Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Helper T cells (Th) are key players in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Th17 and Th17.1 have a prominent function in the early phase of inflammation, while Th1 characterize a well-established disease (Kotake S, 2017). Th22, characterized by synthesis of IL-22 (and IL-13 and TNF-α) but not IL-17A or IFN-γ, are still. In RA animal model, IL-22 hampered Th1 plasticity, favoring Th17 maintenance and survival (Justa S, 2014). Th9 are involved in RA synovitis, IL-9 being an enhancer of Th17 cells differentiation in the synovium (Chowdhury, 2018). Innate lymphoid cells (ILC) were recently described as critical in the perpetuation of immune responses during the autoimmune processes, being resident in the tissues and activating without the presence of antigen-specific cell receptors. The three major groups in the ILC family (1, 2, 3) mirror the canonical T helper subsets Th1, Th2, and Th17 (Wu X, 2020). Considering the crucial role played by the CD28 co-stimulation in the process of Th priming and its effect on inflammatory environment, we hypothesized that its blocker abatacept (ABA) might modulate the circulating levels of Th and ILC cells and their involvement in B-cell maturation and antigen-driven differentiation.
Methods: Sixteen bDMARDs-naïve RA patients [female/male=10/6; median (IQR) age=64 (54.3-67.6) years; disease duration=51 (30-108) months; 13/16 (81.3%) seropositive; C Reactive Protein (CRP)=6 (2.4-11.5) mg/L (normal value < 5 mg/L), CRP-28-joint Disease Activity Score (CRP-DAS28)=4 (3.3-4.4)] were enrolled before starting ABA. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells, obtained from the patients before the start of ABA therapy (T0) and after 12 months (T12), were extracellular stained and evaluated by flow cytometry (FACSCantoII, Beckton Dickinson). EULAR criteria were used to evaluate the treatment response [good and moderate responders (R), n=11 and non-responders (NR), n=5].
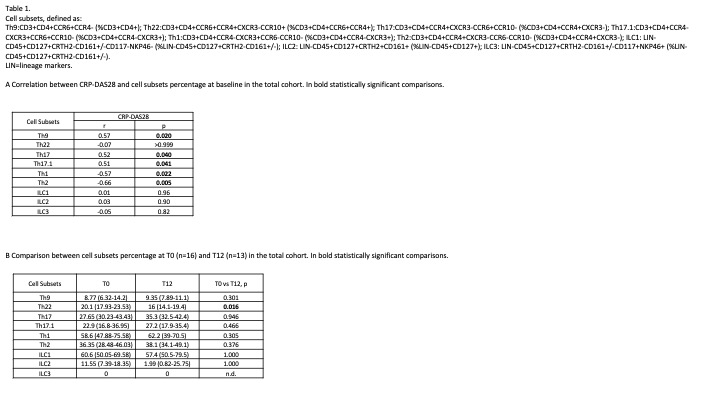
Results: Baseline CRP-DAS28 was differently correlated with various T helper cell subsets, but not with ILC (Table 1A). In the whole cohort, Th and ILC subpopulation levels did not significantly change between T0 and T12, except for Th22 levels (expressed as % of CD3+CD4+CCR6+CCR4+) which decreased [20.1 (17.93-23.53) vs 16 (14.1-19.4); p:0.016] (Table 1B), mainly in the R group [19 (17.75-20.5) vs 15.85 (13-17.45); p:0.004]. The same level of circulating subsets was found when comparing NR vs R patients at T0 and T12.
Conclusion: All the circulating Th cells expressing CCR6, which is the main chemokine receptor of Th17 and Th17-related cells, were positively correlated with the disease activity at baseline, except for Th22, a distinct Th lineage that can display plasticity towards Th1 and Th2 lineages under special circumstances, showing regulatory properties and participating to the early RA pathogenesis. The decrease of Th22 after CD28 blockade may suggest the potential role of ABA in targeting one of the earliest phases of the disease pathophysiology.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Semeraro P, Angeli F, Caproli A, Franceschini F, Airò P, Piantoni S. Evaluation of Circulating Levels of Helper T and Innate Lymphoid Cells Subsets in a Cohort of bDMARDs-naïve Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Treated with Abatacept [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evaluation-of-circulating-levels-of-helper-t-and-innate-lymphoid-cells-subsets-in-a-cohort-of-bdmards-naive-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-treated-with-abatacept/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evaluation-of-circulating-levels-of-helper-t-and-innate-lymphoid-cells-subsets-in-a-cohort-of-bdmards-naive-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-treated-with-abatacept/