Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 14, 2023
Title: Abstracts: Muscle Biology, Myositis & Myopathies – Basic & Clinical Science I
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:00PM-3:30PM
Background/Purpose: Antisynthetase syndrome (ASS) can be very severe affecting the lungs, the skin and the joints next to the muscles. ASS can take a refractory life-threatening course, necessitating the development of new treatment strategies. We recently reported the first case of successful rescue therapy of ASS with CD19-targeted CAR-T-cells [1]. Herein, we present efficacy and safety data for the first three patients with refractory ASS treated with autologous CD19 CAR-T-cells. The objective of this study was to test whether administration of CD19 CAR-T-cells is tolerable and effective in patients with severe refractory ASS.
Methods: Autologous CD19 CAR-T-cells were prepared and given as described previously [1,2,3]. All immunosuppressive treatments were stopped before CD19 CAR-T-cell administration. Tolerability was assessed by monitoring for Cytokine-Release Syndrome (CRS) and Immune-related effector Cell Neurotoxicity Syndrome (ICANS). Efficacy was assessed by CK levels, good response according 2016 ACR/EULAR total improvement score (TIS), imaging of muscles and lungs and successful cessation of all immunosuppressive treatments including glucocorticoids.
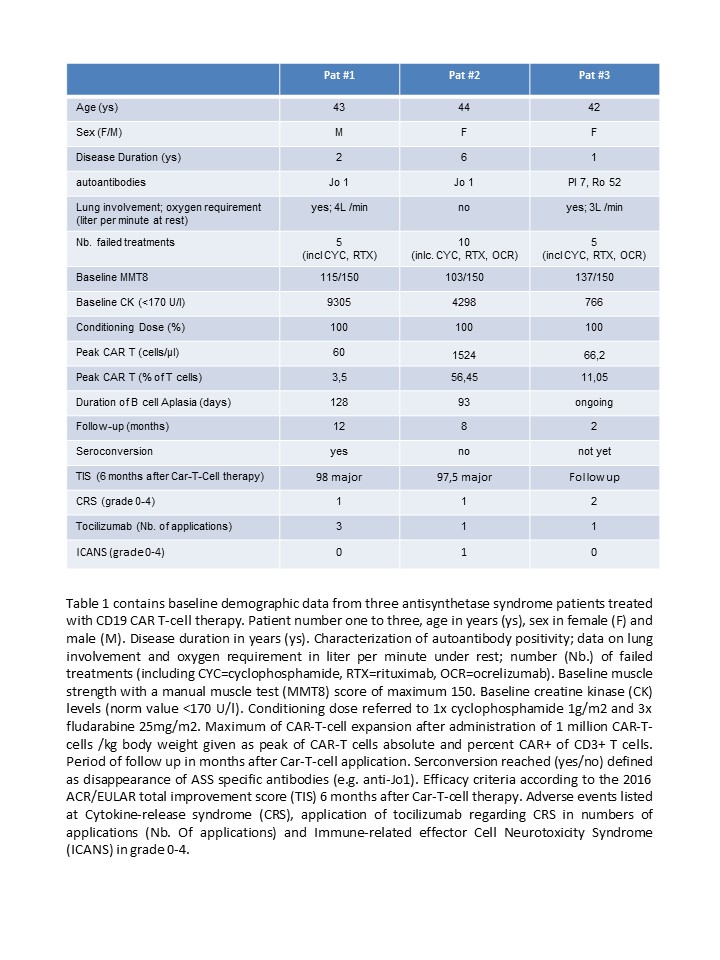
Results: Three ASS patients were treated with CD19 CAR-T-cells (table 1). All patients presented with active myositis and elevated CK levels. Patient 1 showed involvement of the muscles, skin and lungs, patient 2 showed involvement of muscles, skin, joints and lungs, patient 3 showed involvement of muscles and lungs. All patients did not respond to a minimum of 5 different immunosuppressive treatments (table 1). CAR-T-cell treatment was well-tolerated. Mild CRS (grade I) was observed in the first two patients. Patient 3 showed signs off increased O2 requirement (temporarily 10l/min by mask), chills and fever (39.0°C) defined as CRS grade II. All patients were treated with tocilizumab and CRS resolved quickly. Patient 2 had signs of mild self-limited ICANS (grade I discrete ataxia for a few days) two weeks after CAR-T treatment. Expansion of CAR-T-cells paralleled with the complete depletion of circulating B cells. The first two patients experienced normalization of CK levels (patient 1: CK+150 days: 70 U/l, patient 2: CK+150 days: 99 U/l), major clinical improvement according to the 2016 TIS and could stop all immunosuppressive therapy. Follow-up CT scans of the lung done in patient 1 showed resolution of alveolar inflammation. Follow-up MRI of patient 1 and 2 revealed abrogation of inflammatory changes in the thigh muscles and hamstrings. At the latest follow up (365days and 150days) both patients were in drug-free remission, while patient 3 awaits follow up assessment.
Conclusion: Taken together, these data suggest that CD19 CAR-T-cell therapy provides a possibility to intercept with severe ASS leading to drug-free remission and resolution of muscle and lung inflammation.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Taubmann J, Knitza J, Müller F, Boeltz S, Voelkl S, Aigner M, Kleyer A, Minnopoulou I, Gary R, kretschmann S, Mackensen A, Schett G. Efficacy and Safety of Car-T-Cell Treatment in Refractory Antisynthetase Syndrome – Data of the First Three Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-car-t-cell-treatment-in-refractory-antisynthetase-syndrome-data-of-the-first-three-patients/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-car-t-cell-treatment-in-refractory-antisynthetase-syndrome-data-of-the-first-three-patients/