Session Information
Date: Monday, November 14, 2022
Title: Systemic Sclerosis and Related Disorders – Clinical Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Scleroderma (SSc) is a complex multisystem autoimmune disease, characterised by vasculopathy and fibrosis of skin and organs. Involvement of the cardiovascular system occurs frequently and is associated with significant morbidity and mortality. Pulmonary hypertension (PH) may result from a number of causes in SSc, including pulmonary vasculopathy or as a consequence of interstitial lung disease (ILD) or left heart disease (LHD).
This study sought to evaluate the distribution of cardiopulmonary haemodynamic parameters on annual transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) indicative of possible PH, particularly right ventricular systolic pressure (RVSP), and their prognostic associations in a cohort of SSc patients undergoing TTE and respiratory function tests (RFT).
Methods: Consecutive SSc patients, defined according to the ACR/EULAR criteria, who were enrolled in the Australian Scleroderma Cohort Study (ASCS) were included. The ASCS is a multicentre registry which prospectively records SSc disease data annually. Determination of the median and quintile distributions of RVSP was undertaken in the whole cohort and then in those without PH. PH was defined as those with right heart catheter (RHC) confirmed pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), or those with moderate to severe ILD, or TTE evidence of LHD. Kaplan-Meier (KM) survival curves were used to estimate survival in patients by RVSP quintile from time of most recent TTE to all-cause mortality in the whole cohort and in those without PH.
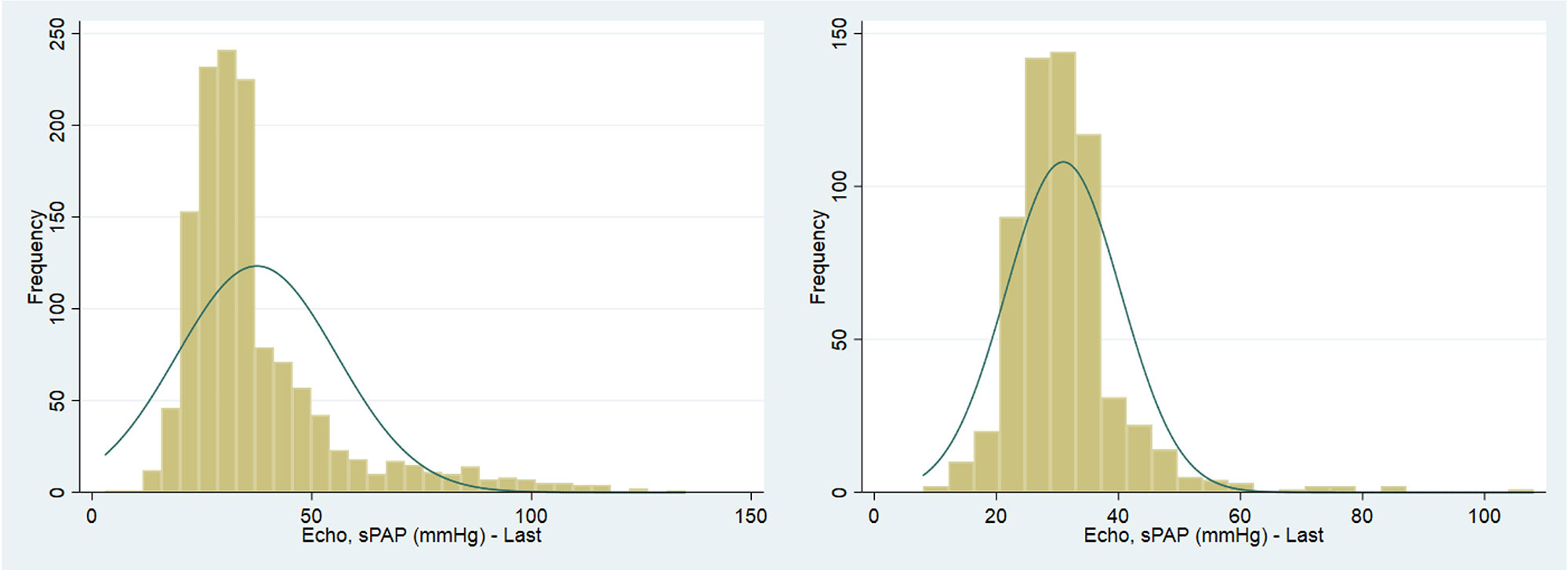
Results: The cohort consisted of 1,829 SSc patients with a mean age at SSc disease onset of 46.5 years (SD 14.3), the majority of whom had limited SSc (1,305, 74.1%). Moderate to severe ILD was present in (216, 11.8%) and PAH in (188, 10.3%). The median RVSP for the whole SSc cohort was 32.0mmHg (IQR 26.0 – 42.0), Figure 1a. In SSc patients without PH (917, 50.14%), the median RVSP was 30.0mmHg (IQR 26.0 – 34.9), Figure 1b. Those without PH were significantly younger 59.5 years (50.0 – 68.4) compared to those with PH at 67.4 years (59.5 – 75.0), p < 0.001.
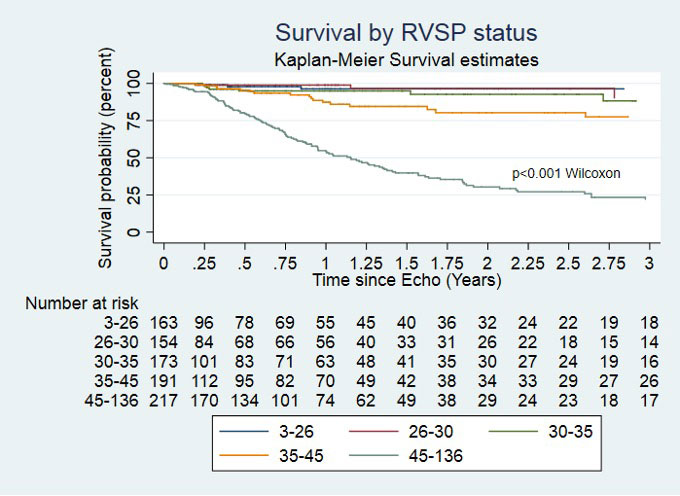
KM curve analysis of the whole cohort showed worse survival among patients with RVSP ≥ 40mmHg compared to < 40mmHg from as early as 1-year; 51.2% compared to 89.17% respectively, p < 0.001. At 1-year, there was statistically significant difference in survival for those with RVSP 30 – 35mmHg compared to RVSP 35 – 45mmHg with 89.20% alive compared to 78.29%, p < 0.001, Figure 2a.
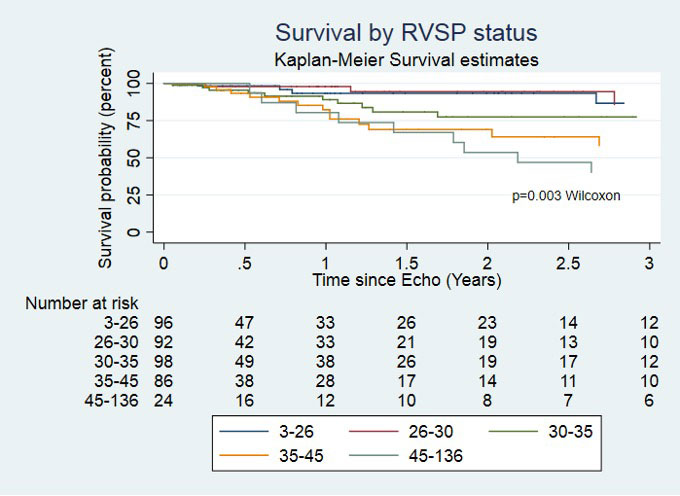
K-M survival curve analysis by RVSP quintiles of those without PH showed survival at 1-year for those with RVSP 30 – 35mmHg was 89.20%, Figure 2b.
Conclusion: The median RVSP in a cohort of SSc patients excluding those with PH is higher than the general Australian population median (RVSP 30.0 compared to 25.0 mmHg (IQR 20.33 to 31.36 mmHg)).(1) Concerningly, those with RVSP of 30 – 35mmHg, in the absence of PH, had increased risk for mortality. Further data are required to better understand this phenomenon and consideration given to further investigation for underlying SSc related vasculopathy at a lower threshold of RVSP than one used to define PH.
1. Strange G, et al. Threshold of Pulmonary Hypertension Associated With Increased Mortality. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;73(21):2660-72.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Brown Z, Hansen D, Stevens W, Ross L, Ferdowsi N, Proudman S, Walker J, Sahhar J, Ngian G, Host L, Major G, Nikpour M, Morrisroe K. Evaluation of the Distribution of Haemodynamic Parameters and Prognostic Impact in a Cohort of Patients with Systemic Sclerosis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evaluation-of-the-distribution-of-haemodynamic-parameters-and-prognostic-impact-in-a-cohort-of-patients-with-systemic-sclerosis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evaluation-of-the-distribution-of-haemodynamic-parameters-and-prognostic-impact-in-a-cohort-of-patients-with-systemic-sclerosis/