Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: LN occurrs in 50 to 75 percent of SLE patients and is associated with a significant morbimortality. LN presents distinct severity, with frequent flares when not adequately treated. Clinical and laboratory test cannot predict histological findings in the most of the LN cases and renal biopsy should be done whenever possible. The need to research biomarkers in LN is because they can non-invasively determine the extent and activity of renal impairment. The principal objectives were to evaluate the histopathologic renal response in the rebiopsy after induction therapy and to correlate with a clinical renal response. The secondary objectives were to correlate serum and urinary biomarkers with creatinine, 24-hour proteinuria, histological class, activity and chronicity index.
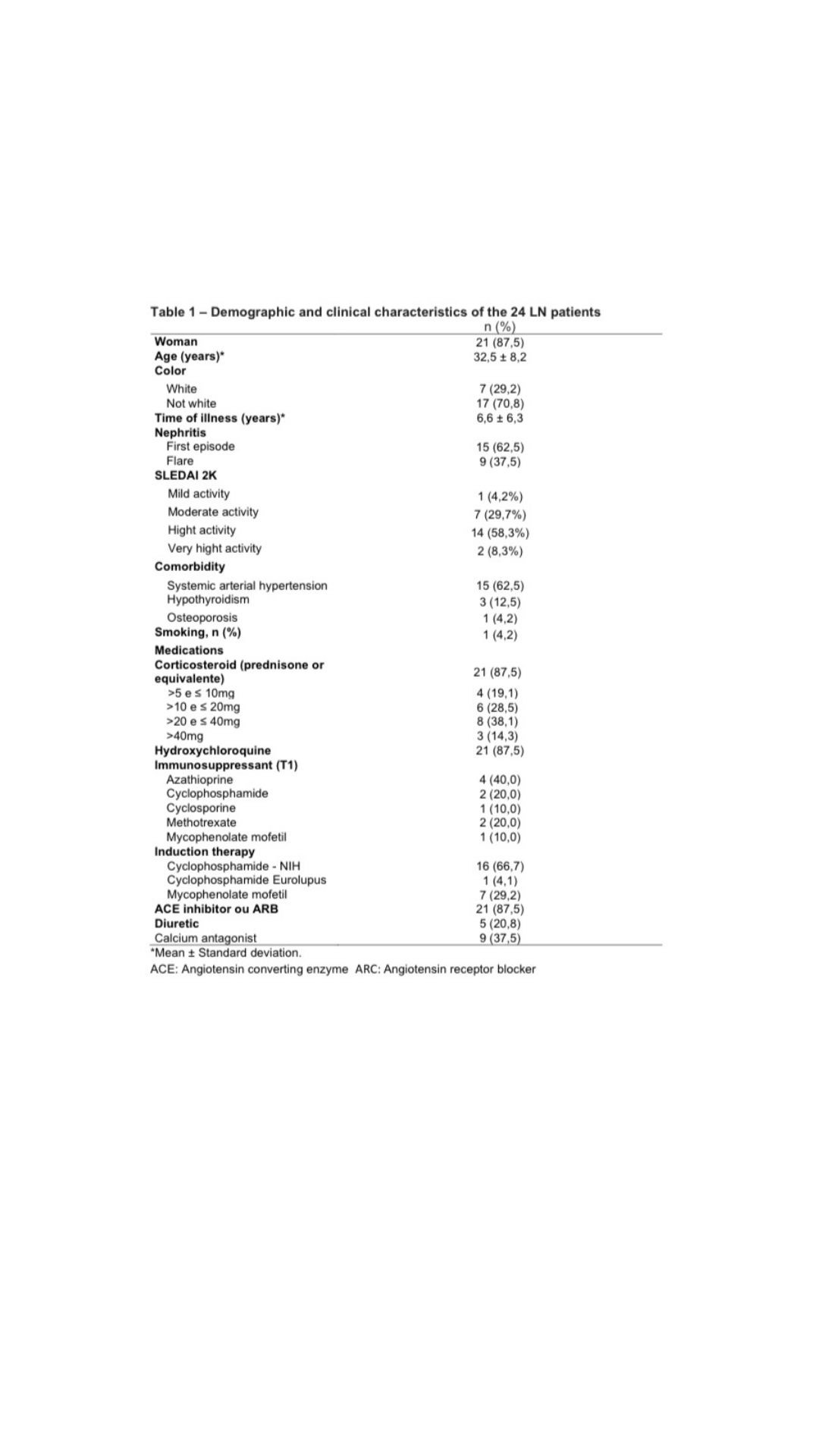
Methods: Open, longitudinal, multicenter study, including LN patients confirmed by renal biopsy (classes III, IV, V, III+V or IV+V). Two kidney biopsies were performed, the first for the diagnosis (T1) and the second after the end of induction therapy (T2). The histopathological study was carried out using standard techniques (optical microscopy and immunofluorescence). Laboratory evaluations included urinary sediment examination, serum creatinine and urea, 24-hour proteinuria, complement levels (C3 and C4), anti-DNAds, anti-nucleosome, anticardiolipin IgM/IgG, and other serum (anti-C1q, MCP-1, NGAL and KIM-1) and urine biomarkers (TWEAK, anti-IL-16, ALCAM, MCP-1, NGAL, KIM-1, adiponectin, hemopexin and ceruloplasmin). These biomarkers were performed at T1 and T2 and correlated with renal response data and activity and chronicity indices.
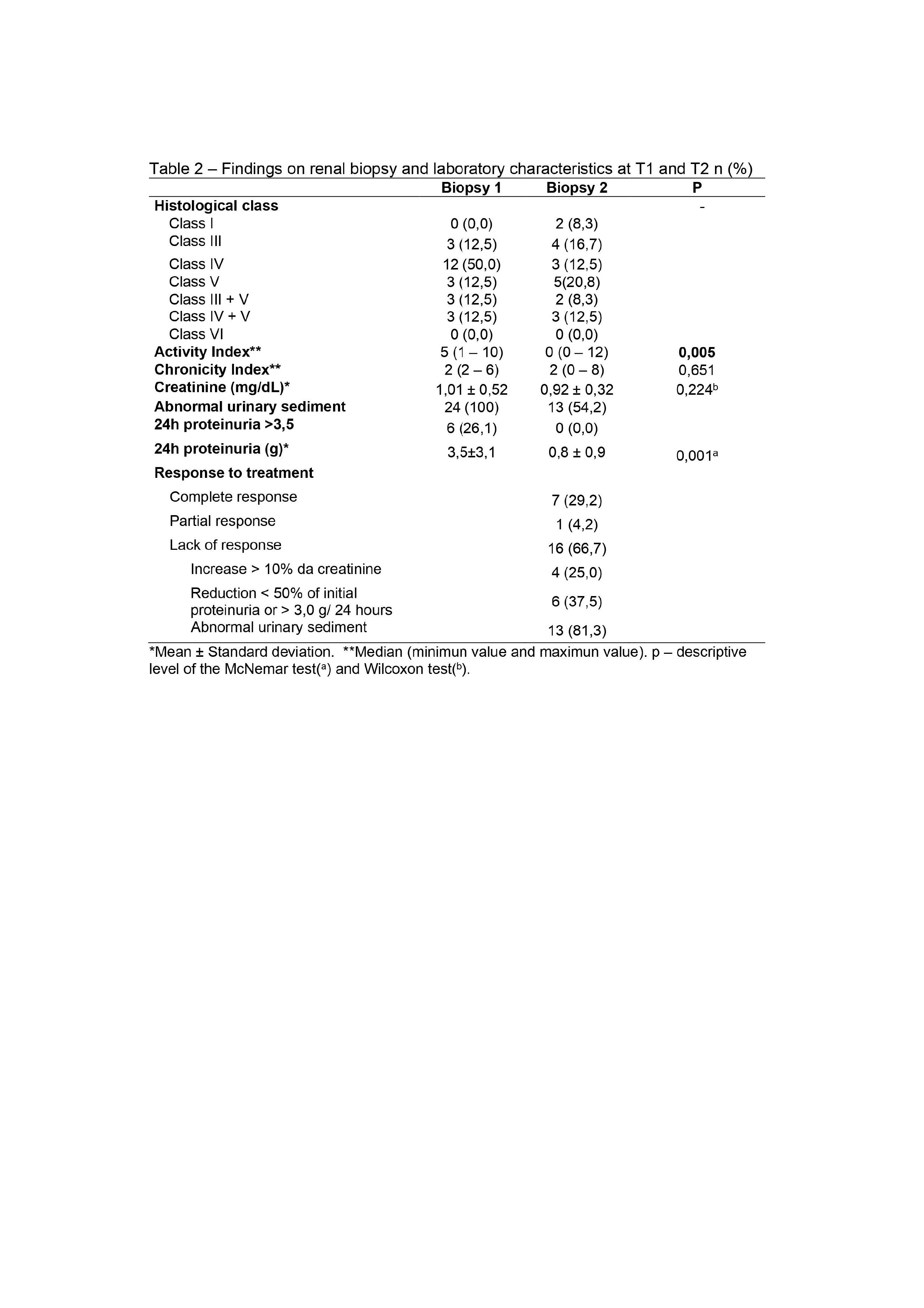
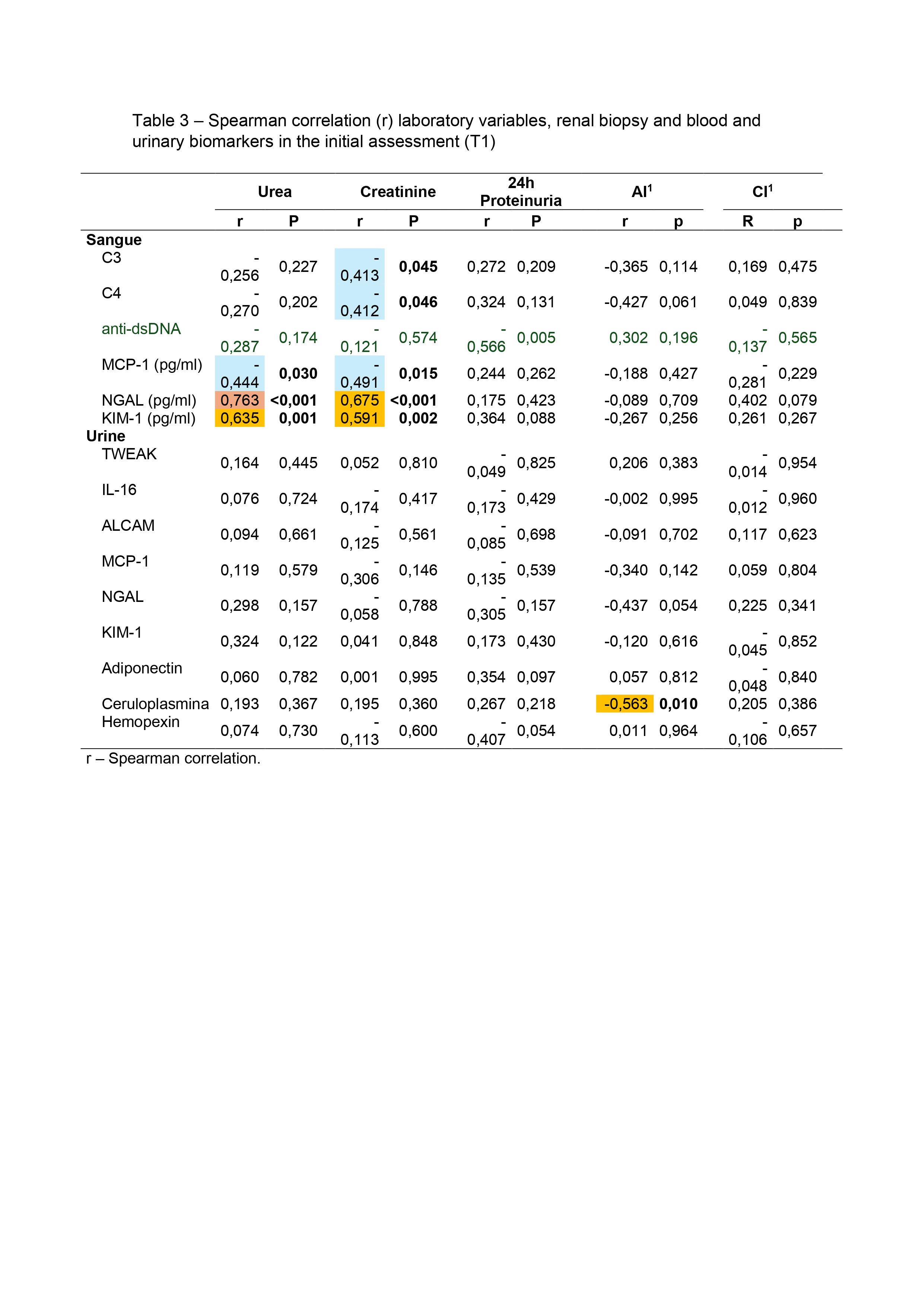
Results: Twenty four patients were included from the three participating centers, with a mean age of 32.5±8.2 years, 87.5% were women and 70,8% non-white. At the end of induction therapy, 29.2% of patients had a complete renal response, 4.2% achieved partial response and 66,7% were classified as non-response. NGAL serum [(r 0.763 x Urea)/(r 0.675 x Creatinine)] p < 0.001; and KIM-1 serum [(r 0.635 x Urea – p < 0.001)/(r 0.591 x Creatinine – p < 0.002) showed a statistically significant correlation with urea and creatinine. Higher level of TWEAK in urine (13.8 ± 5.7 p=0.043) was found in patients who remained with altered hematuria at T2. Distinct distributions of anti-dsDNA (p=0.018) and anti-nucleosome (p=0.040) by variation in proteinuria between T1 and T2 were found, where patients with positive anti-dsDNA and anti-nucleosomes at T1show less variation in the decrease in proteinuria at T2.
Conclusion: There was discordance between clinical and histological response in our study. Around 60% of patients achieved a histological response, however, without a corresponding clinical response; only one patient achieved clinical response and remained active in renal tissue. To date, we have not been able to replace the traditional biomarkers for evaluating lupus nephritis, such as 24-hour proteinuria, abnormalities in urine analysis (hematuria), elevation of serum creatinine, dosage of complements, anti-dsDNA and anti-nucleosomes with new biomarkers, although serum NGAL and KIM-1 have shown correlation with urea and creatinine and urinaryTWEAK and NGAL with hematuria.
Disclosures: D. Egypto: AbbVie/Abbott, 6, AstraZeneca, 6, GlaxoSmithKlein(GSK), 6, Janssen, 1, 6; E. Reis Neto: AbbVie/Abbott, 12, Clinical research, AstraZeneca, 2, 5, 6, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), 12, Clinical research, GlaxoSmithKlein(GSK), 2, 6, Novartis, 1, 6; G. Carlesso: None; L. Andrade: None; L. Moura: None; D. Calderaro: AstraZeneca, 6, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), 5, GlaxoSmithKlein(GSK), 6, Roche, 5; E. Sato: None.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Egypto D, Reis Neto E, Carlesso G, Andrade L, Moura L, Calderaro D, Sato E. Evaluation of Clinical, Histological and Biomarker Response After Induction Treatment of Lupus Nephritis (LN) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evaluation-of-clinical-histological-and-biomarker-response-after-induction-treatment-of-lupus-nephritis-ln/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evaluation-of-clinical-histological-and-biomarker-response-after-induction-treatment-of-lupus-nephritis-ln/