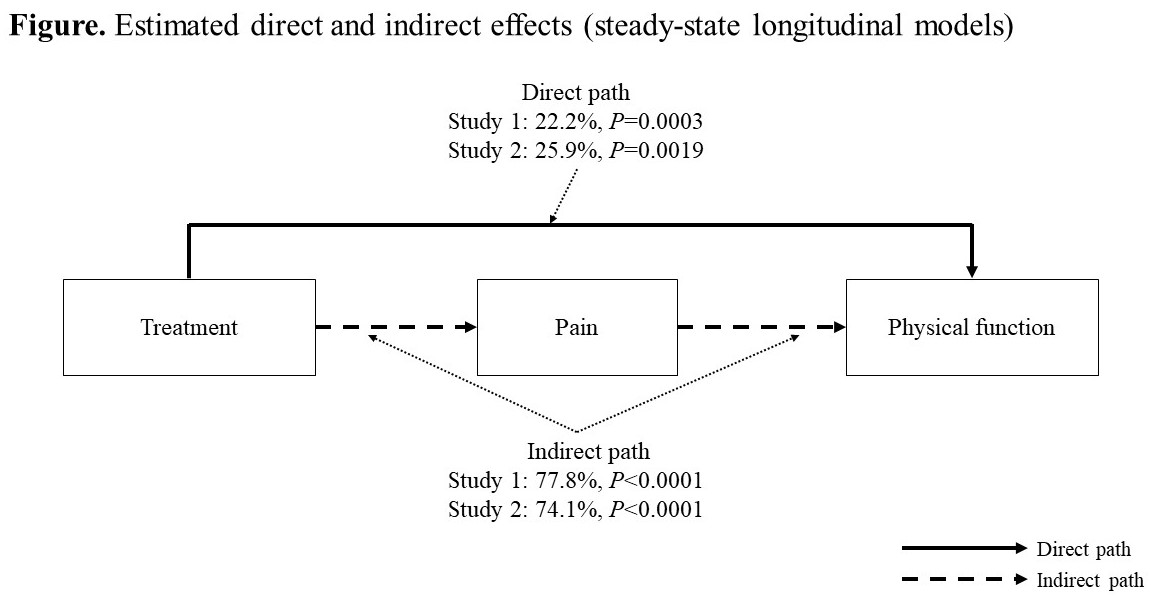
Results: The results of the cross-sectional and longitudinal mediation models showed that the indirect effect of treatment through pain on PF was stable across time (cross-sectional: 78.8–95.1%, all P< 0.0001; longitudinal: 70.5–86.6%, all P< 0.0001), indicating that a pseudo steady-state model is appropriate. The results of the longitudinal steady-state mediation models showed that the indirect effect of the treatment on PF was 77.8% in Study 1 and 74.1% in Study 2 (P< 0.0001, respectively), while the direct effect of the treatment on PF was 22.2% for Study 1 (P=0.0003) and 25.9% for Study 2 (P=0.0019) (Figure).
Conclusion: At least 75% of the treatment effect of tanezumab on physical functioning can be explained by the improvements in pain. However, tanezumab has an additional effect on physical functioning (approximately 25%), which is independent of improvements in pain. Research is needed to explain this effect and evaluate additional mediators (e.g., sleep, fatigue, method variance) that may contribute to the observed direct effect.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Abraham L, Dworkin R, Turk D, Markman J, Williams D, Bushmakin A, Hall J, Semel D, Cappelleri J, Yang R. Examining the Relationships Between Treatment and Pain and Physical Function Outcomes in Patients with Osteoarthritis: A Mediation Modeling Approach [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/examining-the-relationships-between-treatment-and-pain-and-physical-function-outcomes-in-patients-with-osteoarthritis-a-mediation-modeling-approach/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/examining-the-relationships-between-treatment-and-pain-and-physical-function-outcomes-in-patients-with-osteoarthritis-a-mediation-modeling-approach/