Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: RA – Treatment Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: This study aims to investigate the safety and efficacy of butyrate capsules in treating patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and elucidate the underlying mechanisms.
Methods: A 12-week single-arm trial with 30 RA patients collected clinical data, blood for flow cytometry and RNA sequencing, serum for ELISA to measure intestinal injury markers, and fecal samples for metagenomic sequencing and metabolite analysis using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry.
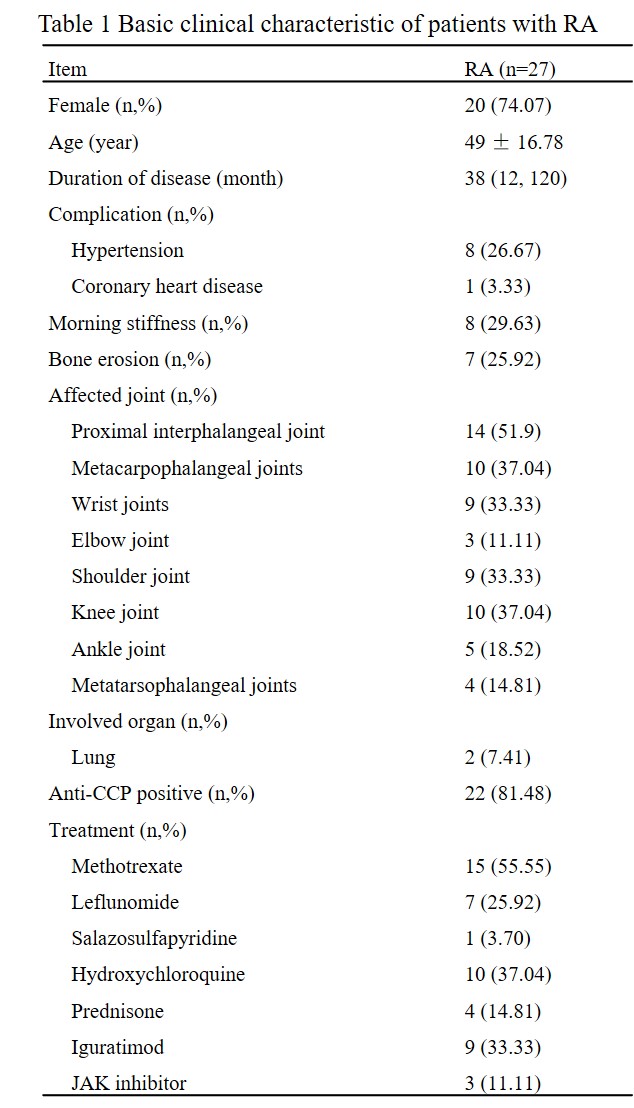
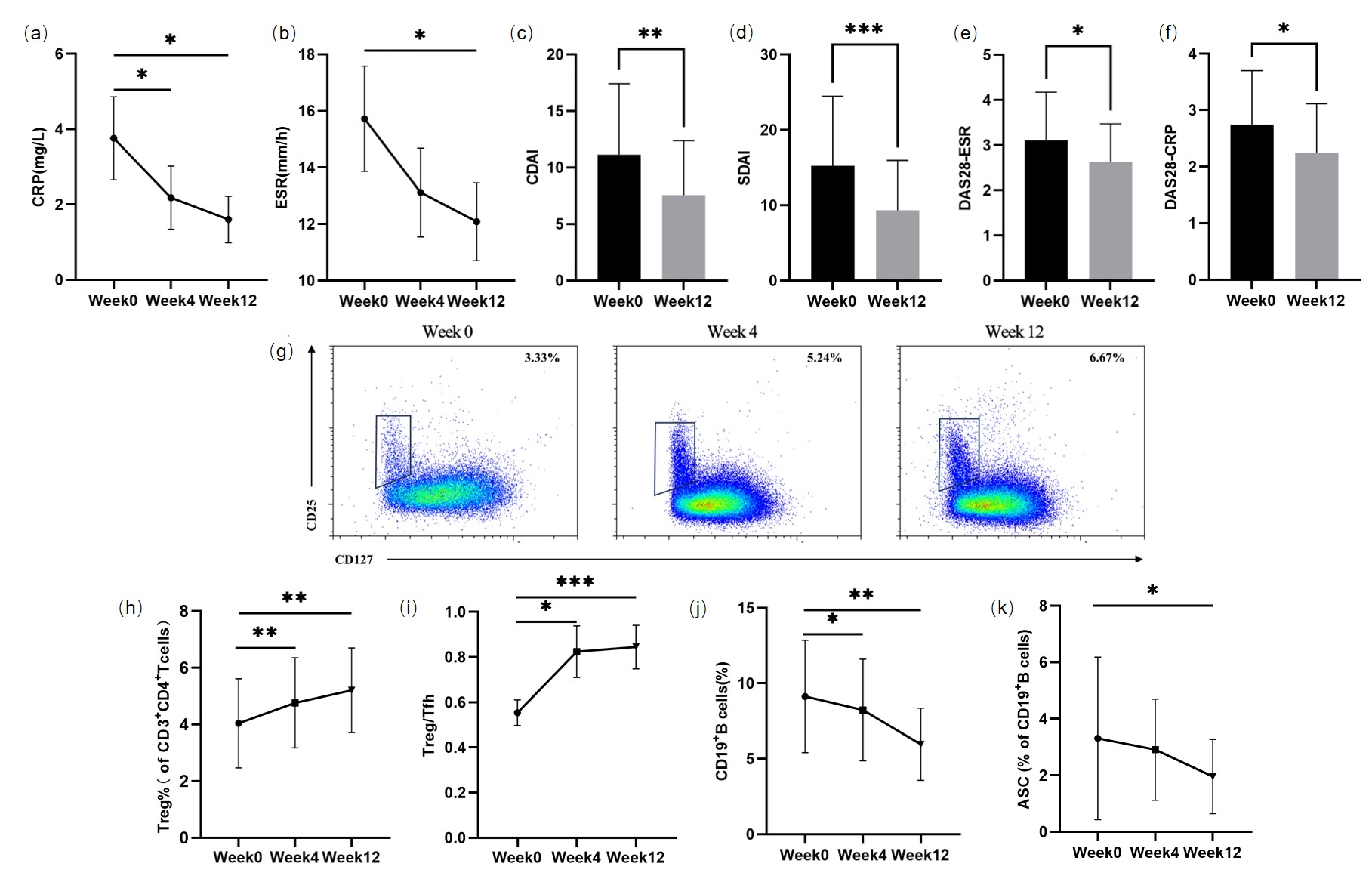
Results: No adverse events were observed in RA patients after taking butyrate. Compared to pre-treatment, the CRP and ESR levels significantly decreased after 12 weeks of treatment [0.25(0.25,1.37) vs 0.6(0.25,6.28) mg/L, P=0.040; 11(7,14) vs 17(7,23) mm/h], P=0.026). The CDAI, SDAI, DAS28-ESR and DAS28-CRP of RA patients also decreased significantly (P=0.002, P<0.001, P=0.027, P=0.023, respectively). LBP levels in RA patients decreased significantly (2.53±2.17 vs 6.01±2.10μg/mL, P<0.001), and sCD14 levels also showed a downward trend (P=0.414). Compared to pre-treatment (4.03±1.57%), Treg cells(5.28±1.52%)increased significantly (P<0.001), as did in Treg/Tfh (P=0.001). The proportion of CD19+B cells and antibody-secreting cells decreased significantly after treatment [5.96±2.39 vs 9.13±3.72%, P<0.001; 1.59(0.95,2.78) vs 2.54(1.21,4.63)%, P=0.031]. Significant differences in the mRNA profile of CD4+ T cells were observed before and after butyrate treatment, with NR4A3 and APOE (two Treg-related genes) significantly up-regulated (P=0.008; P=0.029). Post-treatment, alpha diversity of intestinal flora tended to increase (P >0.05). Serum butyrate levels (21.84±7.48 μM) were significantly higher after treatment compared to pre-treatment (15.38±4.68 μM, P=0.003), while fecal butyrate levels did not change significantly (P=0.631).
Conclusion: Butyrate capsules are safe and effective for RA, reducing disease activity and inflammation, and suggesting new dietary or microbial therapy options.
(a-b) Changes of inflammatory indexes (CRP, ESR, respectively) after butyrate capsule treatment. (a): CRP; (b): ESR. (c-f) Changes of disease activity (CDAI, SDAI, DAS28-ESR, DAS28-CRP, respectively) after butyrate capsule treatment. (c):CDAI; (d):SDAI; (e):DAS28-ESR; (f): DAS28-CRP. (g-h) Changes of the percentage of Treg cells after butyrate capsule treatment. (i) Changes of the ratio of Treg cells to Tfh after butyrate capsule treatment. (j-k) Changes of B cell subsets (CD19+B, ASC, respectively) after butyrate capsule treatment. (j): CD19+B; (k):ASC.
ASC: antibody-secreting plasma cell; CDAI: clinical disease activity index; CRP: C-reactive protein DAS28: disease activity score in 28 joints; ESR: erythrocyte sedimentation rate; SDAI: simplified disease activity index; Treg: regular T cell; Tfh: follicular helper T cell.
(a): Changes of mRNA profile of CD4+T cells after butyrate treatment. (b): Differential genes before and after treatment. Red represents up-regulated genes and green represents down-regulated genes.(c): Differential gene expression in different samples. (d): Changes in expression of differential genes associated with Treg (NR4A3, PLAU and APOE, respectively) before and after treatment. (e): Changes of short-chain fatty acids level in serum and fecal samples after treatment. APOE: apolipoprotein E; NR4A3: nuclear receptor subfamily 4 group A member 3; PLAU: plasminogen activator urokinase.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
He J, Wang N, Li Y, Wang R, Tan X, Zhufeng R, Han Y, Li H, Jin Y, Li Z. Efficacy, Safety and Mechanism of Butyrate in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-safety-and-mechanism-of-butyrate-in-the-treatment-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-ra/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-safety-and-mechanism-of-butyrate-in-the-treatment-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-ra/