Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2020
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: In the INBUILD trial, nintedanib reduced the rate of decline in forced vital capacity (FVC) over 52 weeks compared with placebo in patients with chronic fibrosing ILDs with a progressive phenotype. Several studies have suggested that a usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP) pattern on high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) is associated with faster progression of ILD. We assessed the effect of nintedanib on FVC decline in patients with autoimmune disease-related ILDs in the INBUILD trial in subgroups by fibrotic pattern on HRCT at baseline.
Methods: The INBUILD trial enrolled patients with a fibrosing ILD other than idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, reticular abnormality with traction bronchiectasis (with or without honeycombing) of >10% extent on HRCT, FVC ≥45% predicted, and DLco ≥30%–< 80% predicted. To be eligible to participate, patients had to meet protocol-specified criteria for progression of ILD within the 24 months before screening despite management as deemed appropriate in clinical practice. Patients were randomized to receive nintedanib or placebo, stratified by fibrotic pattern on HRCT (UIP-like fibrotic pattern or other fibrotic patterns) based on central review. In a post-hoc analysis, we analyzed the rate of decline in FVC over 52 weeks in patients with autoimmune disease-related ILDs in subgroups by UIP-like fibrotic pattern on HRCT and other fibrotic patterns on HRCT.
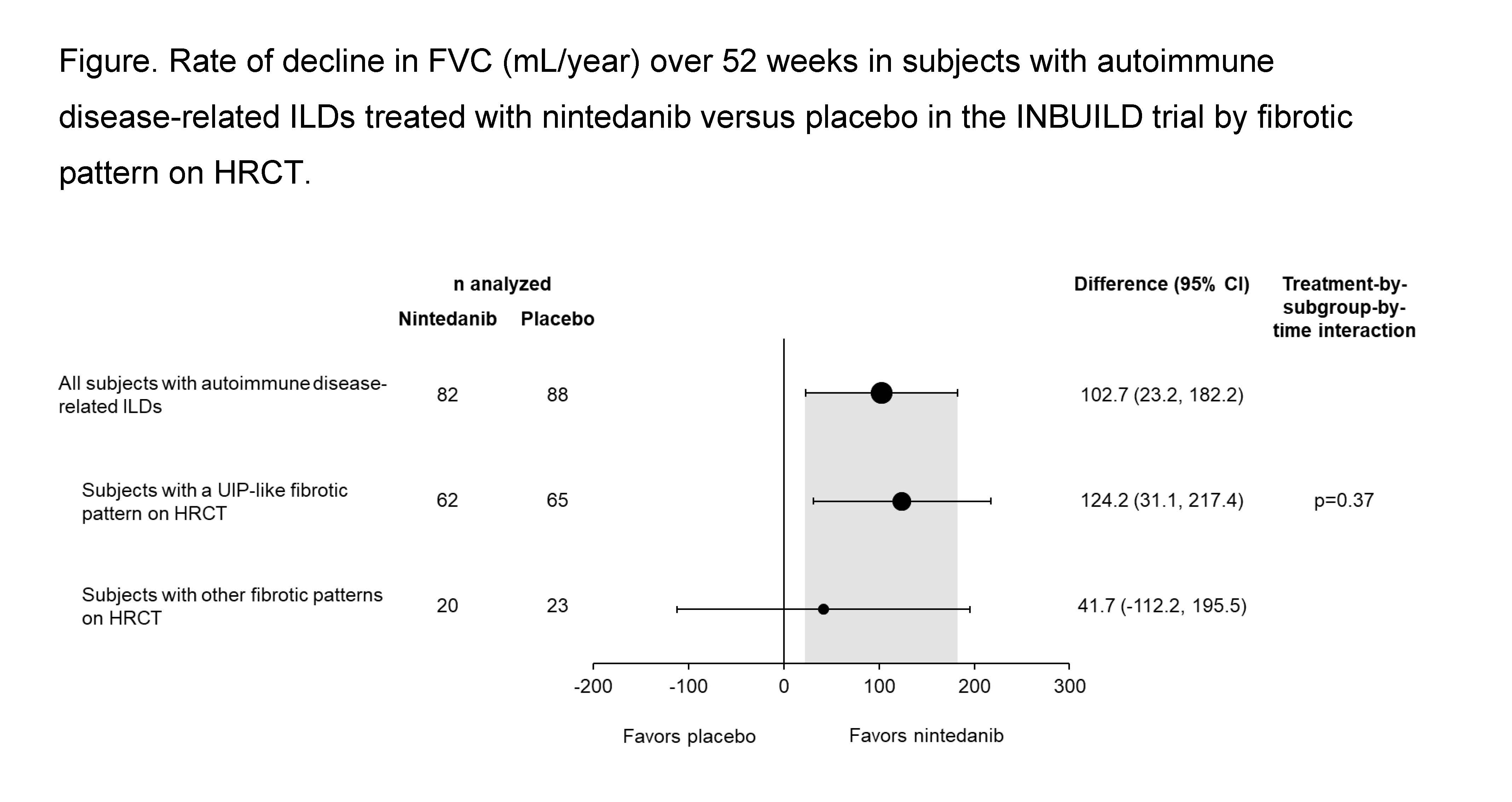
Results: The subgroup with autoimmune disease-related ILDs comprised 170 patients (89 rheumatoid arthritis-ILD, 39 systemic sclerosis-ILD, 19 mixed connective tissue disease-ILD, 23 other autoimmune disease-related ILDs), of whom 127 (74.7%) had a UIP-like fibrotic pattern on HRCT and 43 (25.3%) had other fibrotic patterns on HRCT. In the placebo group, the rate of decline in FVC over 52 weeks was similar in patients with a UIP-like fibrotic pattern on HRCT (n=65) and with other fibrotic patterns on HRCT (n=23) (-182.8 [SE 32.6] vs -168.1 [51.8] mL/year). The effect of nintedanib versus placebo on reducing the rate of decline in FVC was numerically greater in subjects with a UIP-like fibrotic pattern on HRCT than in those with other fibrotic patterns on HRCT (difference 124.2 mL/year [95% CI 31.1, 217.4] vs 41.7 mL/year [95% CI -112.2, 195.5]) but the interaction p-value did not indicate heterogeneity in the treatment effect between the subgroups by HRCT pattern (p=0.37) (Figure).
Conclusion: In patients with progressive fibrosing autoimmune disease-related ILDs in the INBUILD trial, nintedanib slowed the rate of FVC decline both in patients with a UIP-like fibrotic pattern on HRCT and in patients with other fibrotic patterns on HRCT, with a numerically greater effect in patients with a UIP-like fibrotic pattern on HRCT.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Dellaripa P, Aringer M, Hoffmann-Vold A, Kelly C, Mittoo S, James A, Rohr K, Stowasser S, Inoue Y. Effects of Nintedanib in Patients with Progressive Fibrosing Autoimmune Disease-related Interstitial Lung Diseases (ILDs) in the INBUILD Trial: Subgroups by HRCT Pattern [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effects-of-nintedanib-in-patients-with-progressive-fibrosing-autoimmune-disease-related-interstitial-lung-diseases-ilds-in-the-inbuild-trial-subgroups-by-hrct-pattern/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effects-of-nintedanib-in-patients-with-progressive-fibrosing-autoimmune-disease-related-interstitial-lung-diseases-ilds-in-the-inbuild-trial-subgroups-by-hrct-pattern/