Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 28, 2025
Title: (1830–1854) Systemic Lupus Erythematosus – Etiology and Pathogenesis Poster
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: B cells play an essential role in lupus nephritis (LN) pathogenesis. However, abnormalities in specific subtypes like age-associated B cells (ABCs) and double negative (DN) cells have been associated with this clinical manifestation. These cell populations share an increased response to intracytoplasmic TLR (iTLR) stimulation, leading to increased autoantibody production. Besides, diverse cytokines/chemokines have shown to play a role in LN. Nonetheless, the association between B cell subtype-specific expression of iTLRs and the serum levels of diverse cytokines/chemokines with lupus nephritis has not been fully addressed, which is the aim of the present study.
Methods: We carried a cross-sectional study including 54 lupus patients that fulfilled the 2019 EULAR/ACR classification criteria for SLE. 28 with LN according to laboratory and/or histopathological findings and 26 with extrarenal activity (NLN) with SLEDAI-2K ≥6. From each subject we collected clinical, and laboratory data related to disease activity and isolated PBMCs for flow cytometry analysis of TLR7 and TLR9 expression (percentage and absolute number of positive cells and median fluorescence intensity (MFI)) in these B cells subtypes (CD19+): transitional (CD27- CD24hi CD38hi), naïve (CD27- CD24- IgD+), classical (CD27+) and non-classical memory (CD27- CD24+ CD38-/lo), ABCs (CD21- CD11c+ T-bet+), DN (CD24+ CD27- IgD-) and plasmablasts (CD27hi CD38hi). Additionally, serum cytokines were measured by luminometry in a multiplexed assay , including: IL-1α, IL-1β, IL-1ra, IL-2, IL-3, IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-7, IL-8, IL-10, IL-12, IL-12 (p70), IL-13, IL-15, IL-17ª, IP-10, MCP-1, MIP-1α, MIP-1β, TNF-α, TNF-β, VEGF and eotaxin. Demographic variables were compared with the Mann-Whitney U test, potential confounder variables were assessed with the G test and associations with mixed logistic regression.
Results: Demographic, laboratory and treatment data are shown in Table 1. Mycophenolate and azathioprine were the only confounding variables. Therefore, we analysed the association of immunological variables adjusted by treatment. As shown in Table 2, a higher expression of MyD88 was constantly associated with LN, from early stages like transitional and naïve B cells to late ones like memory and DN cells. We found that TLR7 associates with LN when expressed in naïve and DN1 cells, and only through transitional cells, TLR9 is associated with LN. All significant variables competed to create a multivariate predictive model. One was selected according to Akaike information criteria, which resulted from the mixed effect of TLR9 MFI in transitional cells (OR 1.006, CI 95% 1.001-1.01, p 0.013) and serum eotaxin (OR 1.018, CI 95% 1.003-1.03, p 0.017), Figure 1.
Conclusion: Our data shows that TLR7/9 and MyD88 expression in B cells and their relation with LN are subtype-specific. However, further studies are needed to delimitate the functional effects of TLRs signaling by cell subset and their relationship to renal affection. As for eotaxin, its potential as a LN biomarker in serum and urine has been previously reported. Nonetheless, the source and specific cell effect induced by this chemokine in LN context remains to be explored.
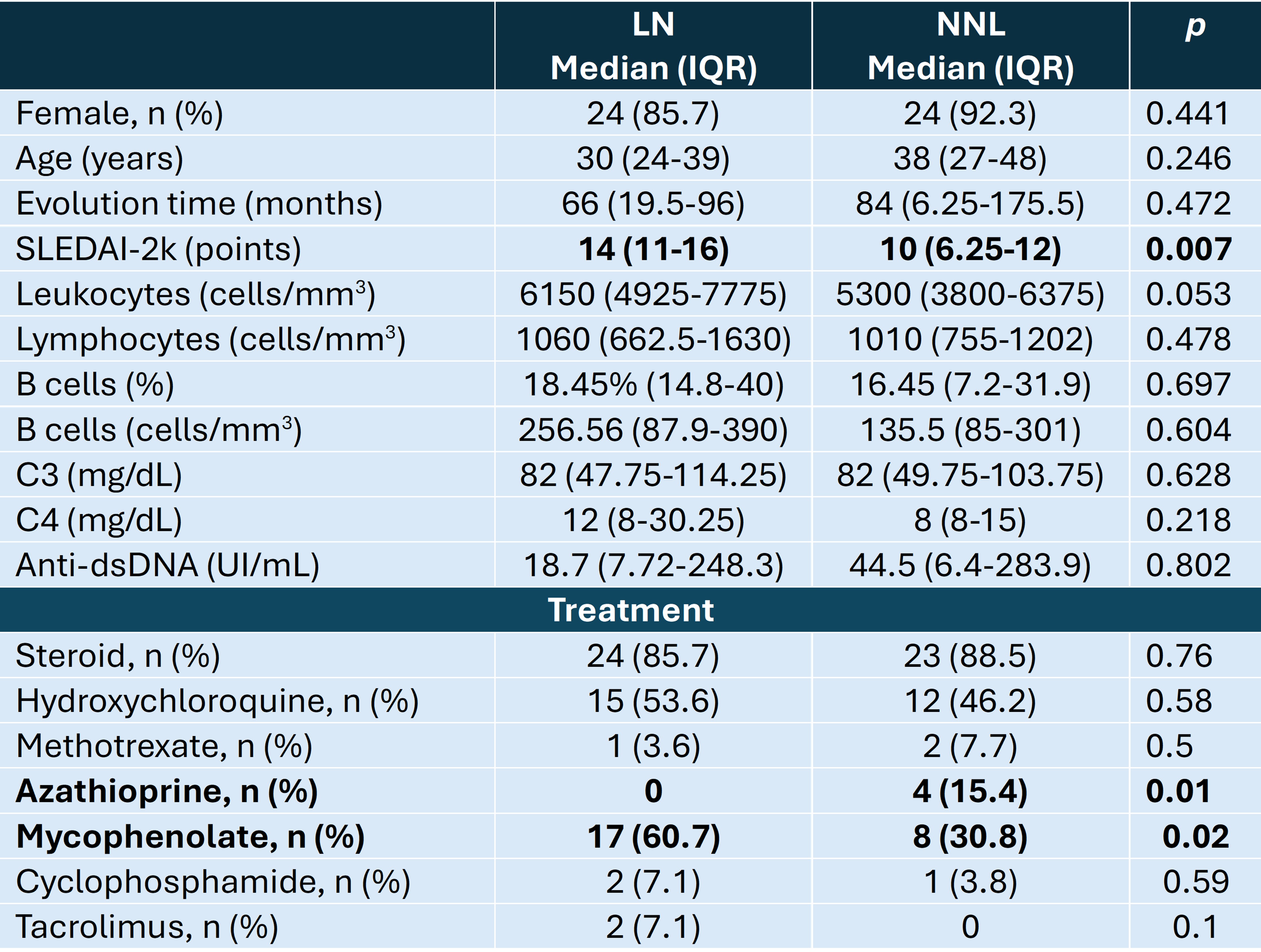 Table 1. Demographic, activity and treatment data by study group.
Table 1. Demographic, activity and treatment data by study group.
LN, lupus nephritis group ; NNL, active non-lupus nephritis ; IQR, interquartile range.
.jpg) Table 2. TLR7, 9 and MyD88 expression by B cell subtype associated with LN.
Table 2. TLR7, 9 and MyD88 expression by B cell subtype associated with LN.
Results obtained by mixed logistic regression adjusted by treatment.
OR, Odd ratio; CI, confidence interval; MFI, median fluorescence intensity; AU, arbitrary units.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Balderas Miranda J, Reyna Juárez Y, Alcalá-Carmona B, Mejía Domínguez N, Ostos Prado M, Maravillas-Montero J, Cassiano-Quezada F, Juárez Vega G, santana k, Torres Ruiz J, Gómez-Martín D. Emerging Role of B Cell Subtype-Specific Intracytoplasmic Toll-Like Receptor Expression and Serum Eotaxin as Biomarkers in Lupus Nephritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/emerging-role-of-b-cell-subtype-specific-intracytoplasmic-toll-like-receptor-expression-and-serum-eotaxin-as-biomarkers-in-lupus-nephritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/emerging-role-of-b-cell-subtype-specific-intracytoplasmic-toll-like-receptor-expression-and-serum-eotaxin-as-biomarkers-in-lupus-nephritis/

.jpg)