Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 3:00PM-4:30PM
Background/Purpose: Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is common pathogen responsible for infectious mononucleosis but also triggers hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH). This variation in the immune response to EBV is unexplained.
Methods: We recruited 352 children who presented to the emergency room with fever for ≥ 3 days. We performed immune profiling on 110 cases with confirmed viral infections using Olink proximity extension assay and flow cytometry. We compared the findings with cases of HLH (n=8), macrophage activation syndrome (MAS; n=18), Kawasaki disease (KD; n=20), and multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C; n=17).
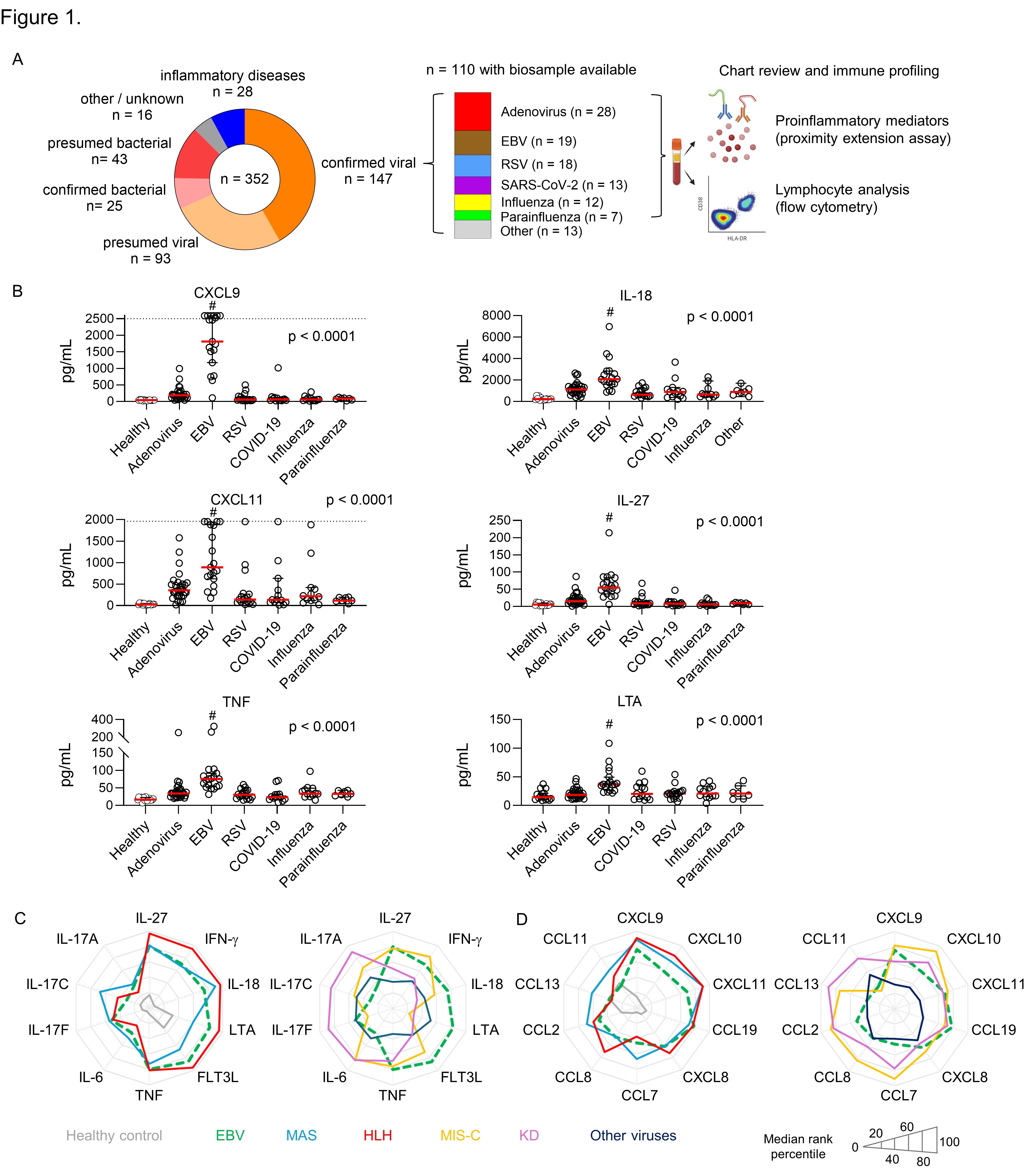
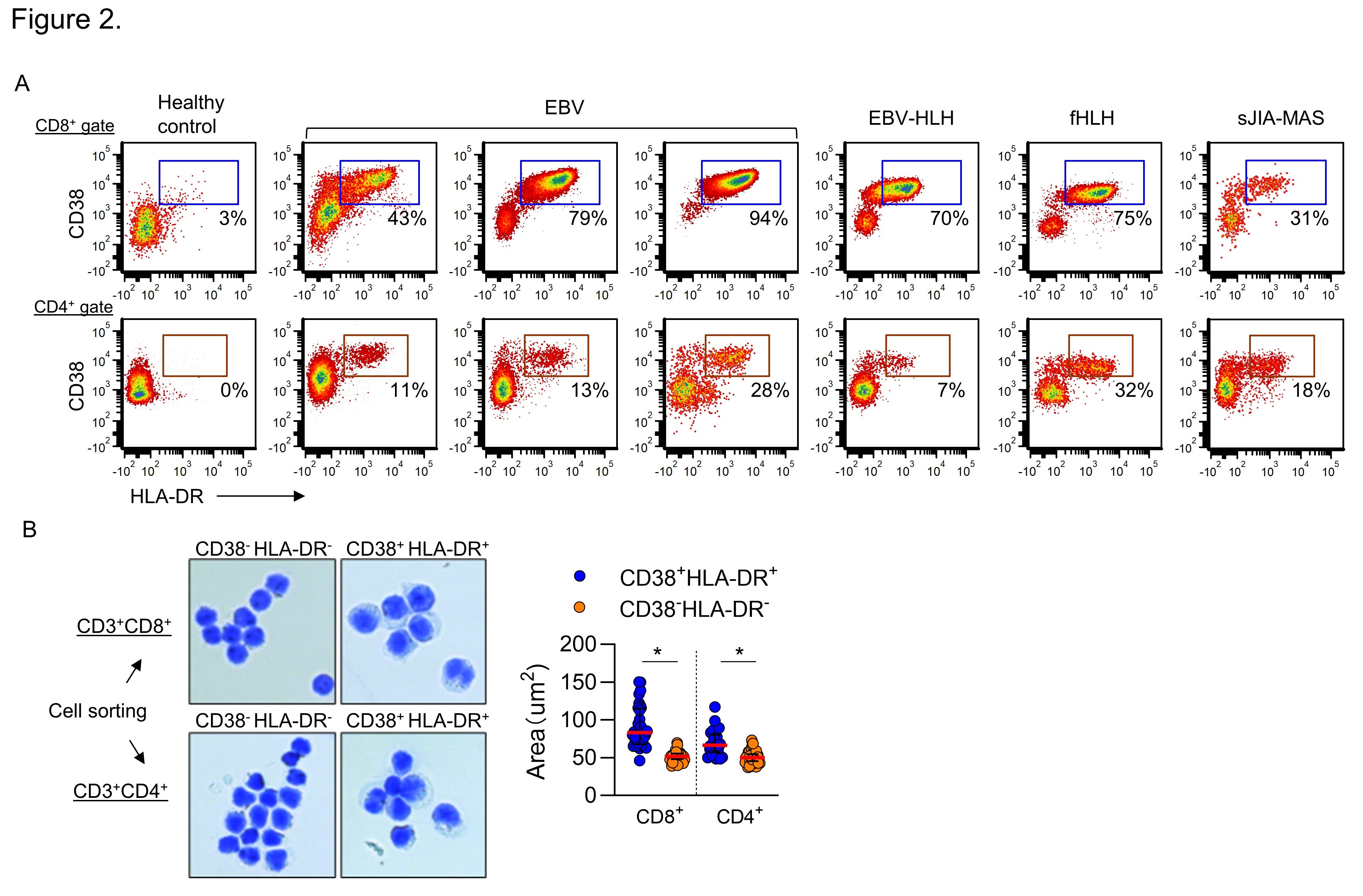
Results: We studied 110 otherwise healthy children with confirmed viral infections, including EBV, adenovirus, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), influenza virus, parainfluenza virus, and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV; Figure 1A). Using Olink proximity assay to profile 45 proinflammatory mediators, we found that acute EBV infection uniquely triggered high levels of multiple cytokines (IL-18, IL-27, tumor necrosis factor, and lymphotoxin alpha) and IFN-γ-induced chemokines (CXCL9 and CXCL11; Figure 1B). The pattern of cytokine and chemokine production are similar to the cytokine storm associated with HLH / MAS, but less consistent with the findings in KD and MIS-C (Figure 1C-D). Flow cytometry analysis revealed that CD38+HLA-DR+ T lymphocytes, which are pathogenic cells responsible for IFN-γ production in HLH / MAS, are vastly expanded in patients with acute EBV infection (Figure 2A), but not other viral infections. Cell sorting and morphology analysis identified CD38+HLA-DR+ T cells as atypical lymphocytes that are classically associated with EBV infection (Figure 2B).
Conclusion: These findings place acute EBV infection in the cytokine storm spectrum and inform both the unique clinical presentation of this disease and its connection to HLH.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Brodeur K, Liu M, Weng R, Hsu E, Henderson L, Dedeoglu F, Newburger J, Nigrovic P, Son M, Lee P. Epstein-Barr Virus Infection Triggers Hyperinflammation and Cytokine Storm in Healthy Children [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/epstein-barr-virus-infection-triggers-hyperinflammation-and-cytokine-storm-in-healthy-children/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/epstein-barr-virus-infection-triggers-hyperinflammation-and-cytokine-storm-in-healthy-children/